Abstract
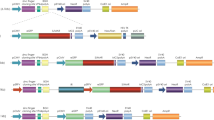
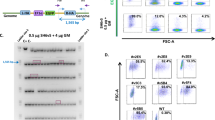
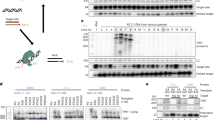
The stable, regulated and tissue-specific expression of a therapeutic transgene can be best achieved by the transfer of a complete genomic locus, which will include the short- and long-range regulatory elements that are critical for the accurate control of gene expression. However, when techniques that rely on the random integration of exogenous DNA into the human genome are used for gene transfer, the risk of insertional mutagenesis remains a major issue. Using components derived from the adeno-associated virus (AAV), we have successfully targeted the integration of 200 kb bacterial artificial chromosomes containing the entire β-globin locus into the AAVS1 site on human chromosome 19. We show that transient expression of the AAV Rep proteins in K562 cells facilitated site-specific transgene integration in 17% (6 of 36) of all analysed integration sites. Southern blot analysis revealed the locus had integrated into AAVS1 as an intact, functional unit in five of the six clones generated. Furthermore, each of the site-specific integrants exhibited sustained and appropriately regulated transgene gene expression over a period of 8 months of continuous culture in the absence of selective pressure. We anticipate that the approach developed in this study may be suitable for facilitating targeted integration of intact genomic loci in adult and embryonic stem cells, and therefore provide a powerful tool not just for functional studies but in establishing model systems for the ex vivo correction of genetic disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bestor TH . Gene silencing as a threat to the success of gene therapy. J Clin Invest 2000; 105: 409–411.
Wilson C, Bellen HJ, Gehring WJ . Position effects on eukaryotic gene expression. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1990; 6: 679–714.
International Human Genome Mapping Consortium. A physical map of the human genome. Nature 2001; 409: 934–941.
Probst FJ, Fridell RA, Raphael Y, Saunders TL, Wang A, Liang Y et al. Correction of deafness in shaker-2 mice by an unconventional myosin in a BAC transgene. Science 1998; 280: 1444–1447.
Yang XW, Wynder C, Doughty ML, Heintz N . BAC-mediated gene-dosage analysis reveals a role for Zipro1 (Ru49/Zfp38) in progenitor cell proliferation in cerebellum and skin. Nat Genet 1999; 22: 327–335.
Wade-Martins R, White RE, Kimura H, Cook PR, James MR . Stable correction of a genetic deficiency in human cells by an episome carrying a 115 kb genomic transgene. Nat Biotechnol 2000; 18: 1311–1314.
Bochukova EG, Jefferson A, Francis MJ, Monaco AP . Genomic studies of gene expression: regulation of the Wilson disease gene. Genomics 2003; 81: 531–542.
Sarsero JP, Holloway TP, Voullaire L, Gazeas S, Fowler KJ, Kirby DM et al. Human BAC-mediated rescue of the Friedreich ataxia knockout mutation in transgenic mice. Mamm Genome 2004; 15: 370–382.
Vadolas J, Wardan H, Bosmans M, Zaibak F, Jamsai D, Voullaire L et al. Transgene copy number-dependent rescue of murine beta-globin knockout mice carrying a 183 kb human beta-globin BAC genomic fragment. Biochim Biophys Acta 2005; 1728: 150–162.
Kotin RM, Siniscalco M, Samulski RJ, Zhu XD, Hunter L, Laughlin CA et al. Site-specific integration by adeno-associated virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87: 2211–2215.
Kotin RM, Menninger JC, Ward DC, Berns KI . Mapping and direct visualization of a region specific viral DNA integration site on chromosome 19q13-qter. Genomics 1991; 10: 831–834.
Kotin RM, Linden RM, Berns KI . Characterization of a preferred site on chromosome19q for integration of adeno-associated virus DNA by non-homologous recombination. EMBO J 1992; 11: 5071–5078.
Samulski RJ, Zhu X, Xiao X, Brook JD, Housman DE, Epstein N et al. Targeted integration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) into human chromosome 19. EMBO J 1991; 10: 3941–3950.
Hauswirth WW, Berns KI . Adeno-associated virus DNA replication: nonunit-length molecules. Virology 1979; 93: 57–68.
McLaughlin S, Collis KP, Hermonat PL, Muzyczka N . Adeno-associated virus general transduction vectors: analysis of proviral structures. J Virol 1988; 62: 1963–1973.
Samulski RJ, Chang LS, Shenk T . Helper-free stocks of recombinant adeno-associated viruses: normal integration does not require viral gene expression. J Virol 1989; 63: 3822–3828.
Owens RA, Weitzman MD, Kyostio SR, Carter BJ . Identification of a DNA-binding domain in the amino terminus of adenoassociated virus Rep proteins. J Virol 1993; 67: 997–1005.
Snyder RO, Im DS, Ni T, Xiao X, Samulski RJ, Muzyczka N . Features of the adeno-associated virus origin involved in substrate recognition by the viral Rep protein. J Virol 1993; 67: 6096–6104.
Kyostio SR, Wonderling RS, Owens RA . Negative regulation of the adeno-associated virus (AAV) p5 promoter involves both the p5 rep binding site and the consensus ATP-binding motif of the AAV Rep68 protein. J Virol 1995; 69: 6787–6796.
Giraud C, Winocour E, Berns KI . Site-specific integration by adeno-associated virus is directed by a cellular DNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 10039–10043.
Weitzman MD, Kyostio SR, Kotin RM, Owens RA . Adeno-associated virus (AAV) Rep proteins mediate complex formation between AAV DNA and its integration site in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 5808–5812.
Linden RM, Ward P, Giraud C, Winocour E, Berns KI . Site-specific integration by adeno-associated virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 11288–11294.
Linden RM, Winocour E, Berns KI . The recombination signals for adeno-associated virus site-specific integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 7966–7972.
Urcelay E, Ward P, Wiener SM, Safer B, Kotin RM . Asymmetric replication in vitro from a human sequence element is dependent on adeno-associated virus Rep protein. J Virol 1995; 69: 2038–2046.
Yang CC, Xiao X, Zhu X, Ansardi DC, Epstein ND, Frey MR et al. Cellular recombination pathways and viral terminal repeat hairpin structures are sufficient for adeno-associated virus integration in vivo and in vitro. J Virol 1997; 71: 9231–9247.
Balague C, Kalla M, Zhang WW . Adeno-associated virus Rep78 protein and terminal repeats enhance integration of DNA sequences into the cellular genome. J Virol 1997; 71: 3299–3306.
Surosky RT, Urabe M, Godwin SG, McQuiston SA, Kurtzman GJ, Ozawa K et al. Adeno-associated virus Rep proteins target DNA sequences to a unique locus in the human genome. J Virol 1997; 71: 7951–7959.
Pieroni L, Fipaldini C, Monciotti A, Cimini D, Sgura A, Fattori E et al. Targeted integration of adeno-associated virus-derived plasmids in transfected human cells. Virology 1998; 249: 249–259.
Tsunoda H, Hayakawa T, Sakuragawa N, Koyama H . Site-specific integration of adeno-associated virus-based plasmid vectors in lipofected HeLa cells. Virology 2000; 268: 391–401.
Kogure K, Urabe M, Mizukami H, Kume A, Sato Y, Monahan J et al. Targeted integration of foreign DNA into a defined locus on chromosome 19 in K562 cells using AAV-derived components. Int J Hematol 2001; 73: 469–475.
Philpott NJ, Gomos J, Berns KI, Falck-Pedersen E . A p5 integration efficiency element mediates Rep-dependent integration into AAVS1 at chromosome 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 12381–12385.
Feng D, Chen J, Yue Y, Zhu H, Xue J, Jia WW . A 16 bp Rep binding element is sufficient for mediating Rep-dependent integration into AAVS1. J Mol Biol 2006; 358: 39–45.
Yang Q, Chen F, Trempe JP . Characterization of cell lines that inducibly express the adeno-associated virus Rep proteins. J Virol 1994; 68: 4847–4856.
Hermanns J, Schulze A, Jansen-Db1urr P, Kleinschmidt JA, Schmidt R, zur Hausen H . Infection of primary cells by adeno-associated virus type 2 results in modulation of cell cycle-regulating proteins. J Virol 1997; 71: 6020–6027.
Christian SL, Fantes JA, Mewborn SK, Huang B, Ledbetter DH . Large genomic duplicons map to sites of instability in the Prader_Willi/Angelman syndrome chromosome region (15q11–q13). Hum Mol Genet 1999; 8: 1025–1037.
Benz EJ, Murnane MJ, Tonkonow BL, Berman BW, Mazur EM, Cavallesco C et al. Embryonic-fetal erythroid characteristics of a human leukemic cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1980; 77: 3509–3513.
Gambari R, Amelotti F, Piva R . Efficient cell proliferation and predominant accumulation of epsilonglobin mRNA in human leukemic K562 cells which produce mostly Hb Gower 1. Experientia 1985; 41: 673–675.
Howden SE, Voullaire L, Vadalos J . The transient expression of mRNA encoding for Rep protein facilitates targeted plasmid integration. J Gene Med 2008; 10: 42–50.
Vadalos J, Wardan H, Orford M, Voullaire L, Zaibak F, Williamson R et al. Development of sensitive fluorescent assays for embryonic and fetal hemoglobin inducers using the b-globin locus in erthropoietic cells. Blood 2002; 100: 4209–4215.
Vadalos J, Wardan H, Orford M, Williamson R, Ioannou PA . Cellular genomic reporter assays for screening and evaluation of inducers of fetal hemoglobin. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 223–233.
Oehmig A, Cortés ML, Perry KF, Sena-Esteves M, Fraefel C, Breakefield XO . Integration of active human b-galactosidase gene (100 kb) into genome using HSV/AAV amplicon vector. Gene Therapy 2007; 14: 1078–1091.
McCarty DM, Young SM, Samulski RJ . Integration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) and recombinant AAV vectors. Annu Rev Genet 2004; 38: 819–845.
Narayanan K, Williamson R, Zhang Y, Stewart AF, Ioannou PA . Efficient and precise engineering of a 200 kb beta-globin human/bacterial artificial chromosome in E. coli DH10B using an inducible homologous recombination system. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 442–447.
Orford M, Nefedov M, Vadolas J, Zaibak F, Williamson R, Ioannou PA . Engineering EGFP reporter constructs into a 200 kb human beta-globin BAC clone using GET Recombination. Nucleic Acids Res 2000; 28: E84.
Blower MD, Sullivan BA, Karpen GH . Conserved organization of centromeric chromatin in flies and humans. Dev Cell 2002; 2: 319–330.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Horace Drew and Dr Gerry for providing the p5-22 and pRep10 plasmids, and for their helpful advice. We also thank Dr Jude Samulski for providing the pHIV68 plasmid. This work was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council, the Murdoch Children's Research Institute and the Thalassaemia Society of Victoria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Howden, S., Voullaire, L., Wardan, H. et al. Site-specific, Rep-mediated integration of the intact β-globin locus in the human erythroleukaemic cell line K562. Gene Ther 15, 1372–1383 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.84
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.84
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
GFP to BFP Conversion: A Versatile Assay for the Quantification of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Genome Editing
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2016)
-
Reply to “Wild-type AAV Insertions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Do Not Inform Debate Over Genotoxicity Risk of Vectorized AAV”
Molecular Therapy (2016)
-
Editing the genome to introduce a beneficial naturally occurring mutation associated with increased fetal globin
Nature Communications (2015)
-
Long-term and efficient expression of human β-globin gene in a hematopoietic cell line using a new site-specific integrating non-viral system
Gene Therapy (2015)
-
Chromatin structure of two genomic sites for targeted transgene integration in induced pluripotent stem cells and hematopoietic stem cells
Gene Therapy (2013)