Abstract
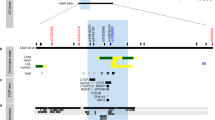
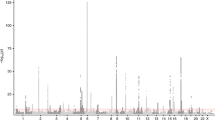
The main genetic determinant of soluble interleukin 6 receptor (sIL-6R) levels is the missense variant rs2228145 that maps to the cleavage site of IL-6R. For each Ala allele, sIL-6R serum levels increase by ∼20 ng ml−1 and asthma risk by 1.09-fold. However, this variant does not explain the total heritability for sIL-6R levels. Additional independent variants in IL6R may therefore contribute to variation in sIL-6R levels and influence asthma risk. We imputed 471 variants in IL6R and tested these for association with sIL-6R serum levels in 360 individuals. An intronic variant (rs12083537) was associated with sIL-6R levels independently of rs4129267 (P=0.0005), a proxy single-nucleotide polymorphism for rs2228145. A significant and consistent association for rs12083537 was observed in a replication panel of 354 individuals (P=0.033). Each rs12083537:A allele increased sIL-6R serum levels by 2.4 ng ml−1. Analysis of mRNA levels in two cohorts did not identify significant associations between rs12083537 and IL6R transcription levels. On the other hand, results from 16 705 asthmatics and 30 809 controls showed that the rs12083537:A allele increased asthma risk by 1.04-fold (P=0.0419). Genetic risk scores based on IL6R regulatory variants may prove useful in explaining variation in clinical response to tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6R monoclonal antibody.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy DM, O’Byrne PM . Recent advances in the pathophysiology of asthma. Chest 2010; 137: 1417–1426.
Doganci A, Sauer K, Karwot R, Finotto S . Pathological role of IL-6 in the experimental allergic bronchial asthma in mice. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2005; 28: 257–270.
Neveu WA, Allard JL, Raymond DM, Bourassa LM, Burns SM, Bunn JY et al. Elevation of IL-6 in the allergic asthmatic airway is independent of inflammation but associates with loss of central airway function. Respir Res 2010; 11: 28.
Rincon M, Irvin CG . Role of IL-6 in asthma and other inflammatory pulmonary diseases. Int J Biol Sci 2012; 8: 1281–1290.
Wang J, Homer RJ, Chen Q, Elias JA . Endogenous and exogenous IL-6 inhibit aeroallergen-induced Th2 inflammation. J Immunol 2000; 165: 4051–4061.
Hibi M, Murakami M, Saito M, Hirano T, Taga T, Kishimoto T . Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell 1990; 63: 1149–1157.
Taga T, Hibi M, Hirata Y, Yamasaki K, Yasukawa K, Matsuda T et al. Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell 1989; 58: 573–581.
Chalaris A, Rabe B, Paliga K, Lange H, Laskay T, Fielding CA et al. Apoptosis is a natural stimulus of IL6R shedding and contributes to the proinflammatory trans-signaling function of neutrophils. Blood 2007; 110: 1748–1755.
Oberg HH, Wesch D, Grussel S, Rose-John S, Kabelitz D . Differential expression of CD126 and CD130 mediates different STAT-3 phosphorylation in CD4+CD25- and CD25high regulatory T cells. Int Immunol 2006; 18: 555–563.
Horiuchi S, Koyanagi Y, Zhou Y, Miyamoto H, Tanaka Y, Waki M et al. Soluble interleukin-6 receptors released from T cell or granulocyte/macrophage cell lines and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells are generated through an alternative splicing mechanism. Eur J Immunol 1994; 24: 1945–1948.
Lust JA, Donovan KA, Kline MP, Greipp PR, Kyle RA, Maihle NJ . Isolation of an mRNA encoding a soluble form of the human interleukin-6 receptor. Cytokine 1992; 4: 96–100.
Mullberg J, Schooltink H, Stoyan T, Gunther M, Graeve L, Buse G et al. The soluble interleukin-6 receptor is generated by shedding. Eur J Immunol 1993; 23: 473–480.
Rose-John S, Heinrich PC . Soluble receptors for cytokines and growth factors: generation and biological function. Biochem J 1994; 300 Pt 2 281–290.
Galicia JC, Tai H, Komatsu Y, Shimada Y, Akazawa K, Yoshie H . Polymorphisms in the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) gene: strong evidence that serum levels of soluble IL-6R are genetically influenced. Genes Immun 2004; 5: 513–516.
Mullberg J, Oberthur W, Lottspeich F, Mehl E, Dittrich E, Graeve L et al. The soluble human IL-6 receptor. Mutational characterization of the proteolytic cleavage site. J Immunol 1994; 152: 4958–4968.
Doganci A, Eigenbrod T, Krug N, De Sanctis GT, Hausding M, Erpenbeck VJ et al. The IL-6R alpha chain controls lung CD4+CD25+ Treg development and function during allergic airway inflammation in vivo. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 313–325.
Ferreira MA, Matheson MC, Duffy DL, Marks GB, Hui J, Le Souef P et al. Identification of IL6R and chromosome 11q13.5 as risk loci for asthma. Lancet 2011; 378: 1006–1014.
Rafiq S, Frayling TM, Murray A, Hurst A, Stevens K, Weedon MN et al. A common variant of the interleukin 6 receptor (IL-6r) gene increases IL-6r and IL-6 levels, without other inflammatory effects. Genes Immun 2007; 8: 552–559.
Raggi P, Su S, Karohl C, Veledar E, Rojas-Campos E, Vaccarino V . Heritability of renal function and inflammatory markers in adult male twins. Am J Nephrol 2010; 32: 317–323.
Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker RE et al. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature 2012; 491: 56–65.
Yang J, Ferreira T, Morris AP, Medland SE, Madden PA, Heath AC et al. Conditional and joint multiple-SNP analysis of GWAS summary statistics identifies additional variants influencing complex traits. Nat Genet 2012; 444: 369–375, S1-3.
Melzer D, Perry JR, Hernandez D, Corsi AM, Stevens K, Rafferty I et al. A genome-wide association study identifies protein quantitative trait loci (pQTLs). PLoS Genet 2008; 4: e1000072.
Ferreira RC, Freitag DF, Cutler AJ, Howson JM, Rainbow DB, Smyth DJ et al. Functional IL6R 358Ala allele impairs classical IL-6 receptor signaling and influences risk of diverse inflammatory diseases. PLoS Genet 2013; 9: e1003444.
Dunham I, Kundaje A, Aldred SF, Collins PJ, Davis CA, Doyle F et al. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012; 489: 57–74.
Cortes A, Hadler J, Pointon JP, Robinson PC, Karaderi T, Leo P et al. Identification of multiple risk variants for ankylosing spondylitis through high-density genotyping of immune-related loci. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 730–738.
Hingorani AD, Casas JP . The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: a mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet 2012; 379: 1214–1224.
Medland SE, Nyholt DR, Painter JN, McEvoy BP, McRae AF, Zhu G et al. Common variants in the trichohyalin gene are associated with straight hair in Europeans. Am J Hum Genet 2009; 85: 750–755.
Ferreira MA, O’Gorman L, Le Souef P, Burton PR, Toelle BG, Robertson CF et al. Variance components analyses of multiple asthma traits in a large sample of Australian families ascertained through a twin proband. Allergy 2006; 61: 245–253.
Powell JE, Henders AK, McRae AF, Caracella A, Smith S, Wright MJ et al. The Brisbane Systems Genetics Study: genetical genomics meets complex trait genetics. PLoS One 2012; 7: e35430.
Zhu G, Montgomery GW, James MR, Trent JM, Hayward NK, Martin NG et al. A genome-wide scan for naevus count: linkage to CDKN2A and to other chromosome regions. Eur J Hum Genet 2007; 15: 94–102.
Boomsma DI, Willemsen G, Sullivan PF, Heutink P, Meijer P, Sondervan D et al. Genome-wide association of major depression: description of samples for the GAIN Major Depressive Disorder Study: NTR and NESDA biobank projects. Eur J Hum Genet 2008; 16: 335–342.
Willemsen G, Vink JM, Abdellaoui A, den Braber A, van Beek JH, Draisma HH et al. The Adult Netherlands Twin Register: twenty-five years of survey and biological data collection. Twin Res Hum Genet 2013; 16: 271–281.
Moffatt MF, Gut IG, Demenais F, Strachan DP, Bouzigon E, Heath S et al. A large-scale, consortium-based genomewide association study of asthma. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 1211–1221.
Howie BN, Donnelly P, Marchini J . A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000529.
Li Y, Willer C, Sanna S, Abecasis G . Genotype imputation. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2009; 10: 387–406.
Li Y, Willer CJ, Ding J, Scheet P, Abecasis GR . MaCH: using sequence and genotype data to estimate haplotypes and unobserved genotypes. Genet Epidemiol 2010; 34: 816–834.
Willer CJ, Li Y, Abecasis GR . METAL: fast and efficient meta-analysis of genomewide association scans. Bioinformatics 2010; 26: 2190–2191.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the participants of the Asthma and Twin moles studies: Ann Eldridge, Marlene Grace, Kerrie McAloney (sample collection); Melinda Richter, Lisa Bowdler, Steven Crooks (DNA processing); David Smyth, Harry Beeby, Daniel Park (IT support). Funding was provided by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC, 613627). The NTR/NESDA data described in this paper were funded by the US National Institute of Mental Health (RC2 MH089951, PI Sullivan) as part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009. MARF is supported by a Career Development Fellowship from the NHMRC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Contributors Melanie C Matheson, Guy B Marks, Jennie Hui, Peter Le Souëf, Patrick Danoy, Svetlana Baltic, Dale R Nyholt, Mark Jenkins, Catherine Hayden, John Beilby, Faang Cheah, Pamela A Madden, Andrew C Heath, John L Hopper, Bill Musk, Stephen R Leeder, Eugene H Walters, Alan James, Graham Jones, Michael J Abramson, Colin F Robertson, Shyamali C Dharmage, Matthew A Brown and Philip J Thompson. Affiliation details for this group can be found in the supplementary information.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Genes and Immunity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Revez, J., Bain, L., Chapman, B. et al. A new regulatory variant in the interleukin-6 receptor gene associates with asthma risk. Genes Immun 14, 441–446 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.38
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.38
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genomics of asthma, allergy and chronic rhinosinusitis: novel concepts and relevance in airway mucosa
Clinical and Translational Allergy (2020)
-
A single nucleotide polymorphism of IL6-receptor is associated with response to tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis patients
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2019)
-
Prognostic role of genetic polymorphisms of the interleukin-6 signaling pathway in patients with severe heart failure
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2019)
-
Influence of IL6R gene polymorphisms in the effectiveness to treatment with tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2018)
-
Lessons from ten years of genome‐wide association studies of asthma
Clinical & Translational Immunology (2017)