Abstract
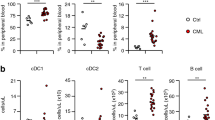
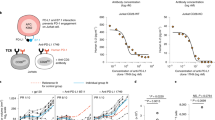
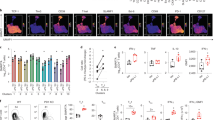
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is characterized by the accumulation of CD5+CD19+ B cells in the peripheral blood, and in primary and secondary lymphoid organs. A major complication associated with CLL is severe recurrent infections, which are often fatal. Vulnerability to infection is due to a wide variety of immunological defects, yet the initiating events of immunodeficiency in CLL are unclear. Using CLL patient samples and a mouse model of CLL, we have discovered that plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), which underpin the activity of effector immune cells critical for anti-viral immunity and anti-tumor responses, are reduced in number and functionally impaired in progressive CLL. As a result, the levels of interferon alpha (IFNα) production, a cytokine critical for immunity, are markedly reduced. Lower pDC numbers with impaired IFNα production was due to the decreased expression of FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 receptor (Flt3) and Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9), respectively. Reduced Flt3 expression was reversed using inhibitors of TGF-β and TNF, an effect correlating with a reduction in tumor load. Defects in pDC numbers and function offer new insight into mechanisms underpinning the profound immunodeficiency affecting CLL patients and provide a potentially novel avenue for restoring immunocompetency in CLL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ternynck T, Dighiero G, Follezou J, Binet JL . Comparison of normal and CLL lymphocyte surface Ig determinants using peroxidase-labeled antibodies. I. Detection and quantitation of light chain determinants. Blood 1974; 43: 789–795.
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, Flandrin G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Vardiman J et al. The World Health Organization classification of hematological malignancies report of the Clinical Advisory Committee Meeting, Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. Modern Pathol 2000; 13: 193–207.
Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Dohner H et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute-Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood 2008; 111: 5446–5456.
Abrisqueta P, Pereira A, Rozman C, Aymerich M, Gine E, Moreno C et al. Improving survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (1980-2008): the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona experience. Blood 2009; 114: 2044–2050.
Orchard JA, Ibbotson RE, Davis Z, Wiestner A, Rosenwald A, Thomas PW et al. ZAP-70 expression and prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2004; 363: 105–111.
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1840–1847.
Rassenti LZ, Jain S, Keating MJ, Wierda WG, Grever MR, Byrd JC et al. Relative value of ZAP-70, CD38, and immunoglobulin mutation status in predicting aggressive disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2008; 112: 1923–1930.
Herling M, Patel KA, Weit N, Lilienthal N, Hallek M, Keating MJ et al. High TCL1 levels are a marker of B-cell receptor pathway responsiveness and adverse outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2009; 114: 4675–4686.
Yan XJ, Albesiano E, Zanesi N, Yancopoulos S, Sawyer A, Romano E et al. B cell receptors in TCL1 transgenic mice resemble those of aggressive, treatment-resistant human chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 11713–11718.
Bichi R, Shinton SA, Martin ES, Koval A, Calin GA, Cesari R et al. Human chronic lymphocytic leukemia modeled in mouse by targeted TCL1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 6955–6960.
Perkins JG, Flynn JM, Howard RS, Byrd JC . Frequency and type of serious infections in fludarabine-refractory B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma: implications for clinical trials in this patient population. Cancer 2002; 94: 2033–2039.
Anaissie EJ, Kontoyiannis DP, O'Brien S, Kantarjian H, Robertson L, Lerner S et al. Infections in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with fludarabine. Ann Int Med 1998; 129: 559–566.
Tsiodras S, Samonis G, Keating MJ, Kontoyiannis DP . Infection and immunity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mayo Clin Proc 2000; 75 (10): 1039–1054.
Freeman JA, Crassini KR, Best OG, Forsyth CJ, Mackinlay NJ, Han P et al. Immunoglobulin G subclass deficiency and infection risk in 150 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2013; 54: 99–104.
Gorgun G, Ramsay AG, Holderried TA, Zahrieh D, Le Dieu R, Liu F et al. E(mu)-TCL1 mice represent a model for immunotherapeutic reversal of chronic lymphocytic leukemia-induced T-cell dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 6250–6255.
Reizis B, Bunin A, Ghosh HS, Lewis KL, Sisirak V . Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: recent progress and open questions. Ann Rev Immunol 2011; 29: 163–183.
Akbar AN . The silent war against CMV in CLL. Blood 2010; 116: 2869–2870.
Yagci M, Ozkurt ZN, Yegin ZA, Aki Z, Sucak GT, Haznedar R . Hepatitus B virus reactivation in HBV-DNA negative and positive patients with hematological malignancies. Hematology 2010; 15: 240–244.
Gonzalez-Navajas JM, Lee J, David M, Raz E . Immunomodulatory functions of type I interferons. Nat Rev Immunol 2012; 12: 125–135.
Swiecki M, Colonna M . Unraveling the functions of plasmacytoid dendritic cells during viral infections, autoimmunity, and tolerance. Immunol Rev 2010; 234: 142–162.
Swiecki M, Gilfillan S, Vermi W, Wang Y, Colonna M . Plasmacytoid dendritic cell ablation impacts early interferon responses and antiviral NK and CD8(+) T cell accrual. Immunity 2010; 33: 955–966.
Zhou LJ, Smith HM, Waldschmidt TJ, Schwarting R, Daley J, Tedder TF . Tissue-specific expression of the human CD19 gene in transgenic mice inhibits antigen-independent B-lymphocyte development. Mol Cell Biol 1994; 14: 3884–3894.
Swiecki M, Wang Y, Vermi W, Gilfillan S, Schreiber RD, Colonna M . Type I interferon negatively controls plasmacytoid dendritic cell numbers in vivo. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 2367–2374.
Baumgarth N . The double life of a B-1 cell: self-reactivity selects for protective effector functions. Nat Rev Immunol 2011; 11: 34–46.
Shodell M, Siegal FP . Circulating, interferon-producing plasmacytoid dendritic cells decline during human ageing. Scand J Immunol 2002; 56: 518–521.
Munn DH, Mellor AL, Rossi M, Young JW . Dendritic cells have the option to express IDO-mediated suppression or not. Blood 2005; 105: 2618.
Maraskovsky E, Pulendran B, Brasel K, Teepe M, Roux ER, Shortman K et al. Dramatic numerical increase of functionally mature dendritic cells in FLT3 ligand-treated mice. Adv Exp Med Biol 1997; 417: 33–40.
Maraskovsky E, Daro E, Roux E, Teepe M, Maliszewski CR, Hoek J et al. In vivo generation of human dendritic cell subsets by Flt3 ligand. Blood 2000; 96: 878–884.
Veiby OP, Jacobsen FW, Cui L, Lyman SD, Jacobsen SE . The flt3 ligand promotes the survival of primitive hemopoietic progenitor cells with myeloid as well as B lymphoid potential. Suppression of apoptosis and counteraction by TNF-alpha and TGF-beta. J Immunol 1996; 157: 2953–2960.
Ramsfjell V, Borge OJ, Cui L, Jacobsen SE . Thrombopoietin directly and potently stimulates multilineage growth and progenitor cell expansion from primitive (CD34+ CD38-) human bone marrow progenitor cells: distinct and key interactions with the ligands for c-kit and flt3, and inhibitory effects of TGF-beta and TNF-alpha. J Immunol 1997; 158: 5169–5177.
Schroeder JT, Chichester KL, Bieneman AP . Toll-like receptor 9 suppression in plasmacytoid dendritic cells after IgE-dependent activation is mediated by autocrine TNF-alpha. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121: 486–491.
Vincent FB, Morand EF, Murphy K, Mackay F, Mariette X, Marcelli C . Antidrug antibodies (ADAb) to tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-specific neutralising agents in chronic inflammatory diseases: a real issue, a clinical perspective. Ann Rheum Dis 2013; 72: 165–178.
Ferrajoli A, Keating MJ, Manshouri T, Giles FJ, Dey A, Estrov Z et al. The clinical significance of tumor necrosis factor-alpha plasma level in patients having chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 1215–1219.
Schiemann WP, Rotzer D, Pfeifer WM, Levi E, Rai KR, Knaus P et al. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta)-resistant B cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients contain recurrent mutations in the signal sequence of the type I TGF-beta receptor. Cancer Detect Prev 2004; 28: 57–64.
Morrison VA . Infectious complications in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: pathogenesis, spectrum of infection, and approaches to prophylaxis. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma 2009; 9: 365–370.
Morrison VA, Rai KR, Peterson BL, Kolitz JE, Elias L, Appelbaum FR et al. Impact of therapy With chlorambucil, fludarabine, or fludarabine plus chlorambucil on infections in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Intergroup Study Cancer and Leukemia Group B 9011. J Clin Oncology 2001; 19: 3611–3621.
Guven H, Gilljam M, Chambers BJ, Ljunggren HG, Christensson B, Kimby E et al. Expansion of natural killer (NK) and natural killer-like T (NKT)-cell populations derived from patients with B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL): a potential source for cellular immunotherapy. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1973–1980.
Colonna M, Trinchieri G, Liu YJ . Plasmacytoid dendritic cells in immunity. Nat Immunol 2004; 5: 1219–1226.
Hartmann G, Battiany J, Poeck H, Wagner M, Kerkmann M, Lubenow N et al. Rational design of new CpG oligonucleotides that combine B cell activation with high IFN-alpha induction in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol 2003; 33: 1633–1641.
Picaud S, Bardot B, De Maeyer E, Seif I . Enhanced tumor development in mice lacking a functional type I interferon receptor. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2002; 22: 457–462.
Oberg K, Alm G, Magnusson A, Lundqvist G, Theodorsson E, Wide L et al. Treatment of malignant carcinoid tumors with recombinant interferon alfa-2b: development of neutralizing interferon antibodies and possible loss of antitumor activity. J Nat Cancer Inst 1989; 81: 531–535.
Ziegler-Heitbrock HW, Schlag R, Flieger D, Thiel E . Favorable response of early stage B CLL patients to treatment with IFN-alpha 2. Blood 1989; 73: 1426–1430.
Peggs KS, Quezada SA, Korman AJ, Allison JP . Principles and use of anti-CTLA4 antibody in human cancer immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol 2006; 18: 206–213.
Peggs KS, Quezada SA, Chambers CA, Korman AJ, Allison JP . Blockade of CTLA-4 on both effector and regulatory T cell compartments contributes to the antitumor activity of anti-CTLA-4 antibodies. J Exp Med 2009; 206: 1717–1725.
Lapenta C, Santini SM, Spada M, Donati S, Urbani F, Accapezzato D et al. IFN-alpha-conditioned dendritic cells are highly efficient in inducing cross-priming CD8(+) T cells against exogenous viral antigens. Eur J Immunol 2006; 36: 2046–2060.
Kranzer K, Bauer M, Lipford GB, Heeg K, Wagner H, Lang R . CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides enhance T-cell receptor-triggered interferon-gamma production and up-regulation of CD69 via induction of antigen-presenting cell-derived interferon type I and interleukin-12. Immunology 2000; 99: 170–178.
Chen YL, Chen TT, Pai LM, Wesoly J, Bluyssen HA, Lee CK . A type I IFN-Flt3 ligand axis augments plasmacytoid dendritic cell development from common lymphoid progenitors. J Exp Med 2013; 210: 2515–2522.
Hartmann E, Wollenberg B, Rothenfusser S, Wagner M, Wellisch D, Mack B et al. Identification and functional analysis of tumor-infiltrating plasmacytoid dendritic cells in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 6478–6487.
Carpentier AF, Xie J, Mokhtari K, Delattre JY . Successful treatment of intracranial gliomas in rat by oligodeoxynucleotides containing CpG motifs. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 2469–2473.
Carpentier AF, Chen L, Maltonti F, Delattre JY . Oligodeoxynucleotides containing CpG motifs can induce rejection of a neuroblastoma in mice. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 5429–5432.
Zent CS, Smith BJ, Ballas ZK, Wooldridge JE, Link BK, Call TG et al. Phase I clinical trial of CpG oligonucleotide 7909 (PF-03512676) in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2012; 53: 211–217.
Liang X, Moseman EA, Farrar MA, Bachanova V, Weisdorf DJ, Blazar BR et al. Toll-like receptor 9 signaling by CpG-B oligodeoxynucleotides induces an apoptotic pathway in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood 2010; 115: 5041–5052.
Ito T, Amakawa R, Inaba M, Ikehara S, Inaba K, Fukuhara S . Differential regulation of human blood dendritic cell subsets by IFNs. J Immunol 2001; 166: 2961–2969.
Cordingley FT, Bianchi A, Hoffbrand AV, Reittie JE, Heslop HE, Vyakarnam A et al. Tumour necrosis factor as an autocrine tumour growth factor for chronic B-cell malignancies. Lancet 1988; 1: 969–971.
Woyach JA, Lin TS, Lucas MS, Heerema N, Moran ME, Cheney C et al. A phase I/II study of rituximab and etanercept in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma. Leukemia 2009; 23: 912–918.
Palucka AK, Blanck JP, Bennett L, Pascual V, Banchereau J . Cross-regulation of TNF and IFN-alpha in autoimmune diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 3372–3377.
Bonnefoy F, Couturier M, Clauzon A, Remy-Martin JP, Gaugler B, Tiberghien P et al. TGF-beta-exposed plasmacytoid dendritic cells participate in Th17 commitment. J Immunol 2011; 186: 6157–6164.
Li L, Liu S, Zhang T, Pan W, Yang X, Cao X . Splenic stromal microenvironment negatively regulates virus-activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TGF-beta. J Immunol 2008; 180: 2951–2956.
Seoane J . The TGFBeta pathway as a therapeutic target in cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 2008; 10: 14–19.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Stephen Jane for critical appraisal of the manuscript, the AMREP flow cytometry team for technical assistance, Dr Meredith O’Keefe for technical suggestions, Dr Pohan Lukito for control BM samples, the AMREP Animal Service staff for colony health management and the ALLG Tissue Bank for provision of BM and PBL samples. We especially thank all patients involved in this study. SBT is supported by an NHMRC RD Wright Career Development Fellowship. This study was funded by the Association for International Cancer Research (AICR) UK and the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) of Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saulep-Easton, D., Vincent, F., Le Page, M. et al. Cytokine-driven loss of plasmacytoid dendritic cell function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 28, 2005–2015 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.105
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.105
This article is cited by
-
Bone marrow dendritic cells support the survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in a CD84 dependent manner
Oncogene (2020)
-
The PTPROt tyrosine phosphatase functions as an obligate haploinsufficient tumor suppressor in vivo in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Oncogene (2017)
-
The BAFF receptor TACI controls IL-10 production by regulatory B cells and CLL B cells
Leukemia (2016)
-
Depletion of CLL-associated patrolling monocytes and macrophages controls disease development and repairs immune dysfunction in vivo
Leukemia (2016)
-
The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic cells
Nature Reviews Immunology (2015)