Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To get accurate measurements of visceral adipose tissue (VAT) using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
DESIGN: DXA and anthropometric data and their combinations were compared to the VAT area calculated from a computed tomography (CT) single scan.
SUBJECTS: 71 overweight subjects (44 women, 27 men), age: 16–70 y, BMI: 27–52 kg/m2.
MEASUREMENTS: Total body and segmental tissue composition, and new parameters obtained from DXA, in addition to waist and hip cicumferences and abdominal sagittal diameter measurements.
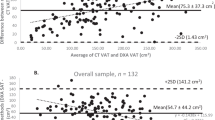
RESULTS: The ratio measured at the umbilical level (sagittal diameter−subcutaneous fat width)×(transverse internal diameter)/(height) was closely related to VAT (r=0.94 for women and 0.88 for men). It gave the most predictive equation for VAT: y=79.6x (s.e. 3.9)−149 cm2 for the whole population (r2=0.86, P<0.0001, root mean square error=38.2 cm2. An independent relationship between lean mass or its index (r=0.52 and 0.72, P<0.001) and VAT was also found in women.
CONCLUSION: This study demonstrates the potential usefulness of DXA to supply accurate measurements of VAT in addition to total body composition determination in obese subjects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lapidus L, Bengtsson C, Larsson B, Pennert K, Rybo E, Sjöström L . Distribution of adipose tissue and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: a 12 year follow-up of participants in the population study of women in Gothenburg, Sweden Br Med J 1984 289: 1261–1263.
Larsson B, Svärdsudd K, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L, Bjorntorp P, Tibblin G . Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 13 year follow-up of participants in the study of men born in 1913 Br Med J 1984 288: 1401–1404.
Lundgren H, Bengtsson C, Blohme G, Lapidus L . Adiposity and adipose tissue distribution in relation to incidence of diabetes in women: results from a prospective population study in Gothenburg, Sweden Int J Obes 1989 13: 413–423.
Björntorp P . “Portal” adipose tissue as a generator of risk factors for cardiovascular disease and diabetes Arteriosclerosis 1990 10: 493–496.
Evans DJ, Hoffman RG, Kalkhoff RD, Kissebah AH . Relationship of body fat topography to insulin sensitivity and metabolic profiles in premenopausal women Metabolism 1984 33: 68–75.
Fujioka S, Matsuzawa Y, Tokunaga K, Tarui S . Contribution of intra-abdominal fat accumulation to the impairment of glucose and lipid metabolism in human obesity Metabolism 1987 36: 54–59.
Yamashita S, Nakamura T, Shimomura I, Nishida M, Yoshida S, Kotani K, Kameda-Takemuara K, Tokunaga K, Matsuzawa Y . Insulin resistance and body fat distribution: contribution of visceral fat accumulation to the development of insulin-resistance and atherosclerosis Diabetes Care 1996 19: 287–291.
Van Der Kooy K, Seidell JC . Techniques for the measurement of visceral fat: a practical guide Int J Obes 1993 17:: 187–196.
Despres J-P, Prud'homme D, Pouliot M-C, Tremblay A, Bouchard C . Estimation of deep abdominal adipose-tissue accumulation from simple anthropometric measurements in men Am J Clin Nutr 1991 54: 471–477.
Kahn HS, Austin H, Williamson DF, Arensberg P . Simple anthropometric indices associated with ischemic heart disease J Clin Epidemiol 1996 49: 1017–1024.
Kvist H, Chowdhury B, Grangard U, Tylen U, Sjöström L . Total and visceral adipose-tissue volume derived from measurements with computed tomography in adult men and women: predictive equations Am J Clin Nutr 1988 48: 1351–1361.
Pouliot M-C, Despres J-P, Lemieux S, Moorjani S, Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, Lupien PJ . Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter: best simple anthropometric indexes of abdominal visceral adipose tissue accumulation and related cardiovascular risk in men and women Am J Cardiol 1994 73: 460–468.
Ross R, Leger L, Morris DV, de Guise J, Guardo R . Quantification of adipose tissue by MRI: relationship with anthropometric variables J Appl Physiol 1992 72: 787–795.
Seidell JC, Oosterlee A, Deurenberg P, Hautvast J, Ruijs J . Abdominal fat depots measured with computed tomography: effects of degree of obesity, sex, and age Eur J Clin Nutr 1988 42: 805–815.
Hayes PA, Sowood PJ, Belyavin A, Cohen JB, Smith FW . Subcutaneous fat thickness measured by magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, and calipers Med Sci Sports Ex 1988 20: 303–309.
Van Der Kooy K, Leenen R, Seidell JC, Deurenberg P, Visser M . Abdominal diameters as indicators of visceral fat: comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and anthropometry Br J Nutr 1993 70: 47–58.
Kvist H, Sjöström L, Tylen U . Adipose tissue volume determinations in women by computed tomography: technical considerations Int J Obes 1986 10: 53–67.
Tokunaga K, Matsuzawa Y, Ishikawa K, Tarui S . A novel technique for the determination of body fat by computed tomography Int J Obes 1983 7: 437–445.
Borkan GA, Gerzof SG, Robbins AH . Assessment of abdominal fat content by computed tomography Am J Clin Nutr 1982 36: 172–177.
Jensen MD, Kanaley JA, Reed JE, Sheedy PF . Measurement of abdominal and visceral fat with computed tomography and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry Am J Clin Nutr 1995 61: 274–278.
Jensen MD, Kanaley JA, Roust LR, O'Brien PC, Braun JS, Dunn WL, Wahner HW . Assessment of body composition with use of DEXA: evaluation and comparison with other methods Mayo Clin Proc 1993 68: 867–873.
Haarbo J, Gotfredsen A, Hassager C, Christiansen C . Validation of body composition by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) Clin Physiol 1991 11: 331–341.
Svendsen OL, Hassager C, Bergmann I, Christiansen C . Measurement of abdominal and intra-abdominal fat in postmenopausal women by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry and anthropometry: comparison with computerized tomography Int J Obes 1993 17: 45–51.
Van Loan MD, Mayclin PL . Body composition assessment: dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) compared to reference methods Eur J Clin Nutr 1992 46: 125–130.
Wellens R, Chumlea WC, Guo S, Roche AF, Reo NV, Siervogel RM . Body composition in white adults by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry, densitometry and total body water Am J Clin Nutr 1994 59: 547–555.
Pietrobelli A, Formica C, Wang Z, Heymsfield B . Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry body composition model: review of physical concepts Am J Physiol 1996 271: E941–E951.
Ley CJ, Lees B, Stevenson JC . Sex- and menopause-associated changes in body-fat distribution Am J Clin Nutr 1992 55: 950–954.
Sjöström L, Kvist H, Cederblad A, Tylen U . Determination of total adipose tissue and body fat in women by computed tomography, 40K, and tritium Am J Physiol 1986 250: E736–E745.
Bland J, Altman D . Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement Lancet 1986 1: 307–310.
Guo SS, Chumlea WC . Statistical methods for the development and testing of predictive equations. In: Roche AF, Heymsfield SB, Lohman TG (eds) Human Body Composition Human Kinetics: Champaign II 1996 pp 191-202.
Treuth MS, Hunter GR, Kekes-Szabo T . Estimating intra-abdominal adipose tissue in women by duel-energy X-ray absorptiometry Am J Clin Nutr 1995 62: 527–532.
Busetto L, Baggio MB, Zurlo F, Digito M, Enzi G . Assessment of abdominal fat distribution in obese patients: anthropometry versus computerized tomography Int J Obes 1992 16: 731–736.
Björntorp P . Are regional metabolic differences of adipose tissue responsible for different risks of obesity? Horm Metab Res Suppl 1988 19: 23–25.
Armellini F, Scalfi L, Zamboni M, Castelli S, Mino A, Bosello O . Relationship between hydration of lean body mass and visceral adipose tissue. A clinical study of women Int J Obes 1996 20: 37–40.
Wang Z-M, Pierson RBN, Heymsfield SB . The five level model: a new approach to organizing body-composition research Am J Clin Nutr 1992 56: 19–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertin, E., Marcus, C., Ruiz, JC. et al. Measurement of visceral adipose tissue by DXA combined with anthropometry in obese humans. Int J Obes 24, 263–270 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801121
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801121
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Probiotics’ effect on visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2022)
-
Computed Tomography Assessment of Fat Distribution and Staple-Line Leak Risk After Sleeve Gastrectomy
Obesity Surgery (2021)
-
An evaluation of low volume high-intensity intermittent training (HIIT) for health risk reduction in overweight and obese men
BMC Obesity (2017)
-
Assessment of EchoMRI-AH versus dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry by iDXA to measure human body composition
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2017)
-
Effect of a high-protein energy-restricted diet combined with resistance training on metabolic profile in older individuals with metabolic impairments
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging (2017)