Abstract
Interest in autophagy has exploded over the last decade, with publications highlighting crosstalk with several other cellular processes including secretion, endocytosis, and cell suicide pathways including apoptosis. Autophagy proteins have also been implicated in other cellular processes independently of their roles in autophagy, creating complexities in the interpretation of autophagy (Atg) mutant gene data. Interestingly, this self-eating process is a survival mechanism that can also promote cell death, but when and how autophagy may ‘switch’ its function is still under debate. Indeed, there are currently many models of how autophagy actually influences cell death. In this review, we highlight some outstanding questions and possible controversies in the autophagy field.
Similar content being viewed by others
Facts
-
Autophagy is a cellular process that delivers cytoplasmic material to the lysosome for recycling.
-
Autophagy or autophagy proteins interact with several other cellular processes such the apoptosis, secretion, and endocytic pathways.
-
Autophagy proteins are involved in development and are implicated in cancer as well as neurogeneration and immune disorders.
Open Questions
-
How does the autophagy pathway interact with other pathways, such as cell suicide, secretion, and endocytic pathways?
-
How common are the proposed non-canonical mechanisms of autophagy? Are there others? What is the physiological relevance of having multiple mechanisms to control autophagy?
-
How far does non-canonical autophagy have to drift before it is no longer considered autophagy?
-
Exactly how does the ULK1 complex, PI3K complex, and ubiquitin-like pathways communicate with each other? When some of these complexes not required, such as in non-canonical mechanisms of autophagy regulation, how is this signalling interrupted or bypassed?
-
How and when do the programmed cell death and cell suicide pathways regulate autophagy? When and how does autophagy switch from facilitating cell health to promotion of programmed cell death?
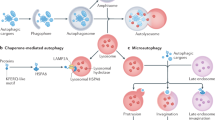
Autophagy, or ‘self-eating,’ is a cellular process that delivers cytoplasmic material to the lysosome for recycling. It is stimulated above the basal or resting rate when nutrients are scarce, when cells are under stress, or intracellular bacteria and damaged organelles need to be degraded. Autophagic membrane formation (i.e., the phagophore) is initiated by both the Unc-51-like autophagy-activating kinase (ULK) complex (ULK1/2(ATG1)/ FAK family kinase-interacting protein of 200 kDa (FIP200)/ATG13/ATG101) and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) complex III (Beclin 1 (BECN1)/VPS34/VPS15/ATG14; Figure 1),1,2 where ATG and VPS stand for autophagy protein and vacuolar protein sorting, respectively. Both of these complexes are major points of regulation in autophagy: both are phosphorylated by AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR).1,3 The regulation of BECN1 is also discussed in more detail in question #3. When autophagy is stimulated, an ATG4-cleaved microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3) named LC3-I is conjugated with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to form LC3-II by an ubiquitin-like pathway, which includes ATG12, ATG7, ATG10, ATG5, and ATG16L. LC3-II is the ‘active form’ that assists in elongating the phagophore membrane, and the recruitment of cargoes to the phagophore.
The canonical mammalian autophagy pathway. The ULK complex and the PI3K complex III initiate autophagy. When autophagy is stimulated, LC3-I is conjugated with PE by two ubiquitin-like conjugation pathways and becomes associated with the growing phagophore membrane. To degrade its contents, the autophagosome fuses with lysosomes to become autolysosomes. ATG, autophagy protein; FIP200, FAK family kinase-interacting protein of 200 kDa; Ub, ubiquitin; VPS, vacuolar protein sorting.
Cytoplasmic material is enveloped by the phagopore to form the autophagosome. To degrade the material the autophagosome needs to fuse with lysosomes (known as the vacuole in yeast and plants), forming an autolysosome (Figure 1). This latter autophagic compartment degrades the encased cellular material and returns ‘building blocks’ such as amino acids back to the cytoplasm. While this, albeit simplified, mechanism is canonical, several alternatives have been reported, which forms our first question.
Question #1: How is either non-canonical or canonical autophagy regulated? How can we define autophagy in experimental settings?
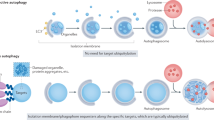
Recent work has suggested that autophagy can occur using multiple variant mechanisms, bypassing seemingly essential complexes (Figure 2). While BECN1 is often touted as essential for autophagy, BECN1 dependency appears to be cell type specific and the protein may not be required for autophagy induced by cytotoxic compounds such as staurosporin, gossypol, or resveratrol.4–6
Proteins thought to be dispensable in non-canonical autophagy (question #1). Autophagy proteins that have been suggested to be dispensable for non-canonical autophagy mechanism(s) are transparent, while proteins or conjugations required only in some forms of non-canonical, but not canonical autophagy, are in green. ATG, autophagy protein; FIP200, FAK family kinase-interacting protein of 200 kDa; Rab9, Ras-related protein 9; VPS, vacuolar protein sorting.
Similarly, the ULK complex is also evaded under some circumstances. Although autophagy stimulated by amino-acid starvation was ULK dependent, autophagy induced by glucose deprivation was not.7 Indeed, the interaction between FIP200 of the ULK complex and ATG16L1 of the ubiquitin-like LC3 lipidation pathway may not be involved in glucose-dependent autophagy.8 Ironically, basal or resting state autophagy appears to be ‘non-canonical’ as ATG12–ATG5 conjugation is reported to be absent. Murrow et al.9 instead argue that ATG12 conjugates with ATG3 and interestingly this also occurs when autophagy proteins are involved in endocytosis, which will be discussed further below.
But perhaps most surprising is evidence suggesting that autophagy can take place without LC3 lipidation, arguably the most common marker of autophagy. Nishida et al.10 have suggested that even though etoposide- and starvation-induced LC3B lipidation requires ATG5 and ATG7 in MEFs, the presence of double-membrane vesicles and continued protein degradation implies that autophagy occurs in the absence of these key ATG factors. They instead propose that Ras-related protein 9 (Rab9), a protein involved in trafficking between endosomes and the trans-Golgi, is involved in this non-canonical autophagy, presumably compensating for the lack of LC3-II. If this ATG5/ATG7/LC3-II-independent, but ULK1/BECN1-dependent, process is truly autophagy or if the ATG proteins are independently involved in (non-canonical) endocytosis will require further investigation (see question #2).
More recently another form of ATG7- and ATG3-independent autophagy was described during the development of the Drosophila midgut.11 In this case, genetic manipulation suggested a large panel of autophagy proteins, including ATG1, ATG2, ATG5, ATG6, ATG12, ATG13, ATG16, VPS34, and LC3 (called ATG8a in Drosophila), were still required for developmental autophagic cell death in these cells. Surprisingly, however, LC3 lipidation was not. The E1 ubiquitinating enzyme ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 1 (Uba1) was obligatory, but does not seem to functionally replace ATG7. The exact role of Uba1 in this ATG7/3-independent autophagy will require further investigation. Importantly, autophagy stimulated by starvation in flies requires the canonical ATG7/3-dependent autophagy mechanism.11–13 These studies highlight that different stimuli may induce autophagy via different mechanisms in distinct cell contexts. As well, it is becoming clear that different cell types have specialised mechanisms to control autophagy, thereby allowing different responses to the same stimuli in multicellular organisms.14
With alternative mechanisms of autophagy proposed in which ATG proteins appear to be dispensable under some circumstances, it is easy to see how monitoring autophagy is becoming a complicated affair. No longer can we perform a simple knockdown or use a mutant to determine without reasonable doubt the role of autophagy in our experiments. These non-canonical pathways highlight our lack of knowledge of the intricacies of the molecular interactions between the autophagy complexes. How exactly does signalling take place between autophagy complexes? When some complexes are not required, how is this signalling interrupted or bypassed? What are the common forms of ‘non-canonical’ autophagy? Are they reproducible in multiple organisms under the same conditions? What is the physiological relevance/advantage of having multiple mechanisms to induce autophagy? The fact that many ATG knockout mice are embryonic lethal could suggest that alternative autophagy mechanisms are not redundant in development,15 although one cannot rule out that lethality is induced by additional autophagy-independent functions of these genes.
Question #2: When does autophagy protein function become pleiotropic?
Autophagy proteins have also been reported to be involved in processes that are apparently independent of their roles in autophagy, further complicating data interpretation (Figure 3). For instance, the core components of the PI3K complex, including Vps34, BECN1, and Vps15 affect endocytosis, potentially at the early endosome stage.16–19 In addition, LC3 has been implicated in LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP) by macrophages, which takes up foreign bodies (beads, yeast) as well as dead mammalian cells killed by multiple cell death pathways.20,21 This process also involves several autophagy proteins, such as BECN1, ATG5, and ATG7, but not ULK1. Loss of ATG7 caused an increase in inflammatory cytokines by macrophages, suggesting that LAPs could be anti-inflammatory, although one cannot completely rule out that inhibition of ATG7-mediated autophagy does not contribute to inflammation. Interestingly, these LAP structures are composed of a single-membrane, not double-membrane structures like classical autophagosomes. Similarly, LC3-dependent but ULK1-independent single-membrane structures have been observed during entosis, a form of cell death involving living cells that invade phagocytes to die in their phagosomes.22
Several autophagy proteins including BECN1, VPS34, and ULK1/2 have been reported to be involved in protein secretion.16 Indeed, links between autophagy (or autophagy proteins) and secretion in inflammation are mostly described in the context of an inhibitory role of autophagy in secretion of inflammatory cytokines.23,24 An example of an activating role is the autophagy-dependent secretion of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β25 and IL-6.26 As well, Atg7, but neither BECN1 nor Atg5, has been implicated in cell cycle arrest via an apparent interaction with p53.27 However, an Atg5- and Atg7-dependent cell cycle arrest has been observed in leukaemic cells, mediated most likely via an altered metabolism leading to increased proliferation in vitro and enhanced leukaemic growth in vivo.28 This topic remains controversial29 and requires more investigation, as it is critical for the understanding of autophagy’s role in cancer. In addition, sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1/p62), a protein that binds ubiquitinated protein aggregates for delivery to autophagosomes, binds to kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1). This displaces and activates the transcription factor nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) thereby helping to protect against oxidative and electrophilic stresses.30 Therefore, a decrease in autophagy would induce SQSTM1/p62 accumulation, thereby regulating this interaction. Several other apparent functions of autophagy proteins have been recently reviewed.31
One question that arises is if these apparent pleiotropic ATG functions are either actually independent of autophagy, or if autophagy is simply non-canonical (see question #1). Although most studies demonstrated that one or two other autophagy proteins are not required, they rarely systematically study the role of a large panel of the autophagy protein-encoding genes. For these types of studies, it is frustrating that we do not yet have specific autophagy inhibitors – chloroquine and bafiolomycin A1 influence the lysosome and therefore impact the trafficking processes that intersect with the lysosomal network.1,32,33 By contrast, 3-methyladenine and wortmannin target multiple PI3Ks including the known pleiotropic Vps34, and only recently have more specific Vps34 and ULK1 inhibitors been reported.34–36 Clearly, even with definitive evidence, we must face the philosophical question: if only part of the pathway is required for delivery of cargoes to lysosomes, is it considered autophagy dependent or independent? When does a vesicle made by autophagy proteins become sufficiently different that the functions of the proteins are considered pleiotropic? Perhaps clearer definitions are needed, but if the original definition of autophagy includes any mechanism enabling delivery of materials to the lysosome, then lysosome-independent functions of ATG genes may need to be defined with new names.
Several autophagy proteins have also been implicated in cell death. A calpain-cleaved fragment of ATG5, which is no longer functional in autophagy, induced cell death by apparently sequestering the pro-survival protein B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL), thereby inducing intrinsic apoptosis.37 As well, ATG5 has been reported to interact with Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) to regulate caspase 8-dependent apoptosis.38
ATG12 has been suggested to induce apoptosis by sequestering the pro-survival B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) family members via its BH3 domain – a domain common to the apoptotic proteins such as Bim.39 It is interesting to note that ATG4D and BECN1 also have a BH3-like domain,40,41 although one would predict that both would have a lower affinity binding to Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL compared with the apoptotic family members. Consistent with this prediction, overexpression of ATG4D stimulated mitochondrial apoptosis, which was not strictly dependent on its BH3 domain.40 As well, apoptotic family members have been implicated in regulating autophagy by binding to BH3 domains, which leads to our next question.
Question #3: How do cell death pathways regulate autophagy?
The most investigated crosstalk in the cell death and autophagy regulatory pathways is between the pro-survival Bcl-2 family members and BECN1.42,43 Multiple models exist for this relationship (Figure 4). The original model has Bcl-2, and its related family members myeloid cell leukaemia 1 (Mcl-1) and Bcl-xL, binding to and inhibiting BECN1 independently of the apoptosis pathway.42,44 Mutagenesis and crystallography data indicate that this interaction occurs via a BH3-like domain on BECN1.41 As the binding affinity of BECN1 appears to be approximately a thousand-fold weaker than that of the canonical apoptotic BH3-containing proteins, such as either Bim or Bcl-2 homologous antagonist killer (Bak),41,45–47 it will be interesting to study if and how these interactions regulate each other in the cell. BECN1 is unusual in that overexpression did not appear to induce apoptosis like other proteins with BH3 domains.42 On the other hand, it has also been reported that phosphorylation of BECN1 by hepatocyte growth factor-like protein (Mst1) can in fact increase the affinity of BECN1 for Bcl-2, thereby supressing autophagy but also importantly inducing apoptosis.48
To complicate matters, recent evidence suggests that modulating the pro-survival Bcl-2 family only influenced autophagy when Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) and/or Bak were present. This led to the proposal of an alternative model where the pro-survival Bcl-2 family members inhibit autophagy by restraining their apoptotic interaction partners Bax and Bak, the effectors of intrinsic apoptosis.43,49 Consistent with this model, overexpression of Bax alone can stimulate autophagy.50 Others, however, report the opposite, presumably owing to later downstream caspase cleavage of autophagy proteins.51,52 Further research will be needed to determine whether these two models are mutually exclusive, can occur in tandem, or whether they are specific to circumstance. For instance, overexpressing Bcl-2 did not inhibit either LC3 lipidation or autophagosome formation during autophagy induced by detachment or growth factor withdrawal.53 However, it appears that Bax/Bak-independent effects of inhibiting the pro-survival Bcl-2 family may be possible, but they occur much later than autophagy instigated by Bax and Bak, which is induced at a similar rate to starvation-induced autophagy.43,54
In addition, several other cell death proteins have been suggested to affect autophagy (Figure 2c).55 FADD, which is involved in extrinsic apoptosis, has been reported to regulate autophagy by binding to ATG5-ATG12.38,56 TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), a ligand that can induce extrinsic apoptosis and necroptosis, has been suggested to activate autophagy in MCF-10A cells, independent of caspase activity.57 However, caspases have also been suggested to inhibit autophagy.58 In the latter study, the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK and caspase 8 inhibition have both been proposed to inhibit RIP-dependent autophagy and cell death in L929 cells. It was therefore suggested to be autophagic cell death, but with our current knowledge of necroptosis (a RIP-dependent cell death induced by caspase inhibition),59 another interpretation could be that this is actually necroptotic cell death with accompanying autophagy. Indeed, this forms a transition to our last topic – autophagic cell death.
Question #4: When is autophagy either a pro-survival or a cell death process?
Autophagic cell death has been a controversy for quite some time (Figure 5).60 Initially it was defined as cell death that correlated with stimulation of autophagy, but the current and accepted definition of autophagic cell death is ‘a cell death subroutine that is limited or delayed by the pharmacologic or genetic inhibition of the autophagic machinery.’61 This is an important distinction as apoptosis, necroptosis, and necrosis are frequently accompanied by autophagic vacuoles. An example is the induction of cell death by cytotoxic compounds. For instance, while it is clear that the apoptosis-inducing chemotherapeutic etoposide can induce autophagy independently of apoptosis (i.e., absence of the effectors Bax and Bak),43,62 the manner of death induced when apoptosis is inhibited is still under dispute. Although cell death was inhibited with autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine, which inhibits multiple PI3Ks,62 genetic inhibition of autophagy did not affect viability.43 In a screen of 1400 cytotoxic compounds, none induced cell death in an ATG7-dependent manner even though knockdown of ATG7 was able to reduce autophagosome formation.63 However, taking into account question #1, there is the possibility that autophagic cell death occurred in an ATG7- and LC3-independent manner. There is some controversy regarding the role of autophagy in luminal formation at least in vitro. For instance, TRAIL-induced autophagy has been suggested to both contribute to cell death and to promote cell survival to induce luminal filling.53,57,64
A subtype of autophagic cell death called autosis has recently been described. When an 18-amino-acid fragment of BECN1 was fused to a HIV Tat peptide and fed to MEF and HeLa cells, autophagy and cell death occurred, which was independent of loss of Bax and Bak (apoptosis) or RIPK1 and RIPK3 (necroptosis).65 Na+, K+-ATPase appears to contribute to this type of cell death, although why this type of Na+, K+-ATPase would either be activated by autophagy or stimulate cell death is unclear. Although Tat-BECN1 peptide was used to characterise autosis the majority of the time, 1% of starved HeLa cells also possess this phenotype. It would be interesting to determine whether the same type of cell death occurs in starved cells that are incapable of undergoing apoptosis or necrosis. Autosis also occurred after hypoxic–ischaemic injury in neonatal rat neurons, but it is unclear how frequently autosis occurs in vivo. Under what stresses is it activated? Is this form of cell death also present when other cell death pathways are genetically inactivated in vivo? This publication raises several interesting questions and leads to the query whether autosis is actually different enough from autophagic cell death (cell death caused by autophagy) to justify a separate name.66,67
Perhaps the purest approach to determining whether autophagy contributes to cell killing is to ask this question in the context of programmed cell deaths that occur in vivo during development. During Drosophila development, programmed cell death removes the larval midgut, which is genetically independent of caspase-mediated apoptosis.68 This cell death was inhibited by the deletion of autophagy genes. Interestingly, this seems to be a type of non-canonical autophagy, which does not require ATG7 or ATG3.11 Is autophagy associated with cell death induced via a different mechanism than autophagy that is pro-survival? Strong data exist in support of this possibility in the fly salivary gland, where immune receptor signalling, micro RNA, and calcium signalling have been shown to be required for autophagy and cell death, but these genes are not required for nutrient deprivation-induced autophagy and cell survival in the fly fatbody.69,70 Alternatively, does autophagy in the context of cell survival and death possess different feedback signalling mechanisms? Another possibility is that different autophagic cargoes are recruited during autophagy associated with cell death than during cell survival.71,72 Although autophagic cell death is quite well characterised in the fly, the question remains whether this type is limited to the fly or whether cells from other organisms undergo programmed autophagic cell death in a similar manner. Indeed, several autophagy genes are required for development in the mouse as well,15 but whether this is as a programmed cell death function or to keep cells alive has not been determined. Autophagic cell death in other organisms, such as other insects, protists, and plants, is discussed in detail in Nelson et al.73
To complicate matters further, autophagy is reported to kill via other cell death pathways as well. For instance, several studies have suggested that autophagy can induce cell death via mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis.39,74,75 In addition, a recent report suggests that autophagy stimulates necroptosis after certain stimuli76 and this may be consistent with previous work,58 but how this occurs is not clear. It would be interesting to determine whether autophagy stimulates necroptosis after ‘classical’ necroptosis stimuli (TNF, cycloheximide, and caspase inhibition) in an MLKL-dependent manner. Obviously there are still many outstanding questions regarding autophagic cell death. When and how does autophagy ‘switch’ from pro-survival to become a cell death process or programmed cell death mechanism? Is this environment specific, organism specific or tissue specific? What pathway(s) ‘create the switch’ if there is one? Why is it different in distinct cell types? When autophagy kills, how are certain mechanisms such as autosis or caspase-dependent cell death activated? Can autophagy also kill by necrosis?
Concluding Remarks
Here we have highlighted a small number of the interesting current questions in the autophagy field. Many questions exist about the fundamental mechanisms that control this important process,77 and differences in cell and tissue biology in multicellular animals require robust genetic investigation of this process in model systems.14 Although efficient and economical, the initial characterisation of cell death and autophagy mechanisms in cell lines has the disadvantage of potentially not being physiologically relevant, especially if work is done in cell lines that have large chromosomal deletions that include pertinent autophagy and apoptosis genes. We now need to focus on finding in vivo evidence for these mechanisms and determining their physiological role, including for non-canonical autophagy.
The autophagy field is in an exciting time. The more we understand about the intricacies of the pathway, its variant mechanisms, and its interactions with other pathways, the closer we will get to translate our knowledge to the clinic. Autophagy has been considered a promising target for disease therapies.78,79 Patients with cancer, neurogeneration, or immune disorders may one day benefit from our increased understanding of the interplay between autophagy and cell death and alternative autophagy pathways. Undoubtedly many of our current models and definitions will be modified or even discarded as our understanding of this complex pathway and its interactions grows. Our different points of view and scientific debate help to foster new ideas and allow science to progress. Indeed, ‘all great ideas are controversial, or have been at one time.’ – Gilbert Seldes.
Abbreviations
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- ATG:
-
autophagy protein/gene
- Bak:
-
Bcl-2 homologous antagonist killer
- Bax:
-
Bcl-2-associated X protein
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2
- Bcl-xL:
-
B-cell lymphoma-extra large
- BECN1:
-
Beclin 1
- FADD:
-
Fas-associated protein with death domain
- FIP200:
-
FAK family kinase-interacting protein of 200 kDa
- Keap1:
-
kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- LAP:
-
LC3-associated phagocytosis
- LC3:
-
microtubule-associated protein light chain 3
- Mcl-1:
-
myeloid cell leukaemia 1
- mTOR:
-
mechanistic target of rapamycin
- Nrf2:
-
nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2
- PE:
-
phosphatidylethanolamine
- Rab1:
-
Ras-related protein 9
- SQSTM1:
-
sequestosome-1
- TRAIL:
-
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- Uba1:
-
ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 1
- ULK:
-
Unc-51-like autophagy-activating kinase
- VPS:
-
vacuolar protein sorting
References
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H, Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy 2012; 8: 445–544.
Yang Z, Klionsky DJ . Mammalian autophagy: core molecular machinery and signaling regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2010; 22: 124–131.
Laplante M, Sabatini DM . mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012; 149: 274–293.
Gao P, Bauvy C, Souquere S, Tonelli G, Liu L, Zhu Y et al. The Bcl-2 homology domain 3 mimetic gossypol induces both Beclin 1-dependent and Beclin 1-independent cytoprotective autophagy in cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 25570–25581.
Scarlatti F, Maffei R, Beau I, Codogno P, Ghidoni R . Role of non-canonical Beclin 1-independent autophagy in cell death induced by resveratrol in human breast cancer cells. Cell Death Differ 2008; 15: 1318–1329.
Grishchuk Y, Ginet V, Truttmann AC, Clarke PG, Puyal J . Beclin 1-independent autophagy contributes to apoptosis in cortical neurons. Autophagy 2011; 7: 1115–1131.
Cheong H, Lindsten T, Wu J, Lu C, Thompson CB . Ammonia-induced autophagy is independent of ULK1/ULK2 kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 11121–11126.
Gammoh N, Florey O, Overholtzer M, Jiang X . Interaction between FIP200 and ATG16L1 distinguishes ULK1 complex-dependent and -independent autophagy. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2013; 20: 144–149.
Murrow L, Malhotra R, Debnath J . ATG12-ATG3 interacts with Alix to promote basal autophagic flux and late endosome function. Nat Cell Biol 2015; 17: 300–310.
Nishida Y, Arakawa S, Fujitani K, Yamaguchi H, Mizuta T, Kanaseki T et al. Discovery of Atg5/Atg7-independent alternative macroautophagy. Nature 2009; 461: 654–658.
Chang TK, Shravage BV, Hayes SD, Powers CM, Simin RT, Wade Harper J et al. Uba1 functions in Atg7- and Atg3-independent autophagy. Nat Cell Biol 2013; 15: 1067–1078.
Juhasz G, Erdi B, Sass M, Neufeld TP . Atg7-dependent autophagy promotes neuronal health, stress tolerance, and longevity but is dispensable for metamorphosis in Drosophila. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 3061–3066.
Scott RC, Juhasz G, Neufeld TP . Direct induction of autophagy by Atg1 inhibits cell growth and induces apoptotic cell death. Curr Biol 2007; 17: 1–11.
Zhang H, Baehrecke EH . Eaten alive: novel insights into autophagy from multicellular model systems. Trends Cell Biol 2015; 25: 376–387.
Mizushima N, Levine B . Autophagy in mammalian development and differentiation. Nat Cell Biol 2010; 12: 823–830.
Shravage BV, Hill JH, Powers CM, Wu L, Baehrecke EH . Atg6 is required for multiple vesicle trafficking pathways and hematopoiesis in Drosophila. Development 2013; 140: 1321–1329.
Rohatgi RA, Janusis J, Leonard D, Bellve KD, Fogarty KE, Baehrecke EH et al. Beclin 1 regulates growth factor receptor signaling in breast cancer. Oncogene 2015; 34: 5352–5362.
Anding AL, Baehrecke EH . Vps15 is required for stress induced and developmentally triggered autophagy and salivary gland protein secretion in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ 2015; 22: 457–464.
Juhasz G, Hill JH, Yan Y, Sass M, Baehrecke EH, Backer JM et al. The class III PI(3)K Vps34 promotes autophagy and endocytosis but not TOR signaling in Drosophila. J Cell Biol 2008; 181: 655–666.
Martinez J, Almendinger J, Oberst A, Ness R, Dillon CP, Fitzgerald P et al. Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 alpha (LC3)-associated phagocytosis is required for the efficient clearance of dead cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 17396–17401.
Sanjuan MA, Dillon CP, Tait SW, Moshiach S, Dorsey F, Connell S et al. Toll-like receptor signalling in macrophages links the autophagy pathway to phagocytosis. Nature 2007; 450: 1253–1257.
Florey O, Kim SE, Sandoval CP, Haynes CM, Overholtzer M . Autophagy machinery mediates macroendocytic processing and entotic cell death by targeting single membranes. Nat Cell Biol 2011; 13: 1335–1343.
Puleston DJ, Simon AK . Autophagy in the immune system. Immunology 2014; 141: 1–8.
Stranks AJ, Hansen AL, Panse I, Mortensen M, Ferguson DJ, Puleston DJ et al. Autophagy controls acquisition of aging features in macrophages. J Innate Immun 2015; 7: 375–391.
Dupont N, Jiang S, Pilli M, Ornatowski W, Bhattacharya D, Deretic V . Autophagy-based unconventional secretory pathway for extracellular delivery of IL-1beta. EMBO J 2011; 30: 4701–4711.
Lock R, Kenific CM, Leidal AM, Salas E, Debnath J . Autophagy-dependent production of secreted factors facilitates oncogenic RAS-driven invasion. Cancer Discov 2014; 4: 466–479.
Lee IH, Kawai Y, Fergusson MM, Rovira II, Bishop AJ, Motoyama N et al. Atg7 modulates p53 activity to regulate cell cycle and survival during metabolic stress. Science 2012; 336: 225–228.
Watson AS, Riffelmacher T, Stranks A, Williams O, De Boer J, Cain K et al. Autophagy limits proliferation and glycolytic metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Discov 2015; 1: 15008.
Kageyama S, Komatsu M . Impaired G1-arrest, autophagy, and apoptosis in Atg7-knockout mice. Circ Res 2012; 111: 962–964.
Komatsu M, Kurokawa H, Waguri S, Taguchi K, Kobayashi A, Ichimura Y et al. The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1. Nat Cell Biol 2010; 12: 213–223.
Subramani S, Malhotra V . Non-autophagic roles of autophagy-related proteins. EMBO Rep 2013; 14: 143–151.
Mrschtik M, Ryan KM . Lysosomal proteins in cell death and autophagy. FEBS J 2015; 282: 1858–1870.
Drose S, Altendorf K . Bafilomycins and concanamycins as inhibitors of V-ATPases and P-ATPases. J Exp Biol 1997; 200 (Pt 1): 1–8.
Dowdle WE, Nyfeler B, Nagel J, Elling RA, Liu S, Triantafellow E et al. Selective VPS34 inhibitor blocks autophagy and uncovers a role for NCOA4 in ferritin degradation and iron homeostasis in vivo. Nat Cell Biol 2014; 16: 1069–1079.
Egan DF, Chun MG, Vamos M, Zou H, Rong J, Miller CJ et al. Small molecule inhibition of the autophagy kinase ULK1 and identification of ULK1 substrates. Mol Cell 2015; 59: 285–297.
Ronan B, Flamand O, Vescovi L, Dureuil C, Durand L, Fassy F et al. A highly potent and selective Vps34 inhibitor alters vesicle trafficking and autophagy. Nat Chem Biol 2014; 10: 1013–1019.
Yousefi S, Perozzo R, Schmid I, Ziemiecki A, Schaffner T, Scapozza L et al. Calpain-mediated cleavage of Atg5 switches autophagy to apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8: 1124–1132.
Young MM, Takahashi Y, Khan O, Park S, Hori T, Yun J et al. Autophagosomal membrane serves as platform for intracellular death-inducing signaling complex (iDISC)-mediated caspase-8 activation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 12455–12468.
Rubinstein AD, Eisenstein M, Ber Y, Bialik S, Kimchi A . The autophagy protein Atg12 associates with antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members to promote mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol Cell 2011; 44: 698–709.
Betin VM, Lane JD . Caspase cleavage of Atg4D stimulates GABARAP-L1 processing and triggers mitochondrial targeting and apoptosis. J Cell Sci 2009; 122 (Pt 14): 2554–2566.
Oberstein A, Jeffrey PD, Shi Y . Crystal structure of the Bcl-XL-Beclin 1 peptide complex: Beclin 1 is a novel BH3-only protein. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 13123–13132.
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R, Liang XH, Mizushima N et al. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005; 122: 927–939.
Lindqvist LM, Heinlein M, Huang DC, Vaux DL . Prosurvival Bcl-2 family members affect autophagy only indirectly, by inhibiting Bax and Bak. Proc Natl Acad Scie USA 2014; 111: 8512–8517.
Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Mizrachy L, Idelchuk Y, Koren I, Eisenstein M et al. DAP-kinase-mediated phosphorylation on the BH3 domain of beclin 1 promotes dissociation of beclin 1 from Bcl-XL and induction of autophagy. EMBO Rep 2009; 10: 285–292.
Feng W, Huang S, Wu H, Zhang M . Molecular basis of Bcl-xL’s target recognition versatility revealed by the structure of Bcl-xL in complex with the BH3 domain of Beclin-1. J Mol Biol 2007; 372: 223–235.
Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG et al. Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell 2005; 17: 393–403.
Ku B, Liang C, Jung JU, Oh BH . Evidence that inhibition of BAX activation by BCL-2 involves its tight and preferential interaction with the BH3 domain of BAX. Cell Res 2011; 21: 627–641.
Maejima Y, Kyoi S, Zhai P, Liu T, Li H, Ivessa A et al. Mst1 inhibits autophagy by promoting the interaction between Beclin1 and Bcl-2. Nat Med 2013; 19: 1478–1488.
Lindqvist LM, Vaux DL . BCL2 and related prosurvival proteins require BAK1 and BAX to affect autophagy. Autophagy 2014; 10: 1474–1475.
Yee KS, Wilkinson S, James J, Ryan KM, Vousden KH . PUMA- and Bax-induced autophagy contributes to apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2009; 16: 1135–1145.
Luo S, Rubinsztein DC . Apoptosis blocks Beclin 1-dependent autophagosome synthesis: an effect rescued by Bcl-xL. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 268–277.
Norman JM, Cohen GM, Bampton ET . The in vitro cleavage of the hAtg proteins by cell death proteases. Autophagy 2010; 6: 1042–1056.
Fung C, Lock R, Gao S, Salas E, Debnath J . Induction of autophagy during extracellular matrix detachment promotes cell survival. Mol Biol Cell 2008; 19: 797–806.
Pedro JM, Wei Y, Sica V, Maiuri C, Zou Z, Kroemer G et al. BAX and BAK1 are dispensable for ABT-737-induced dissociation of the BCL2-BECN1 complex and autophagy. Autophagy 2015; 11: 452–459.
Lalaoui N, Lindqvist LM, Sandow JJ, Ekert PG . The molecular relationships between apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2015; 39: 63–69.
Bell BD, Leverrier S, Weist BM, Newton RH, Arechiga AF, Luhrs KA et al. FADD and caspase-8 control the outcome of autophagic signaling in proliferating T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 16677–16682.
Mills KR, Reginato M, Debnath J, Queenan B, Brugge JS . Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is required for induction of autophagy during lumen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 3438–3443.
Yu L, Alva A, Su H, Dutt P, Freundt E, Welsh S et al. Regulation of an ATG7-beclin 1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science 2004; 304: 1500–1502.
Murphy JM, Silke J . Ars Moriendi; the art of dying well – new insights into the molecular pathways of necroptotic cell death. EMBO Rep 2014; 15: 155–164.
Baehrecke EH . Autophagy: dual roles in life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 505–510.
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV et al. Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ 2012; 19: 107–120.
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB et al. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 1221–1228.
Shen S, Kepp O, Michaud M, Martins I, Minoux H, Metivier D et al. Association and dissociation of autophagy, apoptosis and necrosis by systematic chemical study. Oncogene 2011; 30: 4544–4556.
Herrero-Martin G, Hoyer-Hansen M, Garcia-Garcia C, Fumarola C, Farkas T, Lopez-Rivas A et al. TAK1 activates AMPK-dependent cytoprotective autophagy in TRAIL-treated epithelial cells. EMBO J 2009; 28: 677–685.
Liu Y, Shoji-Kawata S, Sumpter RM Jr., Wei Y, Ginet V, Zhang L et al. Autosis is a Na+,K+-ATPase-regulated form of cell death triggered by autophagy-inducing peptides, starvation, and hypoxia-ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 20364–20371.
Munoz-Pinedo C, Martin SJ . Autosis: a new addition to the cell death Tower of Babel. Cell Death Dis 2014; 5: e1319.
Liu Y, Levine B . Autosis and autophagic cell death: the dark side of autophagy. Cell Death Differ 2015; 22: 367–376.
Denton D, Shravage B, Simin R, Mills K, Berry DL, Baehrecke EH et al. Autophagy, not apoptosis, is essential for midgut cell death in Drosophila. Curr Biol 2009; 19: 1741–1746.
McPhee CK, Logan MA, Freeman MR, Baehrecke EH . Activation of autophagy during cell death requires the engulfment receptor Draper. Nature 2010; 465: 1093–1096.
Nelson C, Ambros V, Baehrecke EH . miR-14 regulates autophagy during developmental cell death by targeting ip3-kinase 2. Mol Cell 2014; 56: 376–388.
Nezis IP, Shravage BV, Sagona AP, Lamark T, Bjorkoy G, Johansen T et al. Autophagic degradation of dBruce controls DNA fragmentation in nurse cells during late Drosophila melanogaster oogenesis. J Cell Biol 2010; 190: 523–531.
Yu L, Wan F, Dutta S, Welsh S, Liu Z, Freundt E et al. Autophagic programmed cell death by selective catalase degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 4952–4957.
Nelson C, Baehrecke EH . Eaten to death. FEBS J 2014; 281: 5411–5417.
Altman BJ, Wofford JA, Zhao Y, Coloff JL, Ferguson EC, Wieman HL et al. Autophagy provides nutrients but can lead to Chop-dependent induction of Bim to sensitize growth factor-deprived cells to apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 2009; 20: 1180–1191.
Gonzalez P, Mader I, Tchoghandjian A, Enzenmuller S, Cristofanon S, Basit F et al. Impairment of lysosomal integrity by B10, a glycosylated derivative of betulinic acid, leads to lysosomal cell death and converts autophagy into a detrimental process. Cell Death Differ 2012; 19: 1337–1346.
Basit F, Cristofanon S, Fulda S . Obatoclax (GX15-070) triggers necroptosis by promoting the assembly of the necrosome on autophagosomal membranes. Cell Death Differ 2013; 20: 1161–1173.
Chen Y, Klionsky DJ . The regulation of autophagy – unanswered questions. J Cell Sci 2011; 124 (Pt 2): 161–170.
White E . Deconvoluting the context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 401–410.
Harris H, Rubinsztein DC . Control of autophagy as a therapy for neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol 2012; 8: 108–117.
Acknowledgements
We apologise to those whose work we did not cover owing to length constraints. Research on this subject is supported by the Victorian State Government Operational Infrastructure Support and Australian Government NHMRC IRIISS to WEHI (LML), a Wellcome Trust New Investigator Award (AKS), the NIHR-funded Biomedical Research Centre Oxford (AKS), and the National Institutes of Health (GM079431, GM111658, CA159314, AI099708) (EHB). LML holds an NHMRC Peter Doherty Early Career Fellowship (1035502) and EHB is an Ellison Medical Foundation Scholar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Lindqvist, L., Simon, A. & Baehrecke, E. Current questions and possible controversies in autophagy. Cell Death Discovery 1, 15036 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.36
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.36
This article is cited by
-
Mapping autophagosome contents identifies interleukin-7 receptor-α as a key cargo modulating CD4+ T cell proliferation
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Hsa-miR-30a-3p overcomes the acquired protective autophagy of bladder cancer in chemotherapy and suppresses tumor growth and muscle invasion
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Inhibiting autophagy potentiates the antitumor efficacy of Euphorbia royleana for canine mammary gland tumors
BMC Veterinary Research (2020)
-
Estrogen and estrogen receptors chauffeur the sex-biased autophagic action in liver
Cell Death & Differentiation (2020)
-
Atg7-dependent canonical autophagy regulates the degradation of aquaporin 2 in prolonged hypokalemia
Scientific Reports (2019)