Abstract
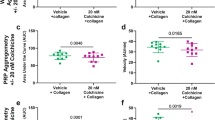
The BTK (Bruton’s tyrosine kinase) inhibitor ibrutinib is associated with an increased risk of bleeding. A previous study reported defects in collagen- and adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-dependent platelet responses when ibrutinib was added ex vivo to patient samples. Whereas the collagen defect is expected given the central role of BTK in glycoprotein VI signaling, the ADP defect lacks a mechanistic explanation. In order to determine the real-life consequences of BTK platelet blockade, we performed light transmission aggregometry in 23 patients receiving ibrutinib treatment. All patients had reductions in collagen-mediated platelet aggregation, with a significant association between the degree of inhibition and the occurrence of clinical bleeding or bruising (P=0.044). This collagen defect was reversible on drug cessation. In contrast to the previous ex vivo report, we found no in vivo ADP defects in subjects receiving standard doses of ibrutinib. These results establish platelet light transmission aggregometry as a method for gauging, at least qualitatively, the severity of platelet impairment in patients receiving ibrutinib treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, Flinn IW, Burger JA, Blum K et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 32–42.
Byrd JC, Brown JR, O'Brien S, Barrientos JC, Kay NE, Reddy NM et al. Ibrutinib versus ofatumumab in previously treated chronic lymphoid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2014; 371: 213–223.
Wang ML, Rule S, Martin P, Goy A, Auer R, Kahl BS et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 507–516.
Advani RH, Buggy JJ, Sharman JP, Smith SM, Boyd TE, Grant B et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) has significant activity in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 88–94.
Quek LS, Bolen J, Watson SP . A role for Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) in platelet activation by collagen. Curr Biol 1998; 8: 1137–1140.
Atkinson BT, Ellmeier W, Watson SP . Tec regulates platelet activation by GPVI in the absence of Btk. Blood 2003; 102: 3592–3599.
Honigberg LA, Smith AM, Sirisawad M, Verner E, Loury D, Chang B et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 blocks B-cell activation and is efficacious in models of autoimmune disease and B-cell malignancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 13075–13080.
Farooqui M, Lozier JN, Valdez J, Saba N, Wells A, Soto S et al. Ibrutinib (PCI 32765) rapidly improves platelet counts in chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) patients and has minimal effects on platelet aggregation. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts 2012; 120: 1789.
Rushworth SA, MacEwan DJ, Bowles KM . Ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369: 1277–1278.
Squizzato A, Keller T, Romualdi E, Middeldorp S . Clopidogrel plus aspirin versus aspirin alone for preventing cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011; (1): CD005158.
Lewis BB, Bates I . Dacie and Lewis Practical Haematology. 10th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier, 2006.
Gratacap MP, Martin V, Valera MC, Allart S, Garcia C, Sie P et al. The new tyrosine-kinase inhibitor and anticancer drug dasatinib reversibly affects platelet activation in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2009; 114: 1884–1892.
Winkelstein JA, Marino MC, Lederman HM, Jones SM, Sullivan K, Burks AW et al. X-linked agammaglobulinemia: report on a United States registry of 201 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2006; 85: 193–202.
Arthur JF, Dunkley S, Andrews RK . Platelet glycoprotein VI-related clinical defects. Br J Haematol 2007; 139: 363–372.
Zahid M, Mangin P, Loyau S, Hechler B, Billiald P, Gachet C et al. The future of glycoprotein VI as an antithrombotic target. J Thromb Haemost 2012; 10: 2418–2427.
Acknowledgements
We thank Bernard Payrastre and Cedric Garcia (Inserm, U1048 and Université Toulouse 3) for assistance in platelet testing, and acknowledge the generosity of the subjects who participated in this study. This work was funded by the authors’ institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr Tam received honorarium from Janssen-Cilag and Pharmacyclics. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamel, S., Horton, L., Ysebaert, L. et al. Ibrutinib inhibits collagen-mediated but not ADP-mediated platelet aggregation. Leukemia 29, 783–787 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.247
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.247
This article is cited by
-
Current concepts and novel targets for antiplatelet therapy
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2023)
-
Managing Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia with BTK inhibitors
Leukemia (2023)
-
BTK Inhibitors and CAR T-Cell Therapy in Treating Mantle Cell Lymphoma—Finding a Dancing Partner
Current Oncology Reports (2022)
-
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase Inhibitors and Cardiotoxicity: More Than Just Atrial Fibrillation
Current Oncology Reports (2021)
-
Atrial fibrillation in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treated with ibrutinib: risk prediction, management, and clinical outcomes
Annals of Hematology (2021)