Abstract
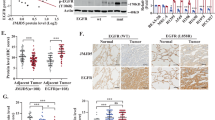
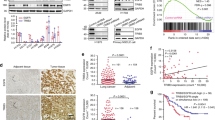
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a cell surface receptor that has an essential role in cell proliferation and survival, and overexpression of EGFR is a common feature of human cancers. In Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), activating mutations of EGFR have also been described. We recently showed that mutant EGFR-L858R inhibits the expression of the p14ARF tumor-suppressor protein to promote cell survival. In this study, we defined the molecular bases by which EGFR controls Arf expression. Using various lung tumor models, we showed that EGF stimulation inhibits Arf transcription by a mechanism involving the nuclear transport and recruitment of EGFR to the Arf promoter. We unraveled the vesicular trafficking protein Vps34 as a mediator of EGFR nuclear trafficking and showed that its neutralization prevents the accumulation of EGFR to the Arf promoter in response to ligand activation. Finally, in lung tumor cells that carry mutant EGFR-L858R, we demonstrated that inhibition of Vps34 using small interfering RNA restrains nuclear EGFR location and restores Arf expression leading to apoptosis. These findings identify the Arf tumor suppressor as a new transcriptional target of nuclear EGFR and highlight Vps34 as an important regulator of the nuclear EGFR/Arf survival pathway. As a whole, they provide a mechanistic explanation to the inverse correlation between nuclear expression of EGFR and overall survival in NSCLC patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicholson RI, Gee JM, Harper ME . EGFR and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer 2001; 37: S9–S15.
Krause DS, Van Etten RA . Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 172–187.
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from "never smokers" and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 13306–13311.
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004; 304: 1497–1500.
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2129–2139.
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX . Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 127–137.
Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett TP, Ward CW, Burgess AW . Epidermal growth factor receptor: mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res 2003; 284: 31–53.
Olayioye MA, Neve RM, Lane HA, Hynes NE . The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J 2000; 19: 3159–3167.
Schlessinger J . Ligand-induced, receptor-mediated dimerization and activation of EGF receptor. Cell 2002; 110: 669–672.
Lill NL, Sever NI . Where EGF receptors transmit their signals. Sci Signal 2012; 5 pe41.
Wang YN, Yamaguchi H, Hsu JM, Hung MC . Nuclear trafficking of the epidermal growth factor receptor family membrane proteins. Oncogene 2010; 29: 3997–4006.
Lo HW . Nuclear mode of the EGFR signaling network: biology, prognostic value, and therapeutic implications. Discov Med 2010; 10: 44–51.
Brand TM, Iida M, Li C, Wheeler DL . The nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor signaling network and its role in cancer. Discov Med 2011; 12: 419–432.
Wang YN, Hung MC . Nuclear functions and subcellular trafficking mechanisms of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Cell Biosci 2012; 2: 13.
Huang WC, Chen YJ, Li LY, Wei YL, Hsu SC, Tsai SL et al. Nuclear translocation of epidermal growth factor receptor by Akt-dependent phosphorylation enhances breast cancer-resistant protein expression in gefitinib-resistant cells. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 20558–20568.
Liccardi G, Hartley JA, Hochhauser D . EGFR nuclear translocation modulates DNA repair following cisplatin and ionizing radiation treatment. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 1103–1114.
Chen DJ, Nirodi CS . The epidermal growth factor receptor: a role in repair of radiation-induced DNA damage. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 6555–6560.
Traynor AM, Weigel TL, Oettel KR, Yang DT, Zhang C, Kim K et al. Nuclear EGFR protein expression predicts poor survival in early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2013; 81: 138–141.
Tao Y, Song X, Deng X, Xie D, Lee LM, Liu Y et al. Nuclear accumulation of epidermal growth factor receptor and acceleration of G1/S stage by Epstein-Barr-encoded oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1. Exp Cell Res 2005; 303: 240–251.
Mao L, Merlo A, Bedi G, Shapiro GI, Edwards CD, Rollins BJ et al. A novel p16INK4A transcript. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 2995–2997.
Quelle DE, Zindy F, Ashmun RA, Sherr CJ . Alternative reading frames of the INK4a tumor suppressor gene encode two unrelated proteins capable of inducing cell cycle arrest. Cell 1995; 83: 993–1000.
Ozenne P, Eymin B, Brambilla E, Gazzeri S . The ARF tumor suppressor: structure, functions and status in cancer. Int J Cancer 2010; 127: 2239–2247.
Sherr CJ . Divorcing ARF and p53: an unsettled case. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 663–673.
Eymin B, Leduc C, Coll JL, Brambilla E, Gazzeri S . p14ARF induces G2 arrest and apoptosis independently of p53 leading to regression of tumours established in nude mice. Oncogene 2003; 22: 1822–1835.
Ozenne P, Dayde D, Brambilla E, Eymin B, Gazzeri S . p14(ARF) inhibits the growth of lung adenocarcinoma cells harbouring an EGFR L858R mutation by activating a STAT3-dependent pro-apoptotic signalling pathway. Oncogene 2013; 32: 1050–1058.
Carpenter G, Liao HJ . Receptor tyrosine kinases in the nucleus. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2013; 5: a008979.
Lo HW, Hsu SC, Ali-Seyed M, Gunduz M, Xia W, Wei Y et al. Nuclear interaction of EGFR and STAT3 in the activation of the iNOS/NO pathway. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 575–589.
Lin SY, Makino K, Xia W, Matin A, Wen Y, Kwong KY et al. Nuclear localization of EGF receptor and its potential new role as a transcription factor. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 802–808.
Burda P, Padilla SM, Sarkar S, Emr SD . Retromer function in endosome-to-Golgi retrograde transport is regulated by the yeast Vps34 PtdIns 3-kinase. J Cell Sci 2002; 115: 3889–3900.
Xia W, Wei Y, Du Y, Liu J, Chang B, Yu YL et al. Nuclear expression of epidermal growth factor receptor is a novel prognostic value in patients with ovarian cancer. Mol Carcinog 2009; 48: 610–617.
Lo HW, Xia W, Wei Y, Ali-Seyed M, Huang SF, Hung MC . Novel prognostic value of nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor in breast cancer. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 338–348.
Psyrri A, Yu Z, Weinberger PM, Sasaki C, Haffty B, Camp R et al. Quantitative determination of nuclear and cytoplasmic epidermal growth factor receptor expression in oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer by using automated quantitative analysis. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 5856–5862.
Mosesson Y, Mills GB, Yarden Y . Derailed endocytosis: an emerging feature of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 835–850.
Massie C, Mills IG . The developing role of receptors and adaptors. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 403–409.
Schu PV, Takegawa K, Fry MJ, Stack JH, Waterfield MD, Emr SD . Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase encoded by yeast VPS34 gene essential for protein sorting. Science 1993; 260: 88–91.
Vanhaesebroeck B, Guillermet-Guibert J, Graupera M, Bilanges B . The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 329–341.
Simonsen A, Tooze SA . Coordination of membrane events during autophagy by multiple class III PI3-kinase complexes. J Cell Biol 2009; 186: 773–782.
Backer JM . The regulation and function of Class III PI3Ks: novel roles for Vps34. Biochem J 2008; 410: 1–17.
Dittmann K, Mayer C, Fehrenbacher B, Schaller M, Kehlbach R, Rodemann HP . Nuclear EGFR shuttling induced by ionizing radiation is regulated by phosphorylation at residue Thr654. FEBS Lett 2010; 584: 3878–3884.
Giri DK, Ali-Seyed M, Li LY, Lee DF, Ling P, Bartholomeusz G et al. Endosomal transport of ErbB-2: mechanism for nuclear entry of the cell surface receptor. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 11005–11018.
Hung LY, Tseng JT, Lee YC, Xia W, Wang YN, Wu ML et al. Nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) interacts with signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) in activating Aurora-A gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: 4337–4351.
Jaganathan S, Yue P, Paladino DC, Bogdanovic J, Huo Q, Turkson J . A functional nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor, SRC and Stat3 heteromeric complex in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One 2011; 6: e19605.
Lo HW, Cao X, Zhu H, Ali-Osman F . Cyclooxygenase-2 is a novel transcriptional target of the nuclear EGFR-STAT3 and EGFRvIII-STAT3 signaling axes. Mol Cancer Res 2010; 8: 232–245.
Maggi Jr LB, Winkeler CL, Miceli AP, Apicelli AJ, Brady SN, Kuchenreuther MJ et al. ARF tumor suppression in the nucleolus. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014; 1842: 831–839.
Zhao ZH, Wang SF, Yu L, Wang J, Chang H, Yan WL et al. Overexpression of Pokemon in non-small cell lung cancer and foreshowing tumor biological behavior as well as clinical results. Lung Cancer 2008; 62: 113–119.
Meng X, Wang Y, Zheng X, Liu C, Su B, Nie H et al. shRNA-mediated knockdown of Bmi-1 inhibit lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and metastasis. Lung Cancer 2012; 77: 24–30.
Dovey JS, Zacharek SJ, Kim CF, Lees JA . Bmi1 is critical for lung tumorigenesis and bronchioalveolar stem cell expansion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 11857–11862.
Vonlanthen S, Heighway J, Altermatt HJ, Gugger M, Kappeler A, Borner MM et al. The bmi-1 oncoprotein is differentially expressed in non-small cell lung cancer and correlates with INK4A-ARF locus expression. Br J Cancer 2001; 84: 1372–1376.
Abhold EL, Kiang A, Rahimy E, Kuo SZ, Wang-Rodriguez J, Lopez JP et al. EGFR kinase promotes acquisition of stem cell-like properties: a potential therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem cells. PLoS One 2012; 7: e32459.
Aggarwal H, Aggarwal A, Agrawal DK . Epidermal growth factor increases LRF/Pokemon expression in human prostate cancer cells. Exp Mol Pathol 2011; 91: 496–501.
Mounawar M, Mukeria A, Le Calvez F, Hung RJ, Renard H, Cortot A et al. Patterns of EGFR, HER2, TP53, and KRAS mutations of p14arf expression in non-small cell lung cancers in relation to smoking history. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 5667–5672.
Cortot AB, Younes M, Martel-Planche G, Guibert B, Isaac S, Souquet PJ et al. Mutation of TP53 and alteration of p14(arf) expression in EGFR- and KRAS-mutated lung adenocarcinomas. Clin Lung Cancer 2014; 15: 124–130.
Marsh T, Debnath J . Ironing out VPS34 inhibition. Nat Cell Biol 2015; 17: 1–3.
Li C, Iida M, Dunn EF, Ghia AJ, Wheeler DL . Nuclear EGFR contributes to acquired resistance to cetuximab. Oncogene 2009; 28: 3801–3813.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor A Gazdar for providing us with the H1719, HCC827 and H1975 cellular models and Dr MC Hung for the CHO-EGFR and CHO-EGFR-pNLS cells. This work was supported by Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale U823, the Fondation ARC pour la recherche sur le cancer (grant no. 20131200109), the Fondation de France and the Ligue Nationale contre Le Cancer Comité de Savoie. DD was supported by the Fond de Dotation pour la Recherche en Santé Respiratoire 2010 and the Fondation ARC pour la recherche sur le cancer. MG was supported by le Fonds Agir pour les Maladies Chroniques. A-SH was supported by the French Research Ministry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dayde, D., Guerard, M., Perron, P. et al. Nuclear trafficking of EGFR by Vps34 represses Arf expression to promote lung tumor cell survival. Oncogene 35, 3986–3994 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.480
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.480
This article is cited by
-
Roles of ARF tumour suppressor protein in lung cancer: time to hit the nail on the head!
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2021)
-
Transketolase (TKT) activity and nuclear localization promote hepatocellular carcinoma in a metabolic and a non-metabolic manner
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
The nuclear transportation routes of membrane-bound transcription factors
Cell Communication and Signaling (2018)
-
MUC1 induces acquired chemoresistance by upregulating ABCB1 in EGFR-dependent manner
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
Long-term exposure to bisphenol A or benzo(a)pyrene alters the fate of human mammary epithelial stem cells in response to BMP2 and BMP4, by pre-activating BMP signaling
Cell Death & Differentiation (2017)