Abstract
Objective: To investigate the trace element transfer from the mother to the newborn.
Design: The concentrations of the eight essential elements calcium (Ca), cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), magnesium (Mg), manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), tin (Sn), and zinc (Zn), and of the non-essential and toxic elements barium (Ba), beryllium (Be), bismuth (Bi), cadmium (Cd), cesium (Cs), lanthanum (La), lithium (Li), lead (Pb), rubidium (Rb), antimony (Sb), strontium (Sr), and thallium (Tl) were determined in umbilical cord (n=29) and corresponding maternal sera (n=29) as well as in colostrum (n=27).
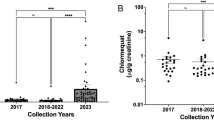
Results: Umbilical cord serum concentrations of Ca, Mn, and Zn were 120%, 150%, and 148% of the maternal value, respectively. Maternal sera had twice the Cu concentrations found in healthy adults and five-times higher Cu than umbilical cord sera. Concentration ratios colostrum/maternal serum and colostrum/umbilical cord serum were approximately one for Co, 1.4 for Mg, two for Ca, Mn, and Sn, five for Cu (maternal serum), eight for Mo, and ten for Zn. Concentrations of the toxic elements Cd and Pb decreased in the order colostrum (Pb 2.6 μg/L; Cd 0.6 μg/L), maternal sera (0.8 μg/L; 0.3 μg/L), umbilical cord sera (0.4 μg/L; 0.2 μg/L). Maternal serum Ba and Rb was 182% and 66% of the umbilical cord value. For Sr and Li, an almost perfect correlation between umbilical cord and maternal sera was found. For Ba, Co, Cu, Mn, Zn none, and for Ca, Cs, Mn, Mo, Rb only weak positive correlations between these two compartments could be established.
Conclusions: The results of this study indicate that an active transport mechanism for the transport of Ca, Mn, Rb, and Zn from the mother to the newborn exists, whereas Cs, Li, and Sr follow concentration gradients. As regards Cu, the placenta showed to have a blocking effect on the transfer from the mother to the baby.
Sponsorship: Gesellschaft zur Föderung der Gesundheit des Kleinkindes, Graz, Austria.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krachler, M., Rossipal, E. & Micetic-Turk, D. Trace element transfer from the mother to the newborn — investigations on triplets of colostrum, maternal and umbilical cord sera. Eur J Clin Nutr 53, 486–494 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600781
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600781
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of mineral nutrients other than iron in pregnancy: under recognized opportunities to improve maternal/fetal outcomes: a literature review
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics (2023)
-
Prenatal metal concentrations and physical abnormalities in the Japan Environment and Children’s Study
Pediatric Research (2023)
-
Lithium administered to pregnant, lactating and neonatal rats: entry into developing brain
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2021)
-
Role of zinc in neonatal growth and brain growth: review and scoping review
Pediatric Research (2021)
-
Evaluating the effects between metal mixtures and serum vaccine antibody concentrations in children: a prospective birth cohort study
Environmental Health (2020)