Abstract
The experience of motherhood is one of the most salient events in a woman’s life. Motherhood is associated with a series of neurophysiological, psychological, and behavioral changes that allow women to better adapt to their new role as mothers. Infants communicate their needs and physiological states mainly through salient emotional expressions, and maternal responses to infant signals are critical for infant survival and development. In this study, we investigated the whole brain functional response to emotional infant faces in 20 new mothers and 22 nulliparous women during functional magnetic resonance imaging scans. New mothers showed higher brain activation in regions involved in infant facial expression processing and empathic and mentalizing networks than nulliparous women. Furthermore, magnitudes of the activation of the left parahippocampal gyrus and the left fusiform gyrus, recruited during facial expression processing, were positively correlated with empathic concern (EC) scores in new mothers when viewing emotional (happy-sad) faces contrasted to neutral faces. Taken together, these results indicate that the experience of being a mother affects human brain responses in visual and social cognitive brain areas and in brain areas associated with theory-of-mind related and empathic processing.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
When a woman experiences pregnancy and becomes a new mother, she undergoes a series of physical, psychological, and behavioral changes1,2,3,4. These changes help new mothers better adapt to their new role and enhance their responsiveness to children5,6,7,8 Reciprocally, infants communicate their needs and mental states mainly through vocalizations and facial expressions, which convey salient information that elicits affection and nurturing from adults9,10,11,12. A mother’s ability to accurately comment on her infant’s mental state is pivotal for the development of a secure attachment relationship and adaptive social functioning in children13,14,15,16,17,18. Thus, an appropriate understanding of the emotional content of infant stimuli by new mothers is of psychological and developmental significance.
Attuned mothers infer children’s needs, mental states, or motivations from the behaviors of their children and respond appropriately. Such social maternal abilities can be viewed as empathetic competence, which include appropriately perceiving infants’ feelings (called emotional or affective empathy) and recognizing infants’ needs (called cognitive empathy)19.
Empathy, the ability to share another’s feelings, is an important contributor to successful social interaction and allows for the prediction and understanding of another’s behavior and for reacting accordingly. The anterior cingulate cortex, with the medial prefrontal cortex and the anterior insula, and the temporo-parietal junction, with the somatosensory cortex, the superior temporal sulcus and the temporal pole, have been identified as key brain structures involved in empathy20,21. Recent research on empathy in humans has sought to dissociate its cognitive and emotional dimensions22. Specifically, cognitive empathy and perspective-taking tasks involve executive, working memory, and visual spatial processes (the dorsomedial and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, superior temporal gyrus, temporo-parietal junction and parietal lobule23). Emotional empathy involves brain regions related to affective and motor-motivational processes (such as the anterior cingulate cortex, thalamus, insula, fusiform gyrus, amygdala, somatosensory and motor cortices, and ventromedial prefrontal cortex23). Brain systems related to empathy overlap significantly and are recruited during the brain responses of parents to infant stimuli24.
Beyond empathy, mentalizing, the ability to understand the mental state of others that underlies behavior, crucially contributes to human social cognition and parenting as well25. Mentalizing network supports the parent’s capacity to read the infant’s nonverbal signals and infer the infant’s intentions25,26. A recent longitudinal study showed that the transition to motherhood induced in women changes in brain regions which partially overlap the theory-of-mind network2, which includes core areas of the temporo-parietal junction, medial prefrontal cortex, precuneus, anterior temporal lobes, and inferior frontal gyrus27. Other studies suggest that motherhood modulates human brain functions and enhances social cognition in response to infant cues2,24,28,29.
Moreover, parental status modulates female brain responses to emotional infant stimuli relevant to social adult-child social interactions. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has been used to examine mothers’ neural responses to emotional infant stimuli, such as infant sounds and facial expressions19,30,31,32,33. For example, mothers exhibit different brain activation patterns when responding to their own baby versus other babies19,34,35. Other studies have investigated brain responses to emotional infant stimuli in nulliparous women34,36, but few fMRI studies have focused on the impact of parental status in human brain responses to emotional infant stimuli through direct comparisons of new mothers and nulliparous women, as we do here.
Neuroimaging evidence using near-infrared spectroscopy suggests that distinguishing infant facial emotions increases activation in the right prefrontal cortex of mothers compared with non-mothers37. Rupp et al. reported reductions in both amygdala activation and subjective negative arousal in mothers (1–6 months postpartum) versus nulliparous women in response to negative infant images38. Parental status also impacts visually evoked potentials; the P110 early brain response over the left hemisphere is significantly larger in mothers versus childless women when examined during a judgment task of happy/distressed infant expressions; this finding may reflect a greater empathic response (or increased arousal) to infant facial expressions in mothers than in childless women39. Hayashi et al. found enhanced No-Go-P3 amplitudes in mothers compared with non-mothers in an emotional Go/No-go task, which indicated that mothers’ emotional regulatory processes may differ from those of non-mothers40. In general, infants’ emotional faces appear to be more salient for mothers than for non-mothers41.
The main purpose of the present study was to clarify differences between mothers and nulliparous women in response to emotional infant faces. In this study, we investigated whole brain functional responses of 20 primiparous mothers and 22 nulliparous women using happy, neutral, and sad emotional infant face stimuli during fMRI scans. We expected that emotional infant stimuli would induce different brain activation patterns in new mothers and nulliparous women. Specifically, we expected that the experience of being a mother would be reflected in different involvement of brain areas underlying (i) empathic processing (somatosensory, anterior cingulate cortex, and anterior insula)20,42 and (ii) theory of mind (medial prefrontal cortex, temporo-parietal junction, and precuneus)27, which play a pivotal role in mother-child social interaction. We also expected (iii) great involvement of cerebral regions previously reported in response to salient emotional infant faces in connection with both the processing of infant facial expressions and maternal memory (the insula, amygdala, hippocampus, parahippocampus, fusiform gyrus and occipital cortex).
Materials and Methods
The experimental protocol was approved by the East China Normal University Committee on Human Research (No. HR201508001). Each participant firstly received an explanation about the experiment, then they are provided an informed consent form that was approved by the committee. All methods were conducted according to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki, including any relevant details.
Participants
Twenty new mothers (M age 29.8 (SD = 2.0) years, range 27 to 33) and 22 nulliparous women (M age 26.5 (SD = 2.0) years, range 24 to 32) participated. The educational level was an average of 14.4 years (SD = 0.5) for new mothers and 15.6 years (SD = 0.6) for nulliparous women. Both the new mothers and the nulliparous women were right-handed, and all psychiatric and neurological diseases were excluded based on clinical examinations and MRI as well as structured interviews. All new mothers were first-time mothers, and their babies were aged 2 months to 11 months (M age 6.5 (SD = 3.0) months).
fMRI Paradigm: affective picture task
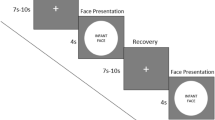
Sixty infant face pictures were presented to evoke different emotions in the participants. The task included 20 happy infant faces, 20 neutral infant faces, and 20 sad infant faces selected from the Chinese affective picture system43. All pictures were previously assessed by 29 non-parental college student volunteers (M age = 25.1 ± 1.8 years old, 17 male and 12 female) from the same university using a 9-point Likert-type scale rating for valence and arousal. The three groups of pictures differed significantly in each valence dimension [F (2, 59) = 91.13, p < 0.0001; M ± SD: happy faces: 6.83 ± 0.25; neutral faces: 5.13 ± 0.20; sad faces: 2.76 ± 0.20] and arousal dimension [F (2, 59) = 16.8, p < 0.0001; M ± SD: happy faces: 6.34 ± 0.20; neutral faces: 4.28 ± 0.34; sad faces: 5.79 ± 0.21]. In each trial, the face picture was displayed for 2 s, and then a fixation crosshair was presented for 2 s, 4 s, or 6 s randomly. All trials were presented randomly. The fMRI task lasted 12 min 6 s. A SAMRTEC SA-9900 system (Shenzhen Sinorad Medical Electronics Inc., Shenzhen, China) was used to present all stimuli. This system could synchronize the stimuli presentation and the MRI scanner.
fMRI Image acquisition
The MRI scanning was performed on a Siemens Trio Tim 3.0 Tesla MRI system at the Shanghai Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance (East China Normal University, Shanghai, China). We used a 12-channel head coil for the whole brain scanning. To minimize the head motion, the custom-fit foam pads were placed around the participants’ heads. High-resolution T1-weighted anatomical images were obtained using the 3-dimensional magnetization-prepared rapid-acquisition gradient-echo pulse sequence with the following acquisition parameters: voxel size = 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.0 mm3, field of view (FOV) = 256 × 256 mm2, slice thickness = 1 mm, number of slices = 192, echo time (TE) = 2.34 ms, repetition time (TR) = 2530 ms, inversion time (TI) = 1100, and flip angle = 7°. T2*-weighted blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) functional brain images were acquired using a gradient-echo echo-planar-imaging pulse sequence. The parameters are as follows: voxel size = 3.4 × 3.4 × 3.5 mm3, FOV = 220 × 220 mm2, slice thickness = 3.5 mm, 25% gap, number of slices = 33, TR = 2000 ms, TE = 30 ms, flip angle = 90°, and number of whole brain volumes = 363.
fMRI Data analysis
Image processing of functional images was performed using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM12) software (http://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/software/spm12). The 6 s dummy scans and first 4 s fixation were discarded to allow the signal to reach steady-state equilibrium. Data analysis included preprocessing procedures and statistical analyses. The preprocessing step contained slice timing correction, realignment, normalization to the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space template, and spatial smooth. Slice timing correction was performed using the middle slice in time as a template. Spatial realignment was performed to correct for head motion. During realignment, 6 linear regressors were obtained describing the correction parameters applied at each volume. Data from participants who showed movements greater than 2 mm or 2 degrees were excluded from further analysis. To transform each participate brain into the MNI space, the functional images were co-registered with the structural images. Then functional images were spatially normalized to the MNI stereotaxic standard space using the parameters obtained from segmentation. The voxel size was interpolated to 3 mm × 3 mm × 3 mm. Finally, spatial smoothing with an 8 mm full-width half-maximum (FWHM) isotropic Gaussian kernel was performed on the functional images. The high-pass filter was 128 s. For each participate, the BOLD signal changes were convolved with a hemodynamic response function. Individual analysis (first level) was performed with a general linear model (GLM) including the 6 rigid body correction parameter regressors as covariates in the design matrix. In the first-level statistical analysis, an event statistical model was constructed, and three conditions were modeled for each subject (happy, neutral, and sad). The contrasts happy minus neutral, sad minus neutral, and happy minus sad were calculated for each participant. The resulting contrast images entered into the second-level group analysis (new mothers, nulliparous women). One-sample t tests were used to determine within-group activation. A flexible factorial design was used to study differences in brain activation, with group (new mothers vs. nulliparous women) as a between-subjects factor and condition (happy vs. neutral, sad vs. neutral, happy vs. sad) as a within-subjects factor. Participant (mother and child) age and education were added as covariates in all analysis. The BOLD value (extracted from contrast images of each group) of the clusters for which the ANOVA showed a significant effect is reported by post hoc analysis. The activation (spm(t) maps) were reported at P < 0.001 uncorrected at the voxel level and a cluster size threshold of P < 0.05 with false discovery rated (FDR) correction and were part of a 45-voxel cluster of contiguous significant voxels.
Assessment of empathic abilities
We assessed participants’ empathic abilities using a multidimensional questionnaire, the Interpersonal Reactivity Index (IRI)44,45. The IRI is a multidimensional scale composed of 28 self-report items measuring cognitive and emotional dimensions of empathy44,45. The IRI assesses four dimensions; each dimension consists of seven items and the total scores for each subscale range from 0 to 28. The ‘fantasy’ (FS) scale measures the tendency of the participant to identify with fictitious characters in books and movies, and the ‘perspective-taking’ (PT) scale assesses the tendency to take the psychological point of view of others. The ‘empathic concern’ (EC) scale measures respondents’ prosocial feelings of warmth, compassion, and concern for others. The ‘personal distress’ (PD) scale measures self-oriented anxiety when observing others in distress. The PT and FS scales were designed to measure cognitive elements of empathy. The EC and PD scales were designed to measure emotional aspects of empathy. Higher subscale scores are associated with higher empathic tendencies 44,45,46,47. Participants completed the IRI independently after the MRI data acquisition.
Exploratory correlation between fMRI data and IRI scores
The relationships between brain activity and IRI scores were analysis performed using SPSS 24.0 (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois). Specific activations identified in the interaction between groups and conditions were used to define regions of interests (ROIs). We extracted these individual mean beta values for Pearson correlation with IRI scores. SPM was used to determine these ROIs as masks. The ROIs signal extractor Marsbar toolbox (http://marsbar.sourceforge.net) was used for each ROI of every subject to extract mean parameter estimates for further correlation analysis in SPSS 24.0. The significant results were reported at p < 0.05 (two-tailed).
fMRI results
First, we examine the main effect of parental status to obtain an overview of the brain regions that show significant variability in the two groups (mothers versus nulliparous women) with all infant emotional faces (SPM (F) maps; Table 1). Then, we detail the differences between mothers and nulliparous women in the following contrasts (SPM (t) maps): happy versus neutral faces, and sad versus neutral faces.
Effect of parental status (mothers versus nulliparous women)
Testing the main effect of group using a flexible factorial analysis, we found significant variability in the clusters centered in the right occipital lobe (extending to the lingual gyrus, superior, middle and inferior occipital gyri, cuneus, fusiform gyrus, middle temporal gyrus and parahippocampal gyrus); the right cuneus (extending to the lingual gyrus, middle and inferior occipital gyri, fusiform gyrus, and parahippocampal gyrus); the left inferior frontal gyrus (extending to the middle frontal gyrus); and the right middle frontal gyrus (extending to the inferior frontal gyrus) (Fig. 1A). For more details, see Table 1. The subsequent t-test revealed that mothers showed higher activation than non-mothers in all reported regions. No brain deactivation was found. (See Table S1 in the Supplementary Materials.)
Brain activation map comparing new mothers to nulliparous women while viewing happy minus neutral infant faces and happy minus neutral infant faces. (A) Regions of activation included the bilateral occipital and frontal lobes. (B) Regions of activation included the bilateral parahippocampal gyri, bilateral superior and middle temporal gyri, left superior and inferior parietal lobule. (C) Regions of activation included the bilateral parahippocampal gyri. P < 0.05 with FDR corrected and cluster > 45.
Happy-neutral faces contrast in mothers versus nulliparous women
When comparing happy faces with neutral faces (Fig. 1B, Table 2), two groups showed different activation in the right parahippocampal gyrus (extended to the fusiform gyrus), left parahippocampal gyrus (extended to the fusiform gyrus), left middle temporal gyrus (extended to middle occipital gyrus), left superior parietal lobule, left inferior frontal gyrus (extended to middle frontal gyrus), right superior temporal gyrus, right middle temporal gyrus (extended to superior temporal gyrus), left inferior parietal lobule (extended to the postcentral gyrus), and right cerebellum posterior lobe. In the supplementary materials, we report for the happy minus neutral contrast the specific cerebral activation in each group separately in Tables S2 and S3.
Sad-neutral faces contrast in mothers versus nulliparous women
In the contrast of sad and neutral faces (Fig. 1C, Table 3), two groups showed different activation in the left parahippocampal gyrus (extended to the left fusiform gyrus, and left cerebellum anterior and posterior lobes), and right parahippocampal gyrus (extended to the right fusiform gyrus and left cerebellum anterior lobe). In the supplementary materials, we report for the sad minus neutral contrast the specific cerebral activation in each group separately in Tables S2 and S3.
IRI scores and results from group comparisons
The four dimensions (FS, PT, EC, PD) and the total IRI scores were as follows: PT 12.2 ± 2.9, EC 18.4 ± 4.3, FS 13.2 ± 3.7 (mean ± SD), PD 10.0 ± 3.4, and total 53.8 ± 9.3 in new mothers; PT 11.8 ± 3.0, EC 15.5 ± 2.3, FS 13.6 ± 4.2, PD 9.4 ± 2.8 and total 50.3 ± 6.4 for nulliparous women. T-test analysis revealed that new mothers showed significantly higher EC scores than nulliparous women (T = 2.78, P = 0.008), and there was no significant difference between the two groups in the PT, FS, PD, and total IRI scores (see Table 4). Statistical calculations were conducted using SPSS 24.0 (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois) for Windows.
Correlations between fMRI data and IRI scores
When comparing happy faces with neutral faces, the activation of the left parahippocampal gyrus extending to the left fusiform gyrus (−33, −33, −18; r = 0.49, P = 0.039, uncorrected) were positively correlated with the EC score in new mothers (see Fig. 2A), and the activation of the right cerebellum posterior lobe (24, −66, −30; r = −0.45, P = 0.048, uncorrected) were negatively correlated with the EC score in nulliparous women (see Fig. 2B).
Correlations between BOLD fMRI activity and IRI scores in mothers and nulliparous women. (A) correlation between BOLD activity and EC score in new mothers for happy faces minus neutral faces. (B) correlation between BOLD fMRI activity and EC score in nulliparous women for happy faces minus neutral faces. (C): correlation between BOLD activity and EC score in new mothers during sad faces minus neutral faces.
When comparing sad faces with neutral faces, the activation of the left parahippocampal gyrus extending to the left fusiform gyrus and left cerebellum anterior/posterior lobes (−30, −30, −21; r = 0.47, P = 0.048, uncorrected) were positively correlated with the EC score in the new mothers group (see Fig. 2C), and no activations were found in nulliparous women that were related to the EC score.
Discussion
Babies and young infants communicate their needs and physiological states mainly through salient emotional cues. Research shows that new mothers undergo a series of adaptive changes that support them in better adapting to their new role2,10,48. The extant literature suggests that some aspects of cognition are enhanced during pregnancy and the early postpartum period. The main purpose of the present study was to investigate differences in brain responses to emotional infant faces in new mothers and nulliparous women. We hypothesized that emotional infant stimuli induce different brain activation patterns in new mothers and nulliparous women in brain areas related to infant facial expression processing and empathic and mentalizing networks. Main effects of parental status are consistent with our hypotheses. Considering all the emotional infant pictures together, our results indicate that new mothers and nulliparous women show different responses in the social cognitive brain areas related to empathic processing and theory of mind, namely the bilateral inferior and middle frontal gyri, right middle temporal gyrus, bilateral lingual gyri, bilateral fusiform gyri, bilateral cuneus, bilateral parahippocampal gyri, and bilateral middle and inferior occipital gyri. Additionally, in new mothers activation of the left parahippocampal gyrus and left fusiform gyrus, and left cerebellum anterior/posterior lobes was positively correlated with the EC score when viewing emotional faces minus neutral faces, while in nulliparous women activation of the right cerebellum posterior lobe was negatively correlated with the EC score when viewing emotional faces minus neutral faces (see Fig. 2). Taken together, the results clearly suggest that new mothers and nulliparous women show different brain responses for emotional infant cues.
Specifically, according to the first expectation, in response to emotional infant faces, mothers showed greater activation in the somatosensory cortex, the medial prefrontal cortex, the middle and inferior temporal gyri, which are proposed to be part of the brain structures involved in emotional empathy (see Table 2 and Table S1)20,21,23. The greater response of these brain regions to emotional infant faces in new mothers may reflect a tagging of the infant stimuli as the current focus, which promotes further processing in maternal brain networks. Compared to nulliparous women, emotional infant faces can elicit higher empathic responsiveness in new mothers, which likely plays a critical role in facilitating caregiving behavior toward the infant49.
In partial accord to the second expectation, mothers show greater brain activation in the medial prefrontal cortex, inferior frontal gyrus extended to the precentral gyrus, the middle and inferior temporal cortices, which are involved in the theory-of-mind networks and its extended brain regions (see Table 2 and Table S1)27,50. Additionally, the inferior frontal gyrus/premotor cortex are known as mirror neurons and play a role in understanding the intentions of others and, for our purpose, in sharing the emotions of others51. Despite, in the present study, no significant temporo-parietal junction activation were found, we found elevated activations in key regions of the theory-of-mind and social cognition in new mothers, compared to the nulliparous women, in response to either happy or sad infant faces (Table S2).
Finally, consistent with the third expectation, the brain areas involved in visually processing salient emotional stimuli, the occipital lobe, lingual gyrus, middle and inferior occipital gyri, cuneus, fusiform gyrus, and parahippocampal gyrus, showed greater involvement. Furthermore, a correlation between the fMRI data and IRI scores of new mothers showed that activation of the left parahippocampal gyrus and left fusiform gyrus was positively correlated with the EC score when viewing emotional faces minus neutral faces. The lingual gyrus, fusiform gyrus, and parahippocampal gyrus have been reported to be associated with the processing of emotional faces (see Table 2 and Table S1)53,54. The fusiform gyrus is a key structure for functionally specialized computations of high-level vision, such as face perception, object recognition, and reading55, and it is involved in processing emotional expressions56,57. The parahippocampal cortex has been associated with many cognitive processes, including visuospatial processing, emotion processing and episodic memory58. The fusiform gyrus is near the parahippocampal gyrus, and these regions have been shown to be more active during the perception of emotional faces than the perception of neutral faces53,54. In the present study, mothers showed weaker deactivation than nulliparous women in these two areas when viewing happy/sad faces minus neutral faces, as found in the present analysis. This finding indicates that there is less inhibition in visual processing among new mothers when viewing emotional faces, which suggests that new mothers may be more sensitive than nulliparous women to infant emotional stimuli59.
In the individual contrasts that examined the specific brain response to positive and negative infant faces separately, mothers and non-mothers showed differentiations consistent with our expectations. When comparing happy or sad faces with neutral faces, mothers showed different activation in brain regions underlie the empathy processing (the postcentral gyrus)20,42, theory-of-mind (middle and inferior frontal gyri, superior and middle temporal gyri, inferior parietal lobule, and angular gyrus)27, as well as infant facial expressions processing and maternal memory (parahippocampal gyrus, fusiform gyrus, and middle occipital gyrus)58.
In line with the literature, new mothers and nulliparous women also showed similar brain activation in the visual areas, limbic, temporo-parietal, prefrontal, and subcortical areas as well as the cerebellum, as reported in previous studies53,57,60. However, an intriguing result concerns the fact that new mothers and nulliparous women also differed in the extension (areas) of brain activation; activated brain regions were more focal in new mothers, while nulliparous women showed more diffuse activation. There is evidence that smaller volume recruitment of task-related regions can reflect an increased ‘neural efficiency’ in the brains of individuals with higher competences in the task61,62. In fact, in our study, primiparous mothers showed increased empathic concern (EC score), which involves prosocial feelings of warmth, compassion, and concern for others (see Table 1). More focal brain activity in new mothers may reflect maternal experience in childcare, and therefore great expertise and inclination in processing emotional cues from children. In accord with the last point, the present study showed that the brain response to infant facial expression processing (such as the left parahippocampal gyrus, the left fusiform gyrus, the left middle occipital gyrus, and the left cerebellum anterior/posterior lobes) correlates with the empathic concern for others in mothers but not in nulliparous women. Indeed, we found that greater empathic concern of mothers is associated with a lower magnitude of activation in brain structures underlying the mentalizing network in response to positive and negative emotional faces contrasted to neutral faces, which can potentially reflect social expertise of motherhood.
Empathy and the mentalizing networks are considered core components of the human parental brain24,52, and maternal sensitivity has been shown to be important for secure parent–infant attachment and for the development of the child’s own social cognitive functions13,63. Research suggests that mother’s ability to comment accurately on an infant’s mental states predicts security of attachment at 12 months13. In fact, social cognitive abilities are important for providing adequate maternal care and successfully rearing offspring in the daily social environment. High social cognitive ability can help new mothers understand their children’s needs, decode social stimuli that may lead to potential threats, and promote the integration of mothers and babies. In our study, primiparous mothers showed increased empathic concern (EC score) and weaker activation and deactivation than nulliparous women when viewing infants’ emotion faces, which may suggest that new mothers may sense infant emotions, such as happiness or sadness, more easily than nulliparous women. The enhanced ability to encode emotional faces may be an evolutionary adaptation to prepare women for the protective and nurturing demands of motherhood by increasing their general emotional sensitivity28.
While our research revealed that new mothers are more sensitive to infant emotional stimuli, our study had several limitations. We focused only on task functional changes and did not examine structural abnormalities. In a future study, we will assess structural changes using voxel-based morphometry or diffusion tensor imaging analyses. Furthermore, the nulliparous women group and the new mother group were not age-matched. In general, the new mothers were older than the nulliparous women, and older nulliparous women are very rare in China. Thus, in the data analysis, we used each subject’s age as a covariate. Besides, each condition of the stimulation task contains 20 trials, and the limited number of trials may have affected the statistical power. For example, there is no significant difference between the two groups when comparing happy vs sad faces conditions at the present statistical threshold.
Conclusion
Taken together, our results indicated that motherhood (new mothers versus nulliparous women) affects human brain responses to emotional infant stimuli in brain areas involved in infant’s face visual processing and in social cognitive brain areas that are related with empathic processing and theory-of-mind. The results of this study indicate that being a mother is associated with alterations in social cognitive function, which may serve an adaptive purpose for pending motherhood.
References
Duarte-Guterman, P., Leuner, B. & Galea, L. A. M. The long and short term effects of motherhood on the brain. Frontiers in neuroendocrinology 53, 100740, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2019.02.004 (2019).
Hoekzema, E. et al. Pregnancy leads to long-lasting changes in human brain structure. Nature neuroscience 20, 287–296, https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4458 (2017).
Kim, P. et al. The plasticity of human maternal brain: longitudinal changes in brain anatomy during the early postpartum period. Behavioral neuroscience 124, 695–700, https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020884 (2010).
Lonstein, J. S., Levy, F. & Fleming, A. S. Common and divergent psychobiological mechanisms underlying maternal behaviors in non-human and human mammals. Hormones and behavior 73, 156–185, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.06.011 (2015).
Rilling, J. K. The neural and hormonal bases of human parental care. Neuropsychologia 51, 731–747, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.12.017 (2013).
Barrett, J. & Fleming, A. S. Annual Research Review: All mothers are not created equal: neural and psychobiological perspectives on mothering and the importance of individual differences. Journal of child psychology and psychiatry, and allied disciplines 52, 368–397, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02306.x (2011).
Kim, P. Human Maternal Brain Plasticity: Adaptation to Parenting. New Dir Child Adolesc Dev 2016, 47–58, https://doi.org/10.1002/cad.20168 (2016).
Kim, P., Strathearn, L. & Swain, J. E. The maternal brain and its plasticity in humans. Hormones and behavior 77, 113–123, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.08.001 (2016).
Liszkowski, U. Two sources of meaning in infant communication: preceding action contexts and act-accompanying characteristics. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences 369, 20130294, https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0294 (2014).
Bornstein, M. H. et al. Neurobiology of culturally common maternal responses to infant cry. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 114, E9465–E9473, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1712022114 (2017).
Brosch, T., Sander, D. & Scherer, K. R. That baby caught my eye… attention capture by infant faces. Emotion 7, 685–689, https://doi.org/10.1037/1528-3542.7.3.685 (2007).
Caria, A. et al. Species-specific response to human infant faces in the premotor cortex. NeuroImage 60, 884–893, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.12.068 (2012).
Meins, E., Fernyhough, C., Fradley, E. & Tuckey, M. Rethinking maternal sensitivity: mothers’ comments on infants’ mental processes predict security of attachment at 12 months. Journal of child psychology and psychiatry, and allied disciplines 42, 637–648 (2001).
Fonagy, P. & Target, M. Attachment and reflective function: their role in self-organization. Dev Psychopathol 9, 679–700, https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579497001399 (1997).
Weinberg, E. M. affect regulation, and development of the self. Panel report. J Am Psychoanal Assoc 54, 251–270, https://doi.org/10.1177/00030651060540012501 (2006).
Laranjo, J., Bernier, A., Meins, E. & Carlson, S. M. The roles of maternal mind-mindedness and infant security of attachment in predicting preschoolers’ understanding of visual perspective taking and false belief. J Exp Child Psychol 125, 48–62, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2014.02.005 (2014).
Meins, E. et al. Maternal mind-mindedness and attachment security as predictors of theory of mind understanding. Child Dev 73, 1715–1726, https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00501 (2002).
Katznelson, H. Reflective functioning: a review. Clin Psychol Rev 34, 107–117, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2013.12.003 (2014).
Leibenluft, E., Gobbini, M. I., Harrison, T. & Haxby, J. V. Mothers’ neural activation in response to pictures of their children and other children. Biological psychiatry 56, 225–232, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.05.017 (2004).
Hein, G. & Singer, T. I feel how you feel but not always: the empathic brain and its modulation. Current opinion in neurobiology 18, 153–158, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2008.07.012 (2008).
Jankowiak-Siuda, K., Rymarczyk, K. & Grabowska, A. How we empathize with others: a neurobiological perspective. Medical science monitor: international medical journal of experimental and clinical research 17, RA18–24 (2011).
Shamay-Tsoory, S. G. The neural bases for empathy. The Neuroscientist: a review journal bringing neurobiology, neurology and psychiatry 17, 18–24, https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858410379268 (2011).
de Waal, F. B. M. & Preston, S. D. Mammalian empathy: behavioural manifestations and neural basis. Nature reviews. Neuroscience 18, 498–509, https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.72 (2017).
Swain, J. E. The human parental brain: in vivo neuroimaging. Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry 35, 1242–1254, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.10.017 (2011).
Feldman, R. The neurobiology of mammalian parenting and the biosocial context of human caregiving. Hormones and behavior 77, 3–17, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.10.001 (2016).
Bernhardt, B. C. & Singer, T. The neural basis of empathy. Annual review of neuroscience 35, 1–23, https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-062111-150536 (2012).
Schurz, M., Radua, J., Aichhorn, M., Richlan, F. & Perner, J. Fractionating theory of mind: a meta-analysis of functional brain imaging studies. Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews 42, 9–34, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.01.009 (2014).
Anderson, M. V. & Rutherford, M. D. Cognitive reorganization during pregnancy and the postpartum period: an evolutionary perspective. Evolutionary psychology: an international journal of evolutionary approaches to psychology and behavior 10, 659–687 (2012).
Pearson, R. M., Lightman, S. L. & Evans, J. Emotional sensitivity for motherhood: late pregnancy is associated with enhanced accuracy to encode emotional faces. Hormones and behavior 56, 557–563, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2009.09.013 (2009).
Nitschke, J. B. et al. Orbitofrontal cortex tracks positive mood in mothers viewing pictures of their newborn infants. NeuroImage 21, 583–592, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.10.005 (2004).
Kim, P. et al. Breastfeeding, brain activation to own infant cry, and maternal sensitivity. Journal of child psychology and psychiatry, and allied disciplines 52, 907–915, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02406.x (2011).
Landi, N. et al. Maternal neural responses to infant cries and faces: relationships with substance use. Frontiers in psychiatry 2, 32, https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2011.00032 (2011).
Moses-Kolko, E. L. et al. Abnormally reduced dorsomedial prefrontal cortical activity and effective connectivity with amygdala in response to negative emotional faces in postpartum depression. The American journal of psychiatry 167, 1373–1380, https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.09081235 (2010).
Elmadih, A. et al. Natural variation in maternal sensitivity is reflected in maternal brain responses to infant stimuli. Behavioral neuroscience 130, 500–510, https://doi.org/10.1037/bne0000161 (2016).
Rigo, P. et al. Specific maternal brain responses to their own child’s face: An fMRI meta-analysis. Developmental Review 51, 58–69 (2019).
Montoya, J. L. et al. Regional brain responses in nulliparous women to emotional infant stimuli. PloS one 7, e36270, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036270 (2012).
Nishitani, S., Doi, H., Koyama, A. & Shinohara, K. Differential prefrontal response to infant facial emotions in mothers compared with non-mothers. Neuroscience research 70, 183–188, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2011.02.007 (2011).
Rupp, H. A. et al. Amygdala response to negative images in postpartum vs nulliparous women and intranasal oxytocin. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience 9, 48–54, https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nss100 (2014).
Proverbio, A. M., Brignone, V., Matarazzo, S., Del Zotto, M. & Zani, A. Gender and parental status affect the visual cortical response to infant facial expression. Neuropsychologia 44, 2987–2999, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.06.015 (2006).
Hayashi, S. et al. Enhanced Nogo-P3 amplitudes of mothers compared with non-mother women during an emotional Go/Nogo task. Journal of physiological anthropology 37, 8, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40101-018-0167-9 (2018).
Thompson-Booth, C. et al. Here’s looking at you, kid: attention to infant emotional faces in mothers and non-mothers. Developmental science 17, 35–46, https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.12090 (2014).
Fan, Y., Duncan, N. W., de Greck, M. & Northoff, G. Is there a core neural network in empathy? An fMRI based quantitative meta-analysis. Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews 35, 903–911, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.10.009 (2011).
Bai, L., Ma, H., Huang, Y. & Luo, J. The development of native chinese affective picture system—a pretest in 46 college students. Chinese Mental Health Journal 19, 719–722 (2005).
Davis, M. H. A multidimensional approach to individual differences in empathy. JSAS Catalog Sel Doc Psychol. 10, 85 (1980).
Davis, M. H. Measuring individual differences in empathy: evidence for a multidimensional approach. J Pers Soc Psychol. 44, 113–126 (1983).
Wang, Q. et al. Anterior insula GABA levels correlate with emotional aspects of empathy: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. PloS one 9, e113845, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113845 (2014).
Sohn, H. S. et al. Impaired Empathic Abilities among Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (Type I). Psychiatry investigation 13, 34–42, https://doi.org/10.4306/pi.2016.13.1.34 (2016).
Zhang, K. et al. Dynamic Alterations in Spontaneous Brain Activity in Mothers: A Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Neuroscience bulletin 35, 766–770, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-019-00392-7 (2019).
Boorman, R. J., Creedy, D. K., Fenwick, J. & Muurlink, O. Empathy in pregnant women and new mothers: a systematic literature review. Journal of reproductive and infant psychology 37, 84–103, https://doi.org/10.1080/02646838.2018.1525695 (2019).
Pineda, J. A. Sensorimotor cortex as a critical component of an ‘extended’ mirror neuron system: Does it solve the development, correspondence, and control problems in mirroring? Behav Brain Funct 4, 47, https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-9081-4-47 (2008).
Iacoboni, M. & Dapretto, M. The mirror neuron system and the consequences of its dysfunction. Nature reviews. Neuroscience 7, 942–951, https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2024 (2006).
Swain, J. E. et al. Approaching the biology of human parental attachment: brain imaging, oxytocin and coordinated assessments of mothers and fathers. Brain research 1580, 78–101, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.03.007 (2014).
Fusar-Poli, P. et al. Functional atlas of emotional faces processing: a voxel-based meta-analysis of 105 functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. Journal of psychiatry & neuroscience: JPN 34, 418–432 (2009).
Sabatinelli, D. et al. Emotional perception: meta-analyses of face and natural scene processing. NeuroImage 54, 2524–2533, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.011 (2011).
Weiner, K. S. & Zilles, K. The anatomical and functional specialization of the fusiform gyrus. Neuropsychologia 83, 48–62, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.06.033 (2016).
Harry, B., Williams, M. A., Davis, C. & Kim, J. Emotional expressions evoke a differential response in the fusiform face area. Frontiers in human neuroscience 7, 692, https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00692 (2013).
Kawasaki, H. et al. Processing of facial emotion in the human fusiform gyrus. Journal of cognitive neuroscience 24, 1358–1370, https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00175 (2012).
Aminoff, E. M., Kveraga, K. & Bar, M. The role of the parahippocampal cortex in cognition. Trends in cognitive sciences 17, 379–390, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2013.06.009 (2013).
Mothersill, O. et al. Altered medial prefrontal activity during dynamic face processing in schizophrenia spectrum patients. Schizophrenia research 157, 225–230, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2014.05.023 (2014).
Zhen, Z., Fang, H. & Liu, J. The hierarchical brain network for face recognition. PloS one 8, e59886, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059886 (2013).
Bernardi, G. et al. How skill expertise shapes the brain functional architecture: an fMRI study of visuo-spatial and motor processing in professional racing-car and naive drivers. PloS one 8, e77764, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077764 (2013).
Jeon, H. A. & Friederici, A. D. What Does “Being an Expert” Mean to the Brain? Functional Specificity and Connectivity in Expertise. Cerebral cortex 27, 5603–5615, https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw329 (2017).
Wright, N., Hill, J., Sharp, H. & Pickles, A. Maternal sensitivity to distress, attachment and the development of callous-unemotional traits in young children. Journal of child psychology and psychiatry, and allied disciplines, https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12867 (2018).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81571658 and 81201082) and the Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 15ZDB016). This research was also supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH/NICHD, USA, and an International Research Fellowship at the Institute for Fiscal Studies (IFS), London, UK, funded by the European Research Council (ERC) under the Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (grant agreement No 695300-HKADeC-ERC-2015-AdG). But the funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.D., K.Z. X.S. and M.B. conceptualized the project. P.R and X.D. designed the protocol and wrote the main manuscript text. K.Z., M.W., Z.C., G.E. and D.P. performed the experiments. K.Z. and M.W. conducted the statistical analyses. All authors reviewed the manuscript. P.R. and X.D. revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Rigo, P., Su, X. et al. Brain Responses to Emotional Infant Faces in New Mothers and Nulliparous Women. Sci Rep 10, 9560 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66511-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66511-x
This article is cited by
-
Gender differences in brain response to infant emotional faces
BMC Neuroscience (2022)
-
Stronger brain activation for own baby but similar activation toward babies of own and different ethnicities in parents living in a multicultural environment
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Increased activation in the bilateral anterior insulae in response to others in pain in mothers compared to non-mothers
Scientific Reports (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.