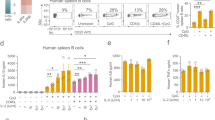
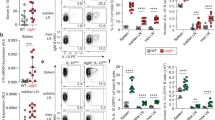
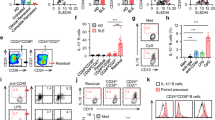
Abstract
Interleukin (IL)-10-producing B cells (B10 cells) have emerged as important regulatory elements with immunosuppressive roles. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) B cells also secrete IL-10 and share features of B10 cells, suggesting a possible contribution of CLL B cells to immunosuppression in CLL patients. Factors controlling the emergence of B10 cells are not known. B-cell-activating factor of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family (BAFF) is critical for B-cell maturation and survival, and is implicated in the development and progression of CLL. We sought to investigate the role of BAFF in the emergence of IL-10-producing regulatory B cells in healthy donors and CLL patients. Here, we report that BAFF signaling promotes IL-10 production by CLL B cells in a mouse model of CLL and in CLL patients. Moreover, BAFF-mediated IL-10 production by normal and CLL B cells is mediated via its receptor transmembrane activator and cyclophilin ligand interactor. Our work uncovered a major targetable pathway important for the generation of regulatory B cells that is detrimental to immunity in CLL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woyach JA, Lozanski G, Ruppert AS, Lozanski A, Blum KA, Jones JA et al. Outcome of patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with flavopiridol: impact of genetic features. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1442–1444.
Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Dohner H et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute-Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood 2008; 111: 5446–5456.
Baumgarth N . The double life of a B-1 cell: self-reactivity selects for protective effector functions. Nat Rev Immunol 2011; 11: 34–46.
Huttmann A, Klein-Hitpass L, Thomale J, Deenen R, Carpinteiro A, Nuckel H et al. Gene expression signatures separate B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia prognostic subgroups defined by ZAP-70 and CD38 expression status. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1774–1782.
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1840–1847.
Rassenti LZ, Jain S, Keating MJ, Wierda WG, Grever MR, Byrd JC et al. Relative value of ZAP-70, CD38, and immunoglobulin mutation status in predicting aggressive disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2008; 112: 1923–1930.
Gorgun G, Holderried TA, Zahrieh D, Neuberg D, Gribben JG . Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce changes in gene expression of CD4 and CD8 T cells. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1797–1805.
Herling M, Patel KA, Weit N, Lilienthal N, Hallek M, Keating MJ et al. High TCL1 levels are a marker of B-cell receptor pathway responsiveness and adverse outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2009; 114: 4675–4686.
Bichi R, Shinton SA, Martin ES, Koval A, Calin GA, Cesari R et al. Human chronic lymphocytic leukemia modeled in mouse by targeted TCL1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 6955–6960.
Hofbauer JP, Heyder C, Denk U, Kocher T, Holler C, Trapin D et al. Development of CLL in the TCL1 transgenic mouse model is associated with severe skewing of the T-cell compartment homologous to human CLL. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1452–1458.
Gorgun G, Ramsay AG, Holderried TA, Zahrieh D, Le Dieu R, Liu F et al. E(mu)-TCL1 mice represent a model for immunotherapeutic reversal of chronic lymphocytic leukemia-induced T-cell dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 6250–6255.
Jak M, Mous R, Remmerswaal EB, Spijker R, Jaspers A, Yague A et al. Enhanced formation and survival of CD4+ CD25hi Foxp3+ T-cells in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia Lymphoma 2009; 50: 788–801.
Giannopoulos K, Schmitt M, Kowal M, Wlasiuk P, Bojarska-Junak A, Chen J et al. Characterization of regulatory T cells in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncol Rep 2008; 20: 677–682.
Ramsay AG, Johnson AJ, Lee AM, Gorgun G, Le Dieu R, Blum W et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia T cells show impaired immunological synapse formation that can be reversed with an immunomodulating drug. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 2427–2437.
Porakishvili N, Kardava L, Jewell AP, Yong K, Glennie MJ, Akbar A et al. Cytotoxic CD4+ T cells in patients with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia kill via a perforin-mediated pathway. Haematologica 2004; 89: 435–443.
Molica S, Levato D, Levato L . Infections in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Analysis of incidence as a function of length of follow-up. Haematologica 1993; 78: 374–377.
Couper KN, Blount DG, Riley EM . IL-10: the master regulator of immunity to infection. J Immunol 2008; 180: 5771–5777.
Mauri C, Bosma A . Immune regulatory function of B cells. Annu Rev Immunol 2012; 30: 221–241.
Balkwill F, Montfort A, Capasso M . B regulatory cells in cancer. Trends Immunol 2013; 34: 169–173.
DiLillo DJ, Weinberg JB, Yoshizaki A, Horikawa M, Bryant JM, Iwata Y et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and regulatory B cells share IL-10 competence and immunosuppressive function. Leukemia 2013; 27: 170–182.
Vincent FB, Saulep-Easton D, Figgett WA, Fairfax KA, Mackay F . The BAFF/APRIL system: emerging functions beyond B cell biology and autoimmunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2013; 24: 203–215.
Mackay F, Schneider P . Cracking the BAFF code. Nat Rev Immun 2009; 9: 491–502.
Novak AJ, Bram RJ, Kay NE, Jelinek DF . Aberrant expression of B-lymphocyte stimulator by B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: a mechanism for survival. Blood 2002; 100: 2973–2979.
Yang M, Sun L, Wang S, Ko KH, Xu H, Zheng BJ et al. Novel function of B cell-activating factor in the induction of IL-10-producing regulatory B cells. J Immunol 2010; 184: 3321–3325.
Zhou LJ, Smith HM, Waldschmidt TJ, Schwarting R, Daley J, Tedder TF . Tissue-specific expression of the human CD19 gene in transgenic mice inhibits antigen-independent B-lymphocyte development. Mol Cell Biol 1994; 14: 3884–3894.
Lech-Maranda E, Mlynarski W, Grzybowska-Izydorczyk O, Borowiec M, Pastorczak A, Cebula-Obrzut B et al. Polymorphisms of TNF and IL-10 genes and clinical outcome of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013; 52: 287–296.
Ferrer G, Hodgson K, Pereira A, Juan M, Elena M, Colomer D et al. Combined analysis of levels of serum B-cell activating factor and a proliferation-inducing ligand as predictor of disease progression in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia Lymphoma 2011; 52: 2064–2068.
Kreuzaler M, Rauch M, Salzer U, Birmelin J, Rizzi M, Grimbacher B et al. Soluble BAFF levels inversely correlate with peripheral B cell numbers and the expression of BAFF receptors. J Immunol 2012; 188: 497–503.
Kern C, Cornuel JF, Billard C, Tang R, Rouillard D, Stenou V et al. Involvement of BAFF and APRIL in the resistance to apoptosis of B-CLL through an autocrine pathway. Blood 2004; 103: 679–688.
Batten M, Groom J, Cachero TG, Qian F, Schneider P, Tschopp J et al. BAFF mediates survival of peripheral immature B lymphocytes. J Exp Med 2000; 192: 1453–1466.
O'Connor BP, Raman VS, Erickson LD, Cook WJ, Weaver LK, Ahonen C et al. BCMA is essential for the survival of long-lived bone marrow plasma cells. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 91–98.
Borsellino G, Kleinewietfeld M, Di Mitri D, Sternjak A, Diamantini A, Giometto R et al. Expression of ectonucleotidase CD39 by Foxp3+ Treg cells: hydrolysis of extracellular ATP and immune suppression. Blood 2007; 110: 1225–1232.
Murai M, Turovskaya O, Kim G, Madan R, Karp CL, Cheroutre H et al. Interleukin 10 acts on regulatory T cells to maintain expression of the transcription factor Foxp3 and suppressive function in mice with colitis. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 1178–1184.
Coffer PJ, Burgering BM . Forkhead-box transcription factors and their role in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2004; 4: 889–899.
Sylvan SE, Rossmann E, Mozaffari F, Porwit A, Norin S, Karlsson C et al. Phase I study of lenalidomide and alemtuzumab in refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: maintaining immune functions during therapy-induced immunosuppression. Br J Haematol 2012; 159: 608–612.
Giannopoulos K, Mertens D, Stilgenbauer S . Treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia with thalidomide and lenalidomide. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2011; 12: 2857–2864.
Saulep-Easton D, Vincent FB, Le Page M, Wei A, Ting SB, Croce CM et al. Cytokine-driven loss of plasmacytoid dendritic cell function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2014; 28: 2005–2015.
Ng LG, Mackay CR, Mackay F . The BAFF/APRIL system: life beyond B lymphocytes. Mol Immunol 2005; 42: 763–772.
Odendahl M, Jacobi A, Hansen A, Feist E, Hiepe F, Burmester GR et al. Disturbed peripheral B lymphocyte homeostasis in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 2000; 165: 5970–5979.
Vincent FB, Northcott M, Hoi A, Mackay F, Morand EF . Association of serum B cell activating factor from the tumour necrosis factor family (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) with central nervous system and renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2013; 22: 873–884.
Amel Kashipaz MR, Huggins ML, Lanyon P, Robins A, Powell RJ, Todd I . Assessment of Be1 and Be2 cells in systemic lupus erythematosus indicates elevated interleukin-10 producing CD5+ B cells. Lupus 2003; 12: 356–363.
Llorente L, Richaud-Patin Y, Wijdenes J, Alcocer-Varela J, Maillot MC, Durand-Gasselin I et al. Spontaneous production of interleukin-10 by B lymphocytes and monocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur Cytokine Network 1993; 4: 421–427.
Iwata Y, Matsushita T, Horikawa M, Dilillo DJ, Yanaba K, Venturi GM et al. Characterization of a rare IL-10-competent B-cell subset in humans that parallels mouse regulatory B10 cells. Blood 2011; 117: 530–541.
Groom JR, Fletcher CA, Walters SN, Grey ST, Watt SV, Sweet MJ et al. BAFF and MyD88 signals promote a lupuslike disease independent of T cells. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 1959–1971.
Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Craxton A, Hendricks DW, Merino MC, Montes CL, Clark EA et al. BAFF and LPS cooperate to induce B cells to become susceptible to CD95/Fas-mediated cell death. Eur J Immunol 2007; 37: 990–1000.
Liang X, Moseman EA, Farrar MA, Bachanova V, Weisdorf DJ, Blazar BR et al. Toll-like receptor 9 signaling by CpG-B oligodeoxynucleotides induces an apoptotic pathway in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood 2010; 115: 5041–5052.
Treml LS, Carlesso G, Hoek KL, Stadanlick JE, Kambayashi T, Bram RJ et al. TLR stimulation modifies BLyS receptor expression in follicular and marginal zone B cells. J Immunol 2007; 178: 7531–7539.
Chu VT, Enghard P, Riemekasten G, Berek C . In vitro and in vivo activation induces BAFF and APRIL expression in B cells. J Immunol 2007; 179: 5947–5957.
Ziegler S, Gartner K, Scheuermann U, Zoeller T, Hantzschmann J, Over B et al. Ca(2+) -related signaling events influence TLR9-induced IL-10 secretion in human B cells. Eur J Immunol 2014; 44: 1285–1298.
Kofler DM, Gawlik BB, Elter T, Gianella-Borradori A, Wendtner CM, Hallek M . Phase 1b trial of atacicept, a recombinant protein binding BLyS and APRIL, in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2012; 26: 841–844.
Matsushita T, Yanaba K, Bouaziz JD, Fujimoto M, Tedder TF . Regulatory B cells inhibit EAE initiation in mice while other B cells promote disease progression. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 3420–3430.
Matsushita T, Horikawa M, Iwata Y, Tedder TF . Regulatory B cells (B10 cells) and regulatory T cells have independent roles in controlling experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis initiation and late-phase immunopathogenesis. J Immunol 2010; 185: 2240–2252.
Carter NA, Vasconcellos R, Rosser EC, Tulone C, Munoz-Suano A, Kamanaka M et al. Mice lacking endogenous IL-10-producing regulatory B cells develop exacerbated disease and present with an increased frequency of Th1/Th17 but a decrease in regulatory T cells. J Immunol 2011; 186: 5569–5579.
Walters S, Webster KE, Sutherland A, Gardam S, Groom J, Liuwantara D et al. Increased CD4+Foxp3+ T cells in BAFF-transgenic mice suppress T cell effector responses. J Immunol 2009; 182: 793–801.
Groux H, O'Garra A, Bigler M, Rouleau M, Antonenko S, de Vries JE et al. A CD4+ T-cell subset inhibits antigen-specific T-cell responses and prevents colitis. Nature 1997; 389: 737–742.
D'Arena G, Laurenti L, Minervini MM, Deaglio S, Bonello L, De Martino L et al. Regulatory T-cell number is increased in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients and correlates with progressive disease. Leukemia Res 2011; 35: 363–368.
Hartung HP, Kieseier BC . Atacicept: targeting B cells in multiple sclerosis. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 2010; 3: 205–216.
Yoshizaki A, Miyagaki T, DiLillo DJ, Matsushita T, Horikawa M, Kountikov EI et al. Regulatory B cells control T-cell autoimmunity through IL-21-dependent cognate interactions. Nature 2012; 491: 264–268.
Fletcher JM, Lonergan R, Costelloe L, Kinsella K, Moran B, O'Farrelly C et al. CD39+Foxp3+ regulatory T Cells suppress pathogenic Th17 cells and are impaired in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 2009; 183: 7602–7610.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Stephen Jane for critical appraisal of the manuscript, the AMREP flow cytometry team for technical assistance, the AMREP Animal Service staff for colony health management and the ALLG Tissue Bank for provision of PBL samples. We especially thank all patients involved in this study. SBT is supported by an NHMRC RD Wright Career Development Fellowship. This study was funded by the Worldwide Cancer Research (formerly Association for International Cancer Research (AICR)) UK and the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) of Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saulep-Easton, D., Vincent, F., Quah, P. et al. The BAFF receptor TACI controls IL-10 production by regulatory B cells and CLL B cells. Leukemia 30, 163–172 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.174
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.174
This article is cited by
-
B-lymphocyte-activating factor is a potential biomarker associated with susceptibility to Graves’ disease in Iraqi women
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2023)
-
Tumour-infiltrating B cells: immunological mechanisms, clinical impact and therapeutic opportunities
Nature Reviews Cancer (2022)
-
Altered expression profile of BAFF receptors on peripheral blood B lymphocytes in Graves’ disease
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2021)
-
B cell heterogeneity, plasticity, and functional diversity in cancer microenvironments
Oncogene (2021)
-
Leukaemia: a model metastatic disease
Nature Reviews Cancer (2021)