Abstract
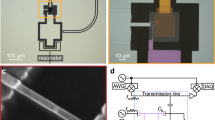
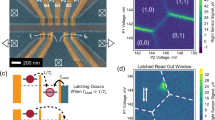
One proposal for a solid-state-based quantum bit (qubit) is to control coupled electron spins on adjacent semiconductor quantum dots1,2. Most experiments have focused on quantum dots made from III–V semiconductors; however, the coherence of electron spins in these materials is limited by hyperfine interactions with nuclear spins3,4,5,6. Ge/Si core/shell nanowires seem ideally suited to overcome this limitation, because the most abundant nuclei in Ge and Si have spin zero and the nanowires can be chemically synthesized defect-free with tunable properties7. Here, we present a double quantum dot based on Ge/Si nanowires in which we can completely control the coupling between the dots and to the leads. We also demonstrate that charge on the double dot can be detected by coupling it capacitively to an adjacent nanowire quantum dot. The double quantum dot and integrated charge sensor serve as an essential building block to form a solid-state qubit free of nuclear spin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loss, D. & DiVincenzo, D. P. Quantum computation with quantum dots. Phys. Rev. A 57, 120–126 (1998).
Hanson, R., Kouwenhoven, L. P., Petta, J. R., Tarucha, S. & Vandersypen, L. M. K. Spins in few-electron quantum dots. cond-mat/0610433 (2006).
Petta, J. R. et al. Coherent manipulation of coupled electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots. Science 309, 2180–2184 (2005).
Koppens, F. H. L. et al. Driven coherent oscillations of a single electron spin in a quantum dot. Nature 442, 766–771 (2006).
Burkard, G., Loss, D. & DiVincenzo, D. P. Coupled quantum dots as quantum gates. Phys. Rev. B 59, 2070–2078 (1999).
Khaetskii, A. V., Loss, D. & Glazman. L. Electron spin decoherence in quantum dots due to interaction with nuclei. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 186802 (2002).
Lu, W., Xiang, J., Timko, B. P., Wu, Y. & Lieber, C. M. One-dimensional hole gas in germanium/silicon nanowire heterostructures. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 10046–10051 (2005).
Fasth, C., Fuhrer, A., Björk, M. T. & Samuelson, L. Tunable double quantum dots in InAs nanowires defined by local gate electrodes. Nano Lett. 5, 1487–1490 (2005).
Fasth, C., Fuhrer, A., Samuelson, L., Golovach, V. N. & Loss, D. Direct measurement of the spin-orbit interaction in a two-electron InAs nanowire quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 266801 (2007).
Pfund, A., Shorubalko, I., Ensslin, K. & Leturcq, R. Suppresion of spin relaxation in an InAs nanowire double quantum dot. cond-mat/0701054 (2007).
Tyryshkin, A. M. et al. Electron spin coherence in Si. Physica E 35, 257–267 (2006).
Kane, B. E. A silicon-based nuclear spin quantum computer. Nature 393, 133–137 (1998).
Vrijen, R. et al. Electron-spin-resonance transistors for quantum computing in silicon–germanium heterostructures. Phys. Rev. A 62, 012306 (2000).
Friesen, M. et al. Practical design and simulation of silicon-based quantum-dot qubits. Phys. Rev. B 67, 121301(R) (2003).
Trauzettel, B., Bulaev, D. V., Loss, D. & Burkard, G. Spin qubits in graphene quantum dots. Nature Phys. 3, 192–196 (2007).
Biercuk, M. J., Garaj, S., Mason, N., Chow, J. M. & Marcus, C. M. Gate-defined quantum dots on carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 5, 1267–1271 (2005).
Sapmaz, S., Meyer, C., Beliczynski, P., Jarillo-Herrero, P. & Kouwenhoven, L. P. Excited state spectroscopy in carbon nanotube double quantum dots. Nano Lett. 6, 1350–1355 (2006).
Gräber, M. R. et al. Molecular states in carbon nanotube double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 74, 075427 (2006).
Chan, V. C. et al. Ion implanted Si:P double dot with gate tunable interdot coupling. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 106104 (2006).
Zhong, Z., Fang, Y., Lu, W. & Lieber, C. M. Coherent single charge transport in molecular-scale silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 5, 1143–1146 (2005).
Klein, L. J., Savage, D. E. & Eriksson, M. A. Coulomb blockade and Kondo effect in a few-electron silicon/silicon–germanium quantum dot. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 033103 (2007).
Berer, T. et al. Lateral quantum dots in Si/SiGe realized by a Schottky split-gate technique. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 162112 (2006).
Sakr, M. R., Jiang, H. W., Yablonovitch, E. & Croke, E. T. Fabrication and characterization of electrostatic Si/SiGe quantum dots with an integrated read-out channel. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 223104 (2005).
van der Wiel, W. G., De Franceschi, S., Elzermann, J. M., Fujisawa, T., Tarucha, S. & Kouwenhoven, L. P. Electron transport through double quantum dots. Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 1–22 (2003).
Elzerman, J. M. et al. Few-electron quantum dot circuit with integrated charge read out. Phys. Rev. B 67, 161308(R) (2003).
Biercuk, M. J. et al. Charge sensing in carbon-nanotube quantum dots on microsecond timescales. Phys. Rev. B 73, 201402(R) (2006).
DiCarlo, L. et al. Differential charge sensing and charge delocalization in a tunable double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 226801 (2004).
Bulaev, D. V. & Loss, D. Spin relaxation and decoherence of holes in quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 076805 (2005).
Heiss, D. et al. Observation of extremely slow spin relaxation in self-assembled quantum dots. cond-mat/0705.1466 (2007).
Schäffler, F. High-mobility Si and Ge structures. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 12, 1515–1549 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. DiCarlo and E. A. Laird for experimental assistance and helpful discussions. C.M.L. acknowledges support from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency and Samsung Electronics. C.M.M. acknowledges support from the Disruptive Technology Office. H.O.H.C. acknowledges support from the National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.H. and H.O.H.C. performed the experiments. Y.H. and J.X. fabricated the devices. Y.H., H.O.H.C., D.J.R., C.M.L. and C.M.M. analysed the data and co-wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures S1 and S2 (PDF 205 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Churchill, H., Reilly, D. et al. A Ge/Si heterostructure nanowire-based double quantum dot with integrated charge sensor. Nature Nanotech 2, 622–625 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.302
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.302
This article is cited by
-
Cryogenic multiplexing using selective area grown nanowires
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Silicon-based qubit technology: progress and future prospects
Bulletin of Materials Science (2022)
-
One-pot synthesis of phosphine-free indium selenide (InSe) QDs and their structural characterization for LPG and humidity sensing
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (2022)
-
Integration of boron arsenide cooling substrates into gallium nitride devices
Nature Electronics (2021)
-
The germanium quantum information route
Nature Reviews Materials (2020)