Abstract
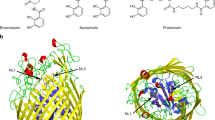
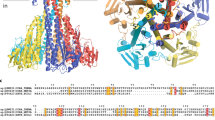
The outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria possess transport proteins essential for uptake of scarce nutrients. In TonB-dependent transporters, a conserved sequence of seven residues, the Ton box, faces the periplasm and interacts with the inner membrane TonB protein to energize an active transport cycle. A critical mechanistic step is the structural change in the Ton box of the transporter upon substrate binding; this essential transmembrane signaling event increases the affinity of the transporter for TonB and enables active transport to proceed. We have solved crystal structures of BtuB, the outer membrane cobalamin transporter from Escherichia coli, in the absence and presence of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12). In these structures, the Ton box is ordered and undergoes a conformational change in the presence of bound substrate. Calcium has been implicated as a necessary factor for the high-affinity binding (Kd ∼0.3 nM) of cyanocobalamin to BtuB. We observe two bound calcium ions that order three extracellular loops of BtuB, thus providing a direct (and unusual) structural role for calcium.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Postle, K. Active transport by customized β-barrels. Nat. Struct. Biol. 6, 3–6 (1999).
Kadner, R.J. Vitamin B12 transport in Escherichia coli: energy coupling between membranes. Mol. Microbiol. 4, 2027–2033 (1990).
Postle, K. TonB protein and energy transduction between membranes. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 25, 591–601 (1993).
Braun, V. Energy-coupled transport and signal transduction through the Gram-negative outer membrane via TonB-ExbB-ExbD–dependent receptor proteins. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 16, 295–307 (1995).
Lundrigan, M.D. & Kadner, R.J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the ferrienterochelin receptor FepA in Escherichia coli. Homology among outer membrane receptors that interact with TonB. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 10797–10801 (1986).
Schramm, E., Mende, J., Braun, V. & Kamp, R.M. Nucleotide sequence of the colicin B activity gene cba: consensus pentapeptide among TonB-dependent colicins and receptors. J. Bacteriol. 169, 3350–3357 (1987).
Heller, K., Mann, B.J. & Kadner, R.J. Cloning and expression of the gene for the vitamin B12 receptor protein in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 161, 896–903 (1985).
Schoffler, H. & Braun, V. Transport across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K12 via the FhuA receptor is regulated by the TonB protein of the cytoplasmic membrane. Mol. Gen. Genet. 217, 378–383 (1989).
Larsen, R.A., Foster-Hartnett, D., McIntosh, M.A. & Postle, K. Regions of Escherichia coli TonB and FepA proteins essential for in vivo physical interactions. J. Bacteriol. 179, 3213–3221 (1997).
Locher, K.P. et al. Transmembrane signaling across the ligand-gated FhuA receptor: crystal structures of free and ferrichrome-bound states reveal allosteric changes. Cell 95, 771–778 (1998).
Ferguson, A.D., Hofmann, E., Coulton, J.W., Diederichs, K. & Welte, W. Siderophore-mediated iron transport: crystal structure of FhuA with bound lipopolysaccharide. Science 282, 2215–2220 (1998).
Buchanan, S.K. et al. Crystal structure of the outer membrane active transporter FepA from Escherichia coli. Nat. Struct. Biol. 6, 56–62 (1999).
Ferguson, A.D. et al. Structural basis of gating by the outer membrane transporter FecA. Science 295, 1715–1719 (2002).
Roth, J.R., Lawrence, J.G. & Bobik, T.A. Cobalamin (coenzyme B12): synthesis and biological significance. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 50, 137–181 (1996).
Bradbeer, C., Reynolds, P.R., Bauler, G.M. & Fernandez, M.T. A requirement for calcium in the transport of cobalamin across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 2520–2523 (1986).
Di Masi, D.R., White, J.C., Schnaitman, C.A. & Bradbeer, C. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli: common receptor sites for vitamin B12 and the E colicins on the outer membrane of the cell envelope. J. Bacteriol. 115, 506–513 (1973).
Bradbeer, C., Woodrow, M.L. & Khalifah, L.I. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli: common receptor system for vitamin B12 and bacteriophage BF23 on the outer membrane of the cell envelope. J. Bacteriol. 125, 1032–1039 (1976).
Locher, K.P., Lee, A.T. & Rees, D.C. The E. coli BtuCD structure: a framework for ABC transporter architecture and mechanism. Science 296, 1091–1098 (2002).
Borths, E.L., Locher, K.P., Lee, A.T. & Rees, D.C. The structure of Esherichia coli BtuF and binding to its cognate ATP binding cassette transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 16642–16647 (2002).
Matthews, B.W. et al. Structure of thermolysin. Nat. New Biol. 238, 41–43 (1972).
Hogle, J., Kirchhausen, T. & Harrison, S.C. Divalent cation sites in tomato bushy stunt virus: difference maps at 2.9 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 171, 95–100 (1983).
Emsley, J. et al. Structure of pentameric human serum amyloid P component. Nature 367, 338–345 (1994).
Shrive, A.K. et al. Three dimensional structure of human C-reactive protein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 3, 346–353 (1996).
Ferguson, A.D. et al. Active transport of an antibiotic rifamycin derivative by the outer-membrane protein FhuA. Structure 9, 707–716 (2001).
Cadieux, N. & Kadner, R.J. Site-directed disulfide bonding reveals an interaction site between energy-coupling protein TonB and BtuB, the outer membrane cobalamin transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 10673–10678 (1999).
Merianos, H.J., Cadieux, N., Lin, C.H., Kadner, R.J. & Cafiso, D.S. Substrate-induced exposure of an energy-coupling motif of a membrane transporter. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7, 205–209 (2000).
Fanucci, G.E. et al. Substrate-induced conformational changes of the periplasmic N-terminus of an outer-membrane transporter by site-directed spin labelling. Biochemistry 42, 1391–1400 (2003).
Langen, R., Oh, K.J., Cascio, D. & Hubbell, W.L. Crystal structures of spin-labelled T4 lysozyme mutants: implications for the interpretation of EPR spectra in terms of structure. Biochemistry 39, 8396–8405 (2000).
Moeck, G.S. & Letellier, L. Characterization of in vitro interactions between a truncated TonB protein from Escherichia coli and the outer membrane receptors FhuA and FepA. J. Bacteriol. 183, 2755–2764 (2001).
Usher, K.C., Özkan, E., Gardner, K.H. & Deisenhofer, J. The plug domain of FepA, a TonB-dependent transport protein from Escherichia coli, binds its siderophore in the absence of the transmembrane barrel domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 10676–10681 (2001).
Cadieux, N. et al. Identification of the periplasmic cobalamin-binding protein BtuF of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 184, 706–717 (2002).
Chimento, D.P., Mohanty, A.K., Kadner, R.J. & Wiener, M.C. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the Escherichia coli outer membrane cobalamin transporter BtuB. Acta Crystallogr. D 59, 509–511 (2003).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Miller, R. & Gallo, S.M. SnB: crystal structure determination via Shake-and-Bake. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 27, 613–621 (1994).
Grosse-Kuntsleve, R.W. & Brunger, A.T. A highly automated heavy-atom search procedure for macromolecular structures. Acta Crystallogr. D 55, 1568–1577 (1999).
Brunger, A.T. et al. Crystallography & NMR System: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
de La Fortelle, E. & Bricogne, G. SHARP: maximum-likelihood heavy-atom parameter refinement for multiple isomorphous replacement and multiwavelength anomalous diffraction methods. Methods Enzymol. 176, 472–494 (1997).
Abrahams, J.P. & Leslie, A.G.W. Methods used in the structure determination of bovine mitochondrial F-1 ATPase. Acta Crystallogr. D 52, 30–42 (1996).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991).
Murshudov, G.N., Vagin, A.A. & Dodson, E.J. Refinement of macromolecular structure by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D 53, 240–255 (1997).
Winn, M.D., Isupov, M.N. & Nurshudov, G.N. Use of TLS parameters to model anisotropic displacements in macromolecular refinement. Acta Crystallogr. D 57, 122–133 (2001).
Read, R.J. Improved Fourier coefficients for maps using phases from partial structures with errors. Acta Crystallogr. A 42, 140–149 (1986).
Terwilliger, T.C. Map-likelihood phasing. Acta Crystallogr. D 57, 1763–1775 (2001).
Navaza, J. Implementation of molecular replacement in AMoRe. Acta Crystallogr. D 57, 1367–1372 (2001).
Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Kraulis, P. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Esnouf, R.M. An extensively modified version of MolScript that includes greatly enhanced coloring capabilities. J. Mol. Graph. 15, 132–134 (1997).
Merrit, E. & Murphy, M. Raster3D version 2.0. A program for photorealistic molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 869–873 (1994).
Nicholls, A., Bharadwaj, R. & Honig, B. GRASP: graphical representation and analysis of surface properties. Biophys. J. 64, 166–170 (1993).
Howlin, B., Butler, S.A., Moss, D.S., Harris, G.W. & Driessen, H.P.C. TLSANL: TLS parameter analysis program for segmented anisotropic refinement of macromolecular structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 26, 622–624 (1993).
Brunger, A.T. The free R value: a novel statistical quantity for assessing the accuracy of crystal structures. Nature 355, 472–474 (1992).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Purdy and S. Derevakonda for assistance with data collection; W. Minor for useful suggestions related to data collection and processing; C. Bradbeer and N. Cadieux for useful discussion; and R. Kretsinger, R. Nakamoto and E. Perozo for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Synchrotron facilities are supported by the Department of Energy (APS SBC, APS IMCA, NSLS X25), Industrial Macromolecular Crystallography Association (APS IMCA), National Science Foundation (CHESS F1) and National Institutes of Health (NSLS X25, CHESS F1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chimento, D., Mohanty, A., Kadner, R. et al. Substrate-induced transmembrane signaling in the cobalamin transporter BtuB. Nat Struct Mol Biol 10, 394–401 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb914
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb914
This article is cited by
-
A deep siamese neural network improves metagenome-assembled genomes in microbiome datasets across different environments
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Metagenomic and chemical characterization of soil cobalamin production
The ISME Journal (2020)
-
Genetic and structural determinants on iron assimilation pathways in the plant pathogen Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri and Xanthomonas sp.
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2020)
-
Metal Binding Antimicrobial Peptides in Nanoparticle Bio-functionalization: New Heights in Drug Delivery and Therapy
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins (2020)
-
HOGPred: artificial neural network-based model for orphan GPCRs
Neural Computing and Applications (2018)