Abstract
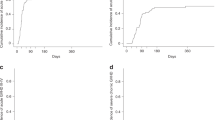
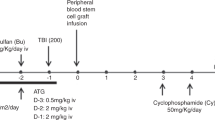
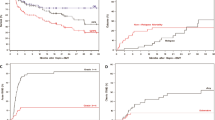
Unmanipulated autologous bone marrow transplant (ABMT) offers patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) a long-term survival of 10%, at best. Immunotherapy has a role in the myeloid leukemias, and there is increasing evidence that of all hematopoietic neoplasms, CML may be the most susceptible to immune regulation. Roquinimex is known to enhance T cell, NK cell and macrophage activity. A phase II study was initiated in March 1992 to evaluate the role of roquinimex in Ph chromosome-positive CML post ABMT. Patients were conditioned with busulfan/ cyclophosphamide followed by reinfusion of unmanipulated Ph-positive bone marrow stem cells (>1 × 108 NBC/kg). When engraftment of neutrophils (ANC) reached 100/μl, patients received oral roquinimex twice weekly, escalating to a maximal dose of 0.2 mg/kg in 2 weeks. Seventeen patients have entered the study; 11 in first chronic phase (CP1); two in second chronic phase (CP2) and four in accelerated phase (AP). All required significant myelosuppressive therapy prior to ABMT to maintain stable blood counts and most had also received prior interferon therapy. All patients survived the transplant. Subsequent toxicity consisted mainly of musculoskeletal aches and peripheral edema. Additionally, specific skin changes were observed including graft-versus-host-like disease and eccrine sweat gland necrosis. Eight out of 17 patients are alive 28–60 months post ABMT. Of the nine patients who died, two were in CP2 and three in AP. All patients in CP1 went into a complete hematological remission post ABMT and seven of the 11 patients had at least a major cytogenetic response (greater than 65% Ph-negative metaphases) at 1 year or beyond and four of the 11 patients had a complete cytogenetic response at 2 years or beyond. Cytogenetic response post transplant often developed over time and did not simply represent post ABMT engraftment with Ph-negative cells. The clinical and cytogenetic data in these patients are encouraging and suggest that roquinimex may have significant activity when given post ABMT to patients with Ph-positive CML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rowe, J., Rapoport, A., Ryan, D. et al. Treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia with autologous bone marrow transplantation followed by roquinimex. Bone Marrow Transplant 24, 1057–1063 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702037
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702037
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic use of Aldara™ in chronic myeloid leukemia
Journal of Translational Medicine (2007)
-
Molecular remission of CML after autotransplantation followed by adoptive transfer of costimulated autologous T cells
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2004)