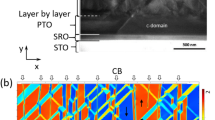
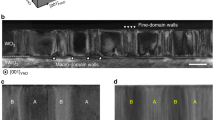
Abstract
Domain walls in ferroic materials have attracted significant interest in recent years, in particular because of the unique properties that can be found in their vicinity1,2,3. However, to fully harness their potential as nanoscale functional entities4,5, it is essential to achieve reliable and precise control of their nucleation, location, number and velocity. Here, using piezoresponse force microscopy, we show the control and manipulation of domain walls in ferroelectric thin films of Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 with Pt top electrodes. This high-level control presents an excellent opportunity to demonstrate the versatility and flexibility of ferroelectric domain walls. Their position can be controlled by the tuning of voltage pulses, and multiple domain walls can be nucleated and handled in a reproducible fashion. The system is accurately described by analogy to the classical Stefan problem6, which has been used previously to describe many diverse systems and is here applied to electric circuits. This study is a step towards the realization of domain wall nanoelectronics utilizing ferroelectric thin films.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aird, A. & Salje, E. K. H. Sheet superconductivity in twin walls: experimental evidence of WO(3−x) . J. Phys. Condens. Matter 10, L377–L380 (1998).
Seidel, J. et al. Conduction at domain walls in oxide multiferroics. Nature Mater. 8, 229–234 (2009).
Sluka, T., Tagantsev, A. K., Damjanovic, D., Gureev, M. & Setter, N. Enhanced electromechanical response of ferroelectrics due to charged domain walls. Nature Commun. 3, 748 (2012).
Seidel, J. Domain walls as nanoscale functional elements. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 2905–2909 (2012).
Catalan, G., Seidel, J., Ramesh, R. & Scott, J. F. Domain wall nanoelectronics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 119–156 (2012).
Gupta, S. C. The Classical Stefan Problem: Basic Concepts, Modelling and Analysis (Elsevier, 2003).
Seidel, J. et al. Domain wall conductivity in La-doped BiFeO3 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 197603 (2010).
Guyonnet, J., Gaponenko, I., Gariglio, S. & Paruch, P. Conduction at domain walls in insulating Pb(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3 thin films. Adv. Mater. 23, 5377–5382 (2011).
Farokhipoor, S. & Noheda, B. Conduction through 71° domain walls in BiFeO3 thin films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 127601 (2011).
Maksymovych, P. et al. Tunable metallic conductance in ferroelectric nanodomains. Nano Lett. 12, 209–213 (2012).
Sluka, T., Tagantsev, A. K., Bednyakov, P. & Setter, N. Free-electron gas at charged domain walls in insulating BaTiO3 . Nature Commun. 4, 1808 (2013).
Feigl, L. et al. Controlled stripes of ultrafine ferroelectric domains. Nature Commun. 5, 4677 (2014).
Feigl, L., McGilly, L. J., Sandu, C. S. & Setter, N. Compliant ferroelastic domains in epitaxial Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 172904 (2014).
Ohtomo, A. & Hwang, H. Y. A high-mobility electron gas at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterointerface. Nature 427, 423–426 (2004).
Allwood, D. A. et al. Magnetic domain-wall logic. Science 309, 1688–1692 (2005).
Parkin, S. S. P., Hayashi, M. & Thomas, L. Magnetic domain-wall racetrack memory. Science 320, 190–194 (2008).
Hayashi, M., Thomas, L., Moriya, R., Rettner, C. & Parkin, S. S. P. Current-controlled magnetic domain-wall nanowire shift register. Science 320, 209–211 (2008).
Thomas, L., Moriya, R., Rettner, C. & Parkin, S. S. P. Dynamics of magnetic domain walls under their own inertia. Science 330, 1810–1813 (2010).
Lewis, E. R. et al. Fast domain wall motion in magnetic comb structures. Nature Mater. 9, 980–983 (2010).
Tybell, T., Paruch, P., Giamarchi, T. & Triscone, J-M. Domain wall creep in epitaxial ferroelectric PbZr0.2Ti0.8O3 thin films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 097601 (2001).
Rodriguez, B. J. et al. Domain growth kinetics in lithium niobate single crystals studied by piezoresponse force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 012906 (2005).
Gruverman, A. et al. Direct studies of domain switching dynamics in thin film ferroelectric capacitors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 082902 (2005).
Gruverman, A., Wu, D. & Scott, J. F. Piezoresponse force microscopy studies of switching behavior of ferroelectric capacitors on a 100-ns time scale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 097601 (2008).
Whyte, J. R. et al. Ferroelectric domain wall injection. Adv. Mater. 26, 293–298 (2014).
Van Dorp, W. F., van Someren, B., Hagen, C. W., Kruit, P. & Crozier, P. A. Approaching the resolution limit of nanometer-scale electron beam-induced deposition. Nano Lett. 5, 1303–1307 (2005).
Rotkina, L., Oh, S., Eckstein, J. N. & Rotkin, S. V. Logarithmic behavior of the conductivity of electron-beam deposited granular Pt/C nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 72, 233407 (2005).
Botman, A., Mulders, J. J. L., Weemaes, R. & Mentink, S. Purification of platinum and gold structures after electron-beam-induced deposition. Nanotechnology 17, 3779–3785 (2006).
Jesse, S. et al. Direct imaging of the spatial and energy distribution of nucleation centres in ferroelectric materials. Nature Mater. 7, 209–215 (2008).
Hoffmann, H. & Fischer, G. Electrical conductivity in thin and very thin platinum films. Thin Solid Films 36, 25–28 (1976).
Chanthbouala, A. et al. A ferroelectric memristor. Nature Mater. 11, 860–864 (2012).
Acknowledgements
The research leading to these results received funding from the European Research Council under the EU 7th Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013)/ERC grant agreement no. 268058 Mobile-W. The Swiss National Science Foundation (grant nos. 200020_140539 and 200020_153177) and the Swiss Federal Office of Education and Science (COST 0904 Action) are acknowledged for additional financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.J.McG conceived the concept of the study, carried out the experiments and wrote the manuscript with input from all authors. L.F. prepared the thin films. P.Y. and A.K.T. developed the model and theory. N.S. initiated the study and was responsible for the overall direction.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information (PDF 818 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGilly, L., Yudin, P., Feigl, L. et al. Controlling domain wall motion in ferroelectric thin films. Nature Nanotech 10, 145–150 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2014.320
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2014.320
This article is cited by
-
Atomic-scale manipulation of polar domain boundaries in monolayer ferroelectric In2Se3
Nature Communications (2024)
-
In-plane charged domain walls with memristive behaviour in a ferroelectric film
Nature (2023)
-
Operando electron microscopy investigation of polar domain dynamics in twisted van der Waals homobilayers
Nature Materials (2023)
-
In-plane charged antiphase boundary and 180° domain wall in a ferroelectric film
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Electrical switching of ferro-rotational order in nanometre-thick 1T-TaS2 crystals
Nature Nanotechnology (2023)