Abstract
The Pleiotropic Drug Resistance (PDR) network is central to the drug response in fungi, and its overactivation is associated with drug resistance. However, gene regulation of the PDR network is not well understood. Here, we show that the histone chaperone Rtt106 and the chromatin remodeller SWI/SNF control expression of the PDR network genes and confer drug resistance. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Rtt106 specifically localises to PDR network gene promoters dependent on transcription factor Pdr3, but not Pdr1, and is essential for Pdr3-mediated basal expression of the PDR network genes, while SWI/SNF is essential for both basal and drug-induced expression. Also in the pathogenic fungus Candida glabrata, Rtt106 and SWI/SNF regulate drug-induced PDR gene expression. Consistently, loss of Rtt106 or SWI/SNF sensitises drug-resistant S. cerevisiae mutants and C. glabrata to antifungal drugs. Since they cooperatively drive PDR network gene expression, Rtt106 and SWI/SNF represent potential therapeutic targets to combat antifungal resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The global incidence of life-threatening Candida infections stands at around 400,000 cases annually, with the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains of Candida species being a major global health concern1,2,3. Undermining the utility of antifungal drugs, the Pleiotropic Drug Resistance (PDR) network of fungi works as the first line of defence against a broad range of xenobiotics4,5, and is central to the fungal drug response6,7. Among the PDR network gene products, Pdr5, a major ATP-binding cassette (ABC) multidrug transporter, is critical for drug resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae8, a fungus closely related to the pathogenic fungus Candida glabrata. Pdr5 pumps a variety of drugs out of cells at the expense of ATP hydrolysis, and Pdr5 overexpression is one of the main causes of drug resistance in S. cerevisiae8. Drug resistance to azole antifungals in clinical isolates of C. glabrata is almost exclusively associated with overexpression of multidrug transporter genes CgCDR1 (homolog of ScPDR5) and CgCDR29.
The expression of PDR5 and the other PDR network genes in S. cerevisiae is regulated by Pdr1 and Pdr3, key transcription factors whose functions are partially redundant10,11,12. Pdr1 and Pdr3 form a heterodimer or homodimers, which through their Zn(2)-Cys(6) finger DNA-binding domains13 recognise the PDR responsive element (PDRE: 5′-TCCG(C/T)GGA-3′) present in promoters of the PDR network genes. Pdr1 and Pdr3 together sustain basal gene expression, and Pdr1 activates increased gene expression in response to direct binding to the azole antifungal ketoconazole7. While Pdr3 also can directly bind ketoconazole7, it has not been shown whether its activity is stimulated by ketoconazole binding. Hyperactivation of Pdr1 or Pdr3 is the main cause of overexpression of PDR5 leading to drug resistance. Such hyperactivation can be caused by gain-of-function (GOF) mutations in PDR1 or PDR314,15 or mitochondrial dysfunction (e.g. loss of the mitochondrial genome), the latter of which only stimulates Pdr3-dependent gene expression16. In C. glabrata also, overexpression of the drug transporter genes is caused by GOF mutations in the transcription factor Pdr19. Given the importance of multidrug transporter levels for drug resistance, it is vital to understand the regulation of their expression.
Accessibility of gene promoters is a key factor in gene regulation17,18. Recruitment of transcription machinery to promoters is restricted by nucleosomes19. Histone chaperones and ATP-dependent chromatin-remodelling complexes are accordingly important for gene regulation given they regulate nucleosome dynamics at promoters, restricting or increasing promoter accessibility for recruitment of transcription factors and RNA polymerase II (Pol II)19,20,21,22,23.
Rtt106, a fungal-specific histone chaperone, functions in histone deposition during DNA replication and transcription elongation in S. cerevisiae, and preferentially binds H3K56-acetylated histone H3-H424,25,26. Loss of Rtt106 causes aberrant ‘cryptic’ transcription initiation within gene bodies26 and compromised silencing at the mating loci and telomeres27,28, likely due to defective nucleosome assembly26,27,29.
Apart from its role in histone deposition during replication and transcription elongation, Rtt106 regulates the activity of the histone gene promoters during the cell cycle in S. cerevisiae30. Rtt106 localises at the promoters of three out of four histone gene pairs (HTA1-HTB1, HHT1-HHF1 and HHT2-HHF2, but not HTA2-HTB2), and restricts their transcription to S phase, when new histone supply is required to package newly synthesised DNA31,32. Outside S phase, Rtt106 forms a repressive complex together with other histone chaperones HIR and Asf1 to recruit RSC (Remodel the Structure of Chromatin), an essential ATP-dependent chromatin-remodelling complex, to the histone promoters31,32,33. In contrast, in the late G1 and early S phase Rtt106 recruits SWI/SNF, another ATP-dependent chromatin-remodelling complex, which activates transcription of the histone genes by releasing HIR- and RSC-mediated repression33,34. Rtt106 recruitment to the histone promoters almost completely depends on Asf1, HIR and acetylation of histone H3 at K56 (H3K56Ac), and is limited by Yta7, a bromodomain- and AAA-ATPase domain-containing boundary protein31,32,35. Although this role of Rtt106 at the histone promoters is relatively well-studied, whether Rtt106 plays a role at promoters other than those of histone genes remains unknown.
The yeast SWI/SNF complex is an ATP-dependent chromatin-remodelling complex, and it is composed of 12 subunits, 5 of which are fungal-specific36. SWI/SNF modulates nucleosome position to regulate the expression of a subset of genes including stress-responsive genes20,37,38,39,40. SWI/SNF localises to nucleosome-depleted regions (NDRs) in promoters and regulates the position of the transcription start site (TSS)-associated (or ‘+1’) nucleosome critical for transcription initiation20. Recruitment of SWI/SNF to promoters can be mediated through sequence-specific transcription factors including Gcn4, Pho4, Swi5 and Hap441,42. However, at the histone promoters, SWI/SNF is recruited by Rtt106, probably through direct physical interactions33.
In this study we show that S. cerevisiae Rtt106 localises at subsets of specific promoters, binding particularly strongly to the promoters of the PDR network genes where it upregulates their expression exclusively through Pdr3. Consistently, loss of Rtt106 sensitised wild-type S. cerevisiae and a drug-resistant mutant (a GOF mutation in PDR3) to azole antifungal drugs. We further show that SWI/SNF acts as an essential activator of the PDR network genes for both basal and azole-induced expression, and therefore is essential for drug resistance of wild-type S. cerevisiae, and of a pdr3-GOF mutant. Lastly, we show that C. glabrata Rtt106 and SWI/SNF also localise at the promoter of the multidrug transporter gene CgCDR1, regulating its expression in response to an antifungal drug and conferring resistance to azole antifungals. Therefore, Rtt106 and SWI/SNF represent potential therapeutic targets for combating antifungal resistance of the pathogenic fungus C. glabrata.
Results
Rtt106 binds the PDR network gene promoters
To examine which gene promoters are bound by Rtt106 genome-wide in S. cerevisiae, we performed ChIP-seq analysis. As expected31,32, Rtt106 localised at the promoter of the histone gene pair HTA1-HTB1 (Fig. 1a). Strikingly, we observed equally strong Rtt106 binding at the promoter of the multidrug transporter gene PDR5 (Fig. 1b). The peak summit of Rtt106 binding to the PDR5 promoter was observed at its four PDREs, which are recognised by transcription factors Pdr1 and Pdr3 (Fig. 1b). To identify further promoters that Rtt106 binds genome-wide, we calculated Rtt106 enrichment at all promoters, defined as the regions within 500 bp upstream of the TSS of each gene. Interestingly, 5 out of the top 10 Rtt106-binding promoters contain at least one PDRE (Fig. 1c). Furthermore, the Rtt106 peak summits coincided with the PDRE in such promoters e.g. PDR5, PDR15, SNQ2 and SPO24 (Fig. 2a, Rtt106 ChIP in WT). These results suggest that Rtt106 binds the regions containing PDRE in promoters of the PDR network genes.
a Association of Rtt106 with the promoter of the histone gene pair HTA1-HTB1, validating ChIP-seq analysis of Rtt106-6HA performed in this study. RTT106-6HA cells in log phase were collected for ChIP-seq analysis. Input, sequence reads of the sonicated genomic DNA before ChIP. Rtt106 ChIP, sequence reads of ChIPed DNA with Rtt106-6HA. b ChIP-seq analysis of Rtt106 showing association of Rtt106 with the promoter of the PDR5 gene. Positions of PDRE indicated by magenta lines. PDRE PDR responsive element. c The top 10 peaks of Rtt106 binding at promoter regions. Enrichment of Rtt106 at promoters was calculated as ChIP sequence reads normalised by Input sequence reads in a region spanning 500 bp upstream of the transcription start site of each gene.
a Specimen views of promoters where Rtt106 binding is dependent on Pdr1/3 and Hir1 and limited by Yta7 (falling into cluster 1, designated as Type A). Yta7 binding tested by ChIP-seq analysis29 is shown alongside Rtt106 binding. Positions of PDRE indicated by magenta lines. b Specimen views of promoters where Rtt106 binding is independent of Pdr1/3, dependent on Hir1 and limited by Yta7 (falling into cluster 2, designated as Type B). ChIP-seq analyses of Rtt106 in WT, pdr1Δ pdr3Δ, hir1Δ and yta7Δ mutants are shown. c Clustering analysis of Rtt106 promoter association based on Rtt106 binding in WT and its changes in pdr1Δ pdr3Δ, hir1Δ and yta7Δ. Log2 fold enrichment of Rtt106 binding in WT at promoters (ChIP/input in WT) and log2 fold changes of Rtt106 binding in pdr1Δ pdr3Δ, hir1Δ and yta7Δ compared to that in WT (pdr1Δ pdr3Δ/WT, hir1Δ/WT and yta7Δ/WT, respectively) were calculated as described in Methods. d Criteria used for clustering in panel c. e Features found in promoters categorised into clusters 1–9. Numbers of gene promoters containing PDRE (PDR responsive element; magenta), centromere (yellow), tRNA (black) or snoRNA (dark grey), and those containing Rtt106 signals leaked from highly expressing neighbour genes (‘neighbour’; light grey) are shown. Histone gene promoters (‘histone’; green) were assessed separately. Other than the above features, numbers of promoters with Rtt106 peaks (‘peak’; blue) or broad signals (‘broad’; white) are shown. Promoters with ‘peaks’ in clusters 7 and 8 designated as Type C. f Gene promoters categorised into clusters 1–4. Log2 changes are shown as in c. Asterisks indicate gene promoters containing PDRE. g Nucleosome occupancy analysed by MNase-seq in WT and rtt106Δ (Lombardi et al. 201529) aligned to transcription start site (TSS). Nucleosome-depleted region (NDR) in average of all gene promoters is indicated.
Since PDRE is recognised by transcription factors Pdr1 and Pdr313, we tested if Pdr1 and Pdr3 are required for the recruitment of Rtt106 to the PDRE-containing promoters. Rtt106 binding to the PDRE-containing promoters was almost completely abolished in the absence of both Pdr1 and Pdr3 (Fig. 2a, Rtt106 ChIP in pdr1Δ pdr3Δ), indicating that recruitment of Rtt106 to the PDRE-containing promoters depends on Pdr1 or Pdr3 or both. Rtt106 binding to the HTA1-HTB1 promoter was not affected by the loss of Pdr1 and Pdr3, as expected since the HTA1-HTB1 promoter does not contain a PDRE (Fig. 2b, Rtt106 ChIP in pdr1Δ pdr3Δ).
To further understand the mechanism of Rtt106 recruitment to PDRE-containing promoters, we tested for regulation by other factors involved in Rtt106 recruitment to histone gene promoters. We observed that the HIR histone chaperone, a crucial factor for recruitment of Rtt106 to the HTA1-HTB1 promoter31,32 (Fig. 2b, hir1Δ), contributes to Rtt106 recruitment to PDRE-containing promoters, since the loss of the HIR subunit Hir1 caused a reduction of Rtt106 binding (Fig. 2a, hir1Δ). We further observed that Yta7, a boundary protein that restricts Rtt106 binding at the histone promoters31,32 (Fig. 2b, yta7Δ), limits Rtt106 binding also at the PDRE-containing promoters, as loss of Yta7 increased Rtt106 binding (Fig. 2a, yta7Δ). However, the yta7Δ mutation did not cause Rtt106 binding to spread from PDRE-containing promoters, unlike at the histone promoters where Rtt106 was observed to spread into regions normally occupied by Yta7 (Fig. 2a, b, compare our Rtt106 ChIP data with the published Yta7 ChIP data shown at bottom29). Yta7 may therefore limit Rtt106 binding through different mechanisms at the PDRE-containing and histone promoter sites. Taken together, our results show that HIR and Yta7 contribute to Rtt106 recruitment at the promoters of both the PDR network genes and the histone genes, but their specific effects differ somewhat in the two classes of promoters.
Three distinct binding modes of Rtt106 at promoters
To classify the types of promoters bound by Rtt106, we performed a clustering analysis of Rtt106-binding profiles obtained in a series of ChIP-seq analyses. Rtt106-binding promoters clustered into 9 groups (clusters 1–9) based on Rtt106 binding in WT and the effects of pdr1Δ pdr3Δ, hir1Δ and yta7Δ mutations (Fig. 2c, d and Supplementary Data 1). Interestingly, 19 out of 20 promoters in cluster 1 belong to PDR network genes (Fig. 2c–f), indicating that Rtt106 generally binds the promoters of the PDR network genes in a common manner that we designate ‘Type A’ i.e. fully dependent on Pdr1/3 and partially on HIR, and limited by Yta7. Note that not all PDRE-containing promoters were bound by Rtt106 (Supplementary Fig. 1a).
Cluster 2 contains promoters bound by Rtt106 dependent on HIR and limited by Yta7, but not dependent on Pdr1/3. This cluster included all histone gene pairs (except HTA2-HTB2 where Rtt106 does not bind strongly), as well as AGP1 and ECL1 (Fig. 2b, e, f), indicating that Rtt106 may be recruited to the AGP1 and ECL1 promoter through the mechanism similar to that at histone promoters. We designated this binding type as ‘Type B’.
Clusters 3–6 were very small groups, preventing any general statement about binding at these sites. In clusters 7 and 8, we found another type of Rtt106-binding promoters, where Rtt106 shows clear peaks (rather than broader signals) that do not depend on Pdr1, Pdr3 or HIR, and are not limited by the loss of Yta7 (Fig. 2e, ‘peaks’ in clusters 7 and 8, and Supplementary Fig. 1b and Supplementary Data 1). No common feature was found in these promoter regions. We designate such promoters with ‘peaks’ in cluster 7 and 8 as ‘Type C’ Rtt106-binding promoters. This third type contains some non-PDR transporter genes, e.g. FUI1, CTR1, FTR1, PMA1, PHO87 and PUT4, but does not include any PDR genes. Gene ontology analysis of the 50 genes with these Type C promoters shows a significant enrichment of ‘Cell Periphery’ (p-value, 0.00015; 19 of 50 genes; Supplementary Fig. 1c). Rtt106 was also enriched at centromeres, tRNA, snoRNA, and gene bodies of highly expressed genes, mainly found in clusters 7–9 (Fig. 2e and Supplementary Fig. 1d and Supplementary Data 1). We did not consider promoters overlapping those Rtt106-binding features as ‘Rtt106-bound promoters’.
Many Rtt106-bound promoters (61 out of 79 gene promoters) show regulated expression, either in response to environmental changes or during the cell cycle (Supplementary Data 2). We surmise that Rtt106 may generally bind a subset of gene promoters where expression is induced by specific cellular or environmental circumstances—such as PDR network genes, histone genes and other transporter genes.
We examined the relationship between Rtt106 binding and nucleosome organisation at promoters, by analysing nucleosome positioning and occupancy in MNase-seq datasets published by Rine and colleagues29. We observed that all three types of Rtt106-bound promoters show atypically wide NDRs (Fig. 2g), possibly reflecting the fact that inducible gene promoters are occupied by specific transcriptional regulators. At the histone promoters, RTT106 deletion causes further reduction of nucleosome occupancy as reported previously31 (Fig. 2g, Type B, compare green dashed line with solid line). Surprisingly, however, at the PDRE-containing (Type A) and the Type C promoters, Rtt106 removal did not alter the NDR profile, suggesting that at these promoters the histone chaperone activity of Rtt106 does not affect nucleosome positioning and occupancy at least under the tested conditions (Fig. 2g, compare rtt106Δ with WT).
Rtt106 upregulates Pdr3-mediated expression of the PDR network genes
Rtt106 regulates the expression of the histone genes31,32, so we tested if it also regulates expression at these newly identified binding sites. We performed RNA-seq analysis of total RNA prepared from WT and rtt106Δ cells in log phase growth in rich medium (YPD). Loss of Rtt106 caused a significant reduction of mRNA levels of the majority of the PDR network genes whose promoters it binds (16 out of 20 genes in Type A), with a particular reduction in PDR5, CIS1 and RSB1 expression (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Fig. 2a and Supplementary Data 3). These results suggest that Rtt106 generally upregulates the expression of the PDR network genes, in contrast to its repressive role in histone gene expression. The effect of Rtt106 loss on mRNA levels of the genes classified in Type C was not uniform. mRNA levels of some of those genes (10 out of 50 genes) were significantly reduced, including the uridine permease FUI1 and the copper transporter CTR1 (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Data 3). Gene ontology analysis of the downregulated genes in rtt106Δ show significant enrichment of ‘Transmembrane transport’ genes (Fig. 3b), and 8 out of the 20 most reduced mRNA in rtt106Δ correspond to transporter genes (Supplementary Fig. 2a). Rtt106 may therefore be generally important for the expression of transporter genes—even though we did not identify Rtt106 bound at all the gene promoters affected, suggesting some effects could be indirect.
a RNA-seq analysis of rtt106Δ versus WT grown in YPD. Read counts of transcripts in rtt106Δ divided by those in WT were plotted against RPKM (reads per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads) in WT. Data shows mean of three biological replicates. Among 1724 differentially expressed genes (black circles, FDR < 0.01), genes in Type A (magenta squares), Type B (green circles) and Type C (blue triangles) as defined in Fig. 2 are highlighted. b Gene Ontology (biological process) analysis of upregulated genes (588 genes, FDR < 0.0001) and downregulated genes (266 genes, FDR < 0.0001) in rtt106Δ, compared to WT, in YPD. P-values were calculated by a hypergeometric distribution with Bonferroni Correction in GO Term Finder. c Correlation of changes in mRNA level of each gene in pdr3Δ with those in rtt106Δ grown in YPD. Colour coding as in panel a. Genes with low expression level in WT (RPKM < 1) are marked by +. d Comparison of changes in mRNA level of each gene in pdr1Δ with those in rtt106Δ grown in YPD. Colour cording used in panel a is used. Genes with low expression level in WT (RPKM < 1) are marked by +. e Correlation of changes in mRNA levels of the PDR network genes in pdr3Δ rtt106Δ with those in rtt106Δ grown in YPD. PDR network genes with promoters bound by Rtt106 are shown by magenta squares, and those not bound by Rtt106 by grey circles. f Normalised read counts of transcripts of the PDR network genes relative to those in WT treated transiently by ketoconazole in YEP. The 22 PDR network genes whose transcripts increased more than 4-fold by ketoconazole treatment in WT are shown. Data are presented as mean values ± SD. Statistical significance determined by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD tests, compared to WT treated with ketoconazole. *p = 0.001. c–f Data shows mean of three biological replicates.
Regarding histone gene expression, in our experiments only HHF1 mRNA was significantly increased in rtt106Δ (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Data 3), unlike previous reports which found additional histone genes affected31,32. This difference may reflect the fact that we prepared RNA from asynchronous cells rather than cells at specific cell-cycle stages31,32.
Remarkably, loss of Rtt106 caused an increase in mRNA levels for most genes that normally show low expression (Fig. 3a) including meiosis genes, for example, genes related to sporulation (Fig. 3b) that are suppressed in vegetative growth. This may reflect increased transcription initiation that could be caused by defective histone deposition or increased nucleosome spacing in rtt106Δ26,27,29. No obvious correlation of genes whose expression increased in rtt106Δ and Rtt106 binding at those genes was observed. We suspect that mildly deregulated transcription initiation occurs fairly ubiquitously in rtt106Δ, resulting in a readily apparent fold increase of mRNA with low abundance, but a less obvious effect on mRNA with a high level of expression. An increase in mRNA levels of ‘Transposition’ genes such as retrotransposons (Fig. 3b) is probably linked to the effect of Rtt106 as a Regulator of Ty1 Transposition (RTT)43, the phenotype for which Rtt106 was originally identified.
To test if Rtt106 is involved in transcription directed by either Pdr1 or Pdr3 or both, we compared effects on mRNA levels in rtt106Δ with those in pdr1Δ or pdr3Δ (grown in YPD without the addition of any drug). Almost all PDR network genes whose mRNA levels were reduced in rtt106Δ showed a similar reduction in pdr3Δ; however, no reduction was observed in the mRNA for most such genes in pdr1Δ (Fig. 3c, d and Supplementary Data 3). These results suggest that Pdr3, not Pdr1, is the main transcription factor responsible for the expression of the PDR network genes at basal levels and that Rtt106 acts with Pdr3 in these conditions. Consistent with that notion, we further observed that deletion of PDR3 in the rtt106Δ background had no additive effect on mRNA changes when compared to the single rtt106Δ mutant (Fig. 3e and Supplementary Table 1). These results suggest that Pdr3-mediated transcription of the PDR network genes is almost completely dependent on Rtt106. Our finding that Pdr3, and not Pdr1, is the main transcription factor responsible for basal expression of the PDR network genes is consistent with previous genome-wide transcriptome analysis44 and other published papers (listed in Supplementary Data 4). A number of papers, however, have arrived at different conclusions (also listed in Supplementary Data 4), in finding Pdr1 as the main contributor12 or suggesting an equal contribution of Pdr1 and Pdr311. The differences in behaviour between Pdr1 and Pdr3 could be due to differences in genetic background, a technique used and/or their combination.
As expected, neither pdr1Δ nor pdr3Δ mutations caused increased mRNA from genes with low expression levels (‘+’ symbols in Fig. 3c, d), consistent with the effect on these genes in rtt106Δ being due to a general histone occupancy defect, occurring independently of Pdr3. mRNA levels of non-PDR genes that are decreased in rtt106Δ also tended to decrease in pdr3Δ (Fig. 3c and Supplementary Data 3). We suspect that this may represent an indirect consequence of PDR network gene dysregulation, since it is unlikely that such genes are directly controlled by Pdr3.
Pdr1, but neither Rtt106 nor Pdr3, is essential for drug-induced PDR network gene expression
Expression of the PDR network genes can be induced by many substances, including the antifungal azole drug ketoconazole7. We tested if Rtt106, Pdr1 and Pdr3 are required for ketoconazole-induced expression of the PDR network genes. We used an established protocol7 in which glucose-starved cells (which have low PDR5 mRNA levels) were transiently treated with ketoconazole, causing rapid induction of PDR5 expression (Supplementary Fig. 2b). YPD was not used for these induction experiments since the azole antifungals tested did not induce PDR5 expression in YPD (Supplementary Fig. 2c). We used ketoconazole to test drug-induced expression since fluconazole did not induce PDR5 expression (Supplementary Fig. 2b). The mRNA levels of 22 genes, all with PDRE in their promoters, were increased more than four-fold in response to ketoconazole in WT (Fig. 3f). We found that PDR1 is essential for the ketoconazole-induced, transient expression of these 22 genes, but neither PDR3 nor RTT106 is required (Fig. 3f).
Overall, the results in Fig. 3 suggest that Rtt106 and Pdr3 are essential for basal expression of the PDR network genes during growth without antifungal agents, while Pdr1 mediates their azole-induced, transient expression.
Rtt106 confers antifungal resistance via Pdr3-mediated expression of PDR5
We next focused on the role of Rtt106 in regulating PDR network gene PDR5, since Pdr5 is the main multidrug transporter critical for resistance to azole antifungal drugs. In addition to RNA-seq (Fig. 3), Northern blot analyses confirmed that Rtt106 acts with Pdr3 to mediate basal expression of PDR5, but Rtt106 is not essential for Pdr1-mediated transient expression of PDR5 in response to ketoconazole (Supplementary Fig. 3a–d). Consistently, ketoconazole treatment did not cause a significant increase in the recruitment of Rtt106 to the PDR5 promoter (Supplementary Fig. 3e).
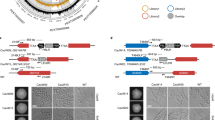
We further found using a luciferase expression assay that Rtt106 is required for activating the PDR5 promoter (Fig. 4a), and therefore for maintaining Pdr5 protein levels under non-drug-treated conditions (western blot analysis; Fig. 4b). Consistently, loss of RTT106 sensitised S. cerevisiae to azole antifungal drugs, to an extent similar to pdr3Δ (Fig. 4c and Supplementary Fig. 3f). We further observed that pdr3Δ and rtt106Δ are sensitive to high doses of ketoconazole, while pdr1Δ is sensitive only to low doses but not to high doses (Supplementary Fig. 3f). This finding suggests that Pdr3 and Rtt106 are more critical for resistance to continuous high doses of azole antifungals than Pdr1; and that Pdr1 function alone cannot mediate resistance to high doses at the condition tested. Although these are unexpected results since Pdr1 is critical for drug-induced expression of PDR5, this observation might reflect the fact that PDR3 undergoes auto-activation of its own transcription45, while PDR1 does not. Overall, these results suggest that Rtt106 regulates basal expression of PDR5 via Pdr3 and also mediates drug resistance. Note that it is still unknown whether basal expression of PDR5 regulated by Rtt106 directly leads to drug resistance, and whether Rtt106 also affects drug-induced PDR5 expression in cells grown long-term with the drug.
a Promoter activity of PDR5 in WT and rtt106Δ assessed by luciferase assay. Data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates). Statistical analysis performed by an unpaired t-test (two-tailed). b Western blot analysis of Pdr5 in WT and rtt106Δ. HA-tagged Pdr5 expressed from its endogenous locus was detected by anti-HA antibody. For loading control, whole proteins were detected by the Stain-free technology. c Sensitivity of WT, rtt106Δ and pdr5Δ to azole antifungal drugs. Five-fold dilutions of WT, rtt106Δ and pdr5Δ cells were spotted on YPD and YPD containing ketoconazole or fluconazole and incubated at 30 °C for 3 days. d ChIP-qPCR analysis testing if Rtt106 binding at the PDR5 promoter is dependent on Pdr1 and/or Pdr3. ChIP efficiency, the recovery of ChIPed DNA relative to the amount of input. Data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates). Statistical significance determined by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD test. ns, P > 0.05. e GST pull-down analysis shows GST-Pdr3 interacts with Rtt106-6HA. Yeast cell lysate containing Rtt106-6HA was incubated with GST-Pdr3 bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads. WB western blot. f ChIP-qPCR analyses assessing dependence of Rtt106 binding to PDR5 (grey) and HTA1-HTB1 (white) promoters on Pdr1, Pdr3, Hir1, Asf1, Rtt109 and Yta7. ChIP efficiencies relative to WT are shown. Data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates). ns, P > 0.05, one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD tests. g Northern blot analysis of PDR5 mRNA in indicated strain backgrounds in YPD. Intensities relative to PDR5 mRNA in WT are shown below the PDR5 blot. rRNAs, loading control, detected by SYBR Gold. The positions of 25 S and 18 S rRNAs are shown. h Sensitivity to ketoconazole of indicated mutant combinations. Five-fold dilutions of indicated strains were spotted on YPD and YPD containing ketoconazole and incubated at 30 °C for 3 days. Two independent isolates of pdr1-3 rtt106Δ and pdr3-2 rtt106Δ strains shown.
To understand why Rtt106 regulates Pdr3-mediated, but not Pdr1-mediated, transcription of PDR5, we tested if Rtt106 recruitment to the PDR5 promoter depends solely on Pdr3. Strikingly, deletion of PDR3 caused almost complete loss of Rtt106 recruitment to the PDR5 promoter, while deletion of PDR1 actually increased recruitment of Rtt106 to the PDR5 promoter (Fig. 4d). Rtt106 recruitment to the PDR5 promoter, therefore, depends on Pdr3, and not Pdr1. Increased recruitment of Rtt106 to the PDR5 promoter in pdr1Δ may reflect an increase of Pdr3 at the PDR5 promoter in the absence of Pdr1. These results suggest that Pdr3 recruits Rtt106 to the PDR5 promoter to upregulate its transcription.
Conversely, Rtt106 is not essential for Pdr3 recruitment to the PDR5 promoter, as Pdr3 is still recruited there in the absence of Rtt106, as shown by ChIP-qPCR using a tagged PDR3-13Myc strain confirmed as retaining protein function (Supplementary Fig. 4a–d). However, we observed ~50% reduction of Pdr3 binding to the PDR5 promoter in rtt106Δ, compared to WT, possibly caused by the reduction of protein and mRNA levels of PDR3 in rtt106Δ (Supplementary Fig. 4d, e and Supplementary Data 3). While not ruling out some direct contribution of Rtt106 to Pdr3 recruitment, these results suggest clearly that Rtt106 regulates the expression of PDR3, one of the PDRE-containing genes. The reduction of Pdr3 protein level and its binding to the PDR5 promoter in rtt106Δ may contribute to the reduction of PDR5 expression in rtt106Δ. Our results nonetheless indicate that Rtt106 regulates PDR5 expression by acting directly at the PDR5 promoter (and not only indirectly through regulating PDR3 expression) as a ~50% reduction of Pdr3 binding at the PDR5 promoter in rtt106Δ cannot alone explain why rtt106Δ and pdr3Δ mutants have similar effects on PDR5 expression.
We next tested the physical interaction of Rtt106 with Pdr3 by an in vitro GST pull-down analysis and observed that Rtt106 shows a higher affinity for GST-Pdr3 than GST alone, when testing cell lysate from the yeast with HA-tagged Rtt106 (Fig. 4e), suggesting that Rtt106 binds Pdr3 in this condition. However, His-Rtt106 purified from E. coli expression system was not co-precipitated with GST-Pdr3 (Supplementary Fig. 4f), implying there may be another molecular requirement for binding, or possibly that recombinant Rtt106 is not properly folded to bind Pdr3 in the condition tested. How Rtt106 binds Pdr3 remains to be elucidated.
We tested if factors important for recruiting Rtt106 to the histone promoters also contribute to its recruitment to the PDR5 promoter. We found that histone chaperone Asf1 and histone acetyltransferase Rtt109 (in addition to HIR and Yta7) also contribute to Rtt106 recruitment to the PDR5 promoter, although their contributions at PDR5 are less than at the HTA1-HTB1 histone promoter (Fig. 4f). Asf1 might affect Rtt106 recruitment to the PDR5 promoter indirectly through Pdr3 since Pdr3 binding to the PDR5 promoter is reduced in asf1Δ (Supplementary Fig. 4d).
We then tested if Rtt106 mediates PDR5 overexpression caused by GOF mutations in PDR1 and PDR3. As expected, loss of Rtt106 caused the reduction of PDR5 mRNA in a pdr3-GOF (pdr3-2) mutant, but not in a pdr1-GOF (pdr1-3) mutant (Fig. 4g). Consistently, loss of Rtt106 sensitised pdr3-GOF, but not pdr1-GOF, to ketoconazole (Fig. 4h). Rtt106 is therefore critical to mediate hyperactivation of Pdr3. These selective effects on pdr3-GOF also suggest that the effect of Rtt106 loss on PDR5 expression is not simply caused indirectly by global change in chromatin structure due to loss of Rtt106. We were unable to test the contribution of Rtt106 to mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated drug resistance16, since we have not observed such phenotype reproducibly in the strain background used (Supplementary Fig. 5a, b).
SWI/SNF is recruited to the PDR5 promoter dependent on Pdr1/3
To further investigate PDR5 gene regulation, we sought to identify proteins assembled on the PDR5 promoter. To capture proteins assembled at the PDR5 promoter in a near-native in vivo context, we utilised a minichromosome isolation technique46 followed by SILAC-based quantitative proteomics (Fig. 5a, b and Supplementary Fig. 6a). In this method, we purified from S. cerevisiae short circular chromosomes containing the PDR5 promoter and eight lactose operators (lacO) by immunoprecipitating FLAG-tagged Lac Repressor (LacI) (Fig. 5a). Proteins bound to the PDR5 promoter will be enriched on the PDR5 promoter-containing minichromosome (PDR5pro), compared to a control minichromosome (Empty). We successfully identified PDR5 promoter-binding proteins including transcription factors Pdr1 and Pdr3, and the RNA polymerase II Mediator complex that binds Pdr1 and Pdr37,47, validating this approach for capturing promoter-binding proteins in a near-native context (Fig. 5b and Supplementary Data 5). Rtt106 enrichment on the PDR5 promoter was confirmed by western blot analysis, although it was not identified by mass spectrometry (Supplementary Fig. 6a). Interestingly, we identified the SWI/SNF ATP-dependent chromatin-remodelling complex and the transcriptional regulatory protein Ume6 (Fig. 5b and Supplementary Data 5) as enriched on the PDR5 promoter. Ume6 likely binds to the DNA sequence 5′-TTGCCGCCGA-3′ located 580 bp upstream of the PDR5 ATG, which is similar to the Ume6 recognition sequence 5′-TAGCCGCCGA-3′.
a Minichromosome purification scheme followed by SILAC-based quantitative proteomics. ARS replication origin. TRP1 an auxotrophic selection marker. IP immunoprecipitation. b Ratios of proteins associated with PDR5 promoter minichromosome compared to control minichromosome. Red diamonds, subunits of SWI/SNF; blue squares, subunits of Mediator; green rectangle, Pdr1 or Pdr3; yellow circle, Ume6. Proteins quantified by at least 5 ratio counts were shown (n = 1 experiment). c–e ChIP-qPCR analyses of the Swp82 subunit of SWI/SNF at PDR5 promoter, in WT and pdr1Δ pdr3Δ (c), pdr1Δ and pdr3Δ (d) in YPD and in response to ketoconazole (e). Data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates). Unpaired t-test, two-tailed (c); one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD tests (d, e). ns, P > 0.05. f, g GST pull-down analyses show that the SWI/SNF complex purified from yeast cells interacts with GST-Pdr3 (f) and GST-Pdr1 (g). h, i Normalised counts of PDR5 mRNA extracted from RNA-seq data of WT and snf2Δ grown in YPD (h) and treated with ketoconazole (i). Data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates). Unpaired t-tests (two-tailed). j Normalised read counts of transcripts of the PDR network genes relative to those in WT treated transiently by ketoconazole in YEP. PDR network genes whose transcripts increased more than four-fold on ketoconazole treatment in WT are shown. Genes whose expression is already higher in snf2Δ than WT in YEP without ketoconazole are excluded. Data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates). One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD tests, compared to WT treated with ketoconazole. *p = 0.001. k Sensitivity to ketoconazole of deletion mutants of the SWI/SNF subunits. l Northern blot analysis of PDR5 mRNA in indicated mutants in YPD. The intensities relative to PDR5 mRNA prepared from WT are shown below the PDR5 blot. rRNAs, loading control. The positions of 25 S and 18 S rRNAs are shown. m, n Sensitivity to ketoconazole of WT and snf6Δ in hyperactive pdr3-2 (m) and pdr1-3 (n) mutant backgrounds. Two and four independent isolates of pdr3-2 snf6Δ and pdr1-3 snf6Δ strains used, respectively.
We further found that SWI/SNF recruitment to the PDR5 promoter is dependent mainly on Pdr3 (Fig. 5c, d). Pdr1 might contribute to the recruitment of SWI/SNF to the PDR5 promoter since residual binding of SWI/SNF was observed in the single pdr3Δ mutant, compared to the double pdr1Δ pdr3Δ mutant (Fig. 5c, d). Consistent with this idea, SWI/SNF recruitment to the PDR5 promoter increased in response to ketoconazole, which stimulates only Pdr1 in the condition tested (Fig. 5e). Furthermore, GST pull-down analyses showed that both Pdr1 and Pdr3 bind purified SWI/SNF (Fig. 5f, g and Supplementary Fig. 6b). Interestingly, a few peptides from Pdr1 were identified in the immunopurified fraction of SWI/SNF, by mass spectrometry (Supplementary Fig. 6c, highlighted in red), providing further supporting evidence for the interaction of SWI/SNF with Pdr1. Note that the checkpoint kinase Mec1 (that binds SWI/SNF48) and its binding partners were also identified in this fraction (Supplementary Fig. 6c, highlighted in yellow), and therefore the involvement of Mec1 in the SWI/SNF-Pdr1/3 interaction is not ruled out.
SWI/SNF upregulates the expression of PDR5 to mediate antifungal resistance
We next explored if SWI/SNF is required for the expression of PDR5. Our RNA-seq analysis showed that PDR5 mRNA was greatly decreased in the absence of Snf2, a catalytic subunit of SWI/SNF, when grown in YPD (Fig. 5h). Interestingly, Snf2 also contributes to ketoconazole-induced, transient expression of PDR network genes including PDR5 (Fig. 5i, j). These results suggest that SWI/SNF is an essential upregulator of the PDR network genes both for basal and drug-induced expression.
As expected, the protein level of Pdr3 in snf2Δ is reduced, compared to WT (Supplementary Fig. 4e), consistent with the reduction of mRNA level of PDR3 in snf2Δ (Supplementary Table 2). Concomitantly, Pdr3 binding to the PDR5 promoter is reduced in snf2Δ, compared to WT (Supplementary Fig. 4d). Taken together, these results and the evidence of SWI/SNF binding to the PDR5 promoter suggest that SWI/SNF regulates PDR5 expression by acting directly at the PDR5 promoter as well as through regulating gene expression of the transcription factor PDR3.
Consistent with an essential role of Snf2 in upregulating PDR5 expression, snf2Δ is highly sensitive to azole antifungals (Fig. 5k and Supplementary Figs. 3f and 6d). Loss of all other SWI/SNF subunits tested also sensitised S. cerevisiae to azole antifungals, except for snf11Δ and swp82Δ in which PDR5 mRNA levels were not reduced44 (Fig. 5k and Supplementary Fig. 6d, e). We further observed that loss of Snf6 (a fungal-specific subunit of SWI/SNF) reduced PDR5 mRNA in the hyperactive pdr3-GOF mutant (pdr3-2) and sensitised it to ketoconazole (Fig. 5l, m). Loss of Snf6 did not reduce PDR5 mRNA in the hyperactive pdr1-GOF (pdr1-3) grown in YPD, but combining pdr1-GOF and snf6Δ caused a major growth defect even in the absence of antifungal drugs (Fig. 5l, n) through an unknown mechanism. Taken together, these results suggest that SWI/SNF is an essential factor mediating resistance to azole antifungals through upregulating PDR5 expression, and therefore represents a potential therapeutic target to combat antifungal resistance.
Cooperation of SWI/SNF and Rtt106 at the PDR network gene promoters
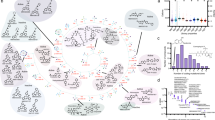
Since both Rtt106 and SWI/SNF bind the PDR5 promoter, we next examined if these factors colocalise at other promoters, by combining the published promoter-binding data for SWI/SNF20 with our Rtt106 ChIP-seq data (Fig. 6a, b). SWI/SNF binds strongly to 16 of the 20 Rtt106-bound promoters classified as Type A (Fig. 6b and Supplementary Data 6), indicating that SWI/SNF colocalises with Rtt106 at the majority of the PDR network gene promoters, and suggesting that these two factors are likely to cooperatively regulate expression of the PDR network genes. Consistently, changes in mRNA levels of genes in Type A in snf2Δ are similar to those in rtt106Δ (Fig. 6c and Supplementary Table 2). Rtt106 and SWI/SNF factors also tended to colocalise at Type B promoters. In contrast, no clear correlation between SWI/SNF and Rtt106 binding was observed for Type C genes (Fig. 6b, c). The possibility that Rtt106 and SWI/SNF cooperate is further supported by their physical interaction (Fig. 6d)33. Note though that Rtt106 and SWI/SNF do not always colocalise at promoters (Supplementary Fig. 7a), suggesting a specific requirement for their colocalisation at a subset of promoters.
a Nucleosome positioning at the PDR5 promoter in the presence and absence of Snf2. Binding of the Swi3 SWI/SNF subunit (ChEC-seq) and nucleosome occupancy (MNase-seq) at the PDR5 promoter were extracted from published datasets20. TSS TSS-seq extracted from Malabat et al. 201549. Snf2 depletion resulted in shift of the +1 nucleosome at the PDR5 promoter (red rectangle). b Percentages of gene promoters strongly bound by SWI/SNF and those by Rtt106. The list of gene promoters strongly bound with SWI/SNF was obtained from Kubik et al. 201920. Promoters bound by Rtt106 were defined as in Fig. 2. c Changes in mRNA levels of genes with promoters bound by both SWI/SNF and Rtt106 (as in b), and correlation of snf2Δ and rtt106Δ effects in YPD. Magenta dashed line shows trend for Type A. Data represents means of three biological replicates. d GST pull-down analysis showing GST-Rtt106 interacts with SWI/SNF purified from yeast cells. e Nucleosome occupancies at Type A promoters bound by SWI/SNF (magenta lines) and promoters not bound by SWI/SNF (grey lines), and those in the absence of Snf2 (dashed lines). Datasets in Kubik et al. 201920 were utilised. Asterisk, region analysed in f and g. f, g Nucleosome occupancy change (f) and TBP binding change (g) caused by loss of Snf2 at Type A promoters bound by SWI/SNF. Normalised reads in regions spanning −100 to 0 bp from the dyad of the +1 nucleosome (indicated by asterisk in e) were extracted from published datasets20. For analysis of TBP binding change, promoters with low TBP binding (<50 normalised reads) were eliminated. Boxplots indicate median (middle line), interquartile range (box), outliers denoted by points greater than ±1.5 × interquartile range (single points) and the rest of the data distribution (whiskers). Mann–Whitney tests (two-sided). h Proposed roles of Rtt106 and SWI/SNF in transcription of the PDR network genes in S. cerevisiae (S288C). Rtt106 and SWI/SNF are recruited to the PDR network gene promoters dependent on Pdr3, to mediate Pdr3-dependent transcription during logarithmic growth phase, while SWI/SNF upregulates their Pdr1-dependent expression in response to ketoconazole.
To understand how SWI/SNF regulates the expression of the PDR network genes, we explored if SWI/SNF regulates the position of the TSS-associated +1 nucleosome, which is critical for transcription initiation. We utilised the published datasets of nucleosome occupancy20 and TSS49 and observed that in the absence of Snf2 the +1 nucleosome is shifted towards the TATA-box at the PDR5 promoter (Fig. 6a, red rectangle). Snf2 loss had a similar effect at other PDR network gene promoters bound by both SWI/SNF and Rtt106 (Fig. 6e, compare dashed and solid magenta lines), while no obvious change was observed at promoters not bound by SWI/SNF (Fig. 6e, grey lines). To test for statistical significance, we analysed nucleosome occupancy change caused by loss of Snf2 in regions spanning −100 to 0 bp from the dyad of the +1 nucleosome (regions indicated by an asterisk in Fig. 6e). We observed that increase of nucleosome occupancy caused by loss of Snf2 in those regions is significantly higher at the PDR network gene promoters bound by SWI/SNF and Rtt106 than at promoters not bound by SWI/SNF (Fig. 6f). These results suggest that SWI/SNF regulates the position of the TSS-associated +1 nucleosome at promoters of the PDR network genes.
The changes in nucleosome occupancy and position caused by the loss of Snf2 likely reduce the accessibility of the TATA-box and therefore reduce its transcription (Fig. 6a lower cartoons). Consistent with this idea, the binding of the TATA-box-binding protein TBP to the PDR network gene promoters is significantly reduced in the absence of Snf2, compared to that of promoters not bound by SWI/SNF (Fig. 6g and Supplementary Fig. 7b). These results are consistent with a role for SWI/SNF in directing the position of the +1 nucleosome at the PDR5 promoter to activate its transcription. In contrast, loss of Rtt106 does not change the steady-state level of nucleosomes at the PDR5 promoter (Supplementary Fig. 7c)29, leaving the possibility that at the PDR5 promoter Rtt106 may regulate nucleosome turnover, an effect not observable by MNase-seq nucleosome mapping.
Taken together, we propose that during logarithmic growth Rtt106 and SWI/SNF bind to promoters of the PDR network genes mainly through Pdr3, and cooperatively drive Pdr3-dependent expression; while in response to ketoconazole SWI/SNF mediates Pdr1-dependent-drug-induced expression of the PDR network genes in S. cerevisiae (Fig. 6h).
Roles of C. glabrata Rtt106 and SWI/SNF in antifungal resistance
We next examined the roles of Rtt106 and SWI/SNF for antifungal resistance in C. glabrata, a pathogenic fungus closely related to S. cerevisiae. A major difference between C. glabrata and S. cerevisiae in the PDR network regulation is that C. glabrata has the single PDRE-binding transcription factor called CgPdr1 which shares homology almost equally with the S. cerevisiae Pdr1 and Pdr3 proteins, and possesses a blend of the properties of each50. Interestingly, loss of CgRtt106 (CAGL0H08041g) caused reduced induction of mRNA of the multidrug transporter genes CgCDR1, CgCDR2 and of other PDR network genes, in cells transiently treated with ketoconazole (Fig. 7a orange bars and Supplementary Fig. 8a). An even more striking reduction was observed in the absence of SWI/SNF subunit CgSnf2 (Fig. 7a grey bars and Supplementary Fig. 8a). In contrast, in YPD without antifungal drugs, loss of CgRtt106 or CgSnf2 did not consistently reduce mRNA of the PDR network genes (Fig. 7a and Supplementary Fig. 8b). These results suggest that CgRtt106 and CgSWI/SNF drive the expression of the PDR network genes in C. glabrata, although their contributions appear limited to drug-induced expression.
a RNA-seq analysis reveals reduction of mRNA of multidrug transporter genes CgCDR1 and CgCDR2 in the absence of CgRtt106 and CgSnf2 upon transient ketoconazole treatment in YEP. Data represents mean of three biological replicates. Significance determined by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD test. ns, P > 0.05. b Positions of PDRE and PDRE-like motif in the CgCDR1 promoter. c, d ChIP-qPCR analyses of CgRtt106 (c) and the CgSwp82 SWI/SNF subunit (d) at the CgCDR1 promoter in YEP with and without ketoconazole. Proximal (blue) and distal (green) PDRE sites (illustrated in b) were analysed. Control locus (white) is coding region of the CgADY3 gene. Data represent mean of three biological replicates. Significance determined by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD test. ns, P > 0.05. e Sensitivity to azole antifungal drugs of the C. glabrata reference strain (ATCC 2001) and C. glabrata lacking CgRtt106, CgSnf2 or CgCdr1. Five-fold dilutions of cell culture were spotted on YPD or YPD containing ketoconazole or fluconazole, and incubated at 30 °C for 2–3 days.
We next tested if CgRtt106 and CgSWI/SNF localise at the CgCDR1 promoter (which contains multiple PDRE and PDRE-like sequences; Fig. 7b), and found they bind at least two sites within the CgCDR1 promoter (Fig. 7c, d, proximal and distal). Ketoconazole treatment did not increase CgRtt106 or CgSWI/SNF binding to the CgCDR1 promoter (Fig. 7c, d), suggesting that these factors are already bound to the CgCDR1 promoter before induction of its expression by the drug. CgRtt106 and CgSWI/SNF also localise at the CgCDR1 promoter in YPD (Supplementary Fig. 8c), with higher background binding of CgRtt106 to a control locus probably because of its function in DNA replication.
We finally observed that along with a hyper-sensitive Cgcdr1Δ, Cgsnf2Δ and, to a lesser extent, Cgrtt106Δ exhibited increased sensitivity to ketoconazole and fluconazole (Fig. 7e). Taken together, these results demonstrate that CgRtt106 and CgSWI/SNF upregulate the expression of multidrug transporter genes and confer antifungal resistance in C. glabrata. CgRtt106 and CgSWI/SNF are therefore potential therapeutic targets to combat antifungal resistance of C. glabrata.
Discussion
Regulation of the PDR network genes is central to the fungal drug response, but is incompletely understood. In this study, we found that Rtt106 and SWI/SNF upregulate PDR network gene expression and confer drug resistance in S. cerevisiae and C. glabrata. In S. cerevisiae, Rtt106 is recruited to the promoter of the multidrug transporter gene PDR5 exclusively through the transcription factor Pdr3, which drives Pdr3-mediated expression of PDR5, and confers resistance to azole antifungals. Furthermore, we showed that SWI/SNF plays a crucial role in both Pdr1- and Pdr3-mediated expression of the PDR network genes and confers azole drug resistance. Finally, we observed that CgRtt106 and CgSWI/SNF are important for the expression of the PDR network genes in response to ketoconazole in C. glabrata, and therefore for its resistance to azole antifungals, highlighting those factors as potential therapeutic targets to combat antifungal resistance of C. glabrata.
Our results and a published report20 suggest that SWI/SNF regulates the expression of PDR5 by shifting the TSS-associated +1 nucleosome, which is critical for transcription initiation. How does Rtt106 upregulate the expression of PDR5? One possible explanation is that Rtt106 recruits SWI/SNF to the PDR5 promoter to activate its expression, similar to the histone promoters33. However, while the +1 nucleosome at the PDR5 promoter was shifted in the snf2 mutant, in the absence of Rtt106 nucleosome positioning was not obviously changed29 (Supplementary Fig. 7c), suggesting that the effect of Rtt106 on PDR5 transcription is not directly mediated through the SWI/SNF effect on nucleosome position. We instead favour a model where Rtt106 regulates ‘turnover’ of the nucleosomes surrounding the NDR at the PDR5 promoter, to enable transient TATA-box region exposure allowing transcriptional regulators to access their binding sites. Although histone exchange at promoters is not simply related to transcriptional activity21,51, we suspect that at the PDR5 promoter nucleosome turnover may depend on Rtt106 and affect transcription. Interestingly, in S. cerevisiae rapid histone turnover also has been shown to occur at other sites where Rtt106 is enriched, including tRNA and snoRNA51 (Fig. 2e and Supplementary Fig. 1d).
Proteins regulating the recruitment of Rtt106 to histone promoters (i.e. Hir1, Asf1, Rtt109 and Yta7) also contribute to its recruitment to the PDR5 promoter. How these proteins contribute to Rtt106 recruitment remains to be elucidated. They might be required to mediate the physical interaction between Rtt106 and Pdr3, which would be consistent with our observation that purified Pdr3 and Rtt106 did not interact (Supplementary Fig. 4f). Another possibility is that these factors contribute to Rtt106 recruitment indirectly, e.g. through regulating the binding of Pdr3 to the PDR5 promoter and/or regulating the abundance of Pdr3 (Supplementary Fig. 4d, e).
Do other histone chaperones have a role at the promoters? It has been reported that histone chaperone Asf1 mediates nucleosome disassembly from the PHO5 promoter for its activation in yeast22,23. In human, histone chaperones HIRA and ASF1a localise at active promoters where BRG1, a human SWI/SNF complex subunit, also localises52. Interestingly, at promoters, human HIRA and ASF1a essentially localise to nucleosome-free TSSs52, reminiscent of our findings that yeast Rtt106 is enriched at wider nucleosome-free regions upstream of TSSs (Fig. 2g). HIRA mediates the replacement of canonical H3 with the H3.3 variant at promoters52, and continuous H3.3 exchange has been proposed to keep these sites transiently exposed, allowing transcription factors to access their binding sites53. These findings suggest that histone chaperones have a conserved role at promoters in yeast and human.
CgRtt106 regulates drug-induced expression of the PDR network genes in C. glabrata, although in S. cerevisiae ScRtt106 does not. We suspect this difference reflects the fact that CgPdr1 possesses a blend of ScPdr1 and ScPdr3 properties, so that CgRtt106 binds CgPdr1 (like ScRtt106 binds ScPdr3) and regulates CgPdr1-mediated, drug-induced expression. We detected no obvious contribution of CgRtt106 nor CgSWI/SNF to the basal expression of the PDR network genes in C. glabrata, which might reflect the fact that without drugs PDR gene expression is very low, compared to expression upon ketoconazole treatment (Fig. 7a, YPD vs YEP + ketoconazole). This difference is less marked in S. cerevisiae. How CgRtt106 and CgSWI/SNF upregulate drug-induced expression of the PDR network genes remains to be elucidated. GOF mutations in CgPdr1 make it hyperactive, resulting in high multidrug transporter expression and thus driving antifungal resistance in clinical isolates of C. glabrata9,54. It will be of great interest to test whether loss of CgRtt106 or CgSWI/SNF re-sensitises clinical isolates of C. glabrata that have developed antifungal resistance to azole antifungal drugs. SWI/SNF and Rtt106 might also contribute to drug resistance and virulence in other Candida species. C. albicans SWI/SNF mediates overexpression of the drug efflux protein Mdr1 due to GOF mutations in the transcription factor Mrr1, thus conferring fluconazole resistance55. C. albicans Rtt106 and C. albicans SWI/SNF affect hyphae formation56,57, which indirectly influences drug tolerance and pathogenicity.
Our findings in this study suggest that Rtt106 and SWI/SNF are general regulators of the PDR network genes and confer drug resistance in S. cerevisiae, and their roles are largely conserved in the pathogenic fungus C. glabrata. Interfering with the binding of CgRtt106 and CgSWI/SNF to CgPdr1 would be a strategy to prevent overexpression of the multidrug transporter genes in drug-resistant clinical isolates of C. glabrata. In this context, a small molecule inhibitor disrupting the interaction between CgPdr1 and CgMediator has already been successfully used to re-sensitise drug-resistant clinical isolates to azole antifungals58. Since Rtt106 and some SWI/SNF subunits are fungal-specific, these factors offer attractive therapeutic targets to combat antifungal drug resistance in C. glabrata and potentially other Candida species.
Methods
Yeast strains and plasmids
S. cerevisiae strains and C. glabrata strains used are listed in Supplementary Table 3. Oligonucleotides used are listed in Supplementary Data 7. Epitope-tagging and gene disruptions were carried out using standard PCR-based gene insertion methods59. The hyperactive pdr1-3 mutant in the S288C (BY4741) background was constructed by replacing pdr1Δ::natNT2 in the genome of strain VNY70 with a PCR product containing the entire pdr1-3 locus amplified from the original pdr1-3 strain (congenic to W303-1A)15 following DNA break induction at natNT2 using CRISPR-Cas960. Hyperactive pdr3-2 in the S288C (BY4741) background was constructed by the same approach, but with pdr3Δ::natMX (VNY45) and the original pdr3-2 mutant15. Sequencing of the inserted pdr1-3 and pdr3-2 genes in the S288C backgrounds confirmed that pdr1-3 contains the following mutations compared to the S288C reference genome: Q411K, F815S, T820A, T921I and loss of 5Ns at 1011 aa, while pdr3-2 contains Q56R, H110Q, G834S, A885T, N916S and E941G. Strains for minichromosome isolation were constructed from the SILAC compatible strain SHY20161 by replacing the TRP1 gene with the fragment containing LacI-3FLAG and URA3 (amplified from pRS406-CMV-LacI-3FLAG46 by PCR), followed by transformation with minichromosome plasmids pUC-TALO8 or pUC-TALO8-PDR5pr. Plasmid pUC-TALO8-PDR5pr (PDR5pro) was constructed by inserting the fragment of the PDR5 promoter (from −997 to −241 bp upstream of ATG, not including the TATA-box) into the NdeI site of plasmid pUC-TALO8 (Empty)46, using NEBuilder HiFi Assembly Master Mix (E2621L, NEB). The inserted sequences were confirmed by sequencing. For luciferase reporter assay, YCplac22-based plasmid containing the luciferase gene fused to the PDR5 promoter (from −1000 bp to −1 bp upstream of ATG) was used. E. coli expression vectors, pGEX-6P-1-ScPDR1, pGEX-6P-1-ScPDR3, pGEX-6P-1-ScRTT106, and pET28a-ScRTT106 were constructed using NEBuilder HiFi Assembly Master Mix (E2621L, NEB).
ChIP-sequencing and ChIP-qPCR analyses
Cells were fixed with 1% formaldehyde at room temperature for 30 min and then at 4 °C overnight with gently shaking. The fixed cells were washed in ice-cold PBS three times and used for ChIP. ChIP was performed essentially as described62 using mouse monoclonal anti-HA antibody (5 μg, HA.11 clone 16B12, Covance or Biolegend) or mouse monoclonal anti-myc antibody (5 μg, M047-3, MBL, purchased from Caltag Medsystems) with modifications: cells were disrupted using a FastPreP-24 bead beater (MP Biomedicals), and sonication of DNA was performed using a Bioruptor (Diagnode). For ChIP-seq analysis, libraries of input and ChIP DNA were generated by NEBNext Ultra II DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (E7645L, NEB) and sequenced on NextSeq 500 to generate single-end 75 bp reads. For ChIP-qPCR analysis, input and ChIP DNA were analysed by LightCycler 480 II (Roche) using Light cycler SYBR Green master reagent (4707516001, Roche) or Takyon No ROX SYBR MasterMix (UF-NSMT-B0701, Eurogentic). ChIP efficiency (ChIP/Input) at each locus was calculated as the mean of three biological replicates, each one of which has three technical replicates.
Bioinformatic analysis of ChIP-sequencing data
The Galaxy web interface (https://usegalaxy.org) was used for bioinformatics analysis of ChIP-seq data. Sequence reads from fastq files were mapped against the latest version of the yeast genome sacCer3 using BWA (version 0.7.17.4). Non-uniquely mapped reads were removed by filtering out all reads with mapping quality less than 20 using SAMtools Filter SAM or BAM. To view read coverage distribution across the genome, BAM files generated with BWA were first converted into bigWig format using DeepTools bamCoverage (version 3.1.2.0.0), with the following settings: Bin size, 25 bp; Scaling/Normalisation method, normalise coverage to 1×; and Extend reads to the given average fragment size, 300 bp. BigWig datasets of Input and ChIP DNA were then displayed separately using Integrated Genome Browser (IGV, version 2.4.16).
To calculate Rtt106 enrichment or occupancy at each promoter region, enrichment of sequence reads in ChIP samples over corresponding Input samples was first calculated using DeepTools bamCompare (version 3.1.2.0.0), with bin size 50 bp. To extract values around the TSS of each gene, heatmap was then plotted using annotation of TSS63, DeepTools computeMatrix (version 3.1.2.0.0) and plotHeatmap (version 3.1.2.0.1). Finally, the data table underlying the plots was exported and utilised for calculating Rtt106 enrichment in a region spanning 500 bp upstream of the TSS of each gene. To calculate the fold change of Rtt106 signals in pdr1Δ pdr3Δ, hir1Δ or yta7Δ over WT at each promoter, enrichment of ChIP sequence reads in those mutants over WT was calculated.
In clustering analysis, promoters bound by Rtt106 were classified into nine clusters based on Rtt106 enrichment at promoters in WT and its change in pdr1Δ pdr3Δ, hir1Δ and yta7Δ. The thresholds were determined to classify PDRE-containing promoters into cluster 1. All the promoters bound by Rtt106 were inspected manually to find features within promoters.
Treatment of yeast cultures with azole antifungal drugs
Cells were treated with azole antifungal drugs as described7 with minor modifications. Briefly, cells grown in YPD (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 2% glucose) at 30 °C overnight until stationary phase were pelleted and washed with sterilised MilliQ purified water twice, resuspended in YEP (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone) to an optical density (OD600) of 0.6, and further incubated for 24 h at 30 °C. Cells were treated with 40 μM ketoconazole (K1003, Merck) or 130 μM fluconazole (PHR1160, Merck) for 15 min for RNA preparation and ChIP-qPCR. For sampling cells in the glucose-starved condition (YEP), cells were collected before the addition of azole antifungal drugs to the cultures.
RNA sequencing
Total RNA was prepared from cells using Macherey-Nagel NucleoSpin RNA Columns (11922402, Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. ERCC (External RNA Controls Consortium) spike-in controls were added to the RNA samples to be used as internal controls. Libraries were prepared with the Illumina TruSeq Stranded mRNA kit and sequenced using the High Output 1 × 75 kit on the Illumina NextSeq 500 platform producing 75 bp single-end reads.
Bioinformatic analysis of RNA sequencing data
Raw reads were filtered using TrimGalore! (version 0.6.4) with a phred quality score threshold of 30. ERCC spike-in reads were removed by alignment to the ERCC reference genome using HISAT2 (version 2.1.0)64. The cleaned reads were aligned to the S. cerevisiae reference genome using HISAT2 (version 2.1.0)64. SAMtools (version 1.9)65 was used to process the alignments and reads were counted at gene locations using featureCounts (part of the sub read version 1.6.2 package)66 utilising the parameter to split multi-mapped reads as a fraction across all genes that they align to and the parameter for stranded analysis. edgeR (version 3.26.8)67 was used normalise reads counts, retaining genes that had a CPM (count per million) value of more than one in three or more samples, and to detect which of the genes had a significant differential change in expression (FDR < 0.05). Gene Ontology Term Finder (https://www.yeastgenome.org/goTermFinder, version 0.86) was used for gene ontology analysis.
Northern blot analysis
Northern blot analysis was performed as described68. Briefly, total RNA was separated on the HT (HEPES-Triethanolamine) gel and then transferred onto Hybond N + membrane (GERPN203B, Merck) by capillary transfer. RNA was crosslinked with the membrane by UV irradiation. PDR5 mRNA and a loading control ARF1 mRNA69 were detected using biotin-labelled oligo DNA probes (Merck) and North2South Chemiluminescent Hybridisation and Detection Kit (17097, Thermo Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. rRNAs were detected as loading controls, by SYBR Gold staining (S11494, Thermo Scientific). The images were captured using ChemiDoc system (Bio-Rad).
Luciferase reporter assay
Cells carrying luciferase reporter plasmids were grown in SC-Trp (Kaiser synthetic complete media lacking tryptophan (Formedium), supplemented with 2% glucose) at 30 °C until log phase and harvested. Cells were washed with sterilised MilliQ purified water, and resuspended in Lysis buffer A (100 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.8, 0.2% Triton X-100). Cells were disrupted using a FastPreP-24 bead beater (MP Biomedicals). The cleared lysate was prepared by centrifugation at 15,000 × g for 10 min at 4 °C. Luciferase activity was measured using Bright-Glo Luciferase Assay System (E2610, Promega) and Omega Plate Reader (BMG Labtech) and calculated as relative luminescence units per mg of total soluble protein.
Total protein preparation
To detect Pdr5-3HA, total protein was prepared from cells by the TCA method as follows. Cells grown in 7 ml of YPD at 30 °C until log phase were washed in ice-cold water, then resuspended in 150 μl of ice-cold YEX lysis buffer (1.85 M NaOH, 7.5% 2-mercaptoethanol) and incubated on ice for 10 min on ice. After adding 150 μl of ice-cold 50% (w/v) TCA to the cell suspension, the samples were incubated on ice for 10 min, and then span for 5 min at 10,000 × g at 4 °C to precipitate proteins. The precipitated proteins were resuspended in the protein sample buffer (40 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 8 M Urea, 5% SDS, 0.1 mM EDTA, 1% 2-mercaptothanol) and incubated at 37 °C for 15 min. Total proteins for detecting epitope-tagged Pdr3 were prepared by alkaline method: cells were washed once with water, incubated in 0.1 M NaOH for 5 min at room temperature, spun down, resuspended in SDS sample buffer (1610737, Bio-Rad) and incubated at 85 °C for 5 min. Total proteins prepared were separated by SDS-PAGE using 4–20% TGX stain-free gel (4568095, Bio-Rad), and transferred onto the PVDF membrane using the Trans-Blot Turbo Transfer system (Bio-Rad). Tagged proteins were detected using anti-HA antibody (1:5000, Covance or Biolegend, HA.11, clone 16B12), anti-FLAG M2 antibody (1:5000, Sigma or Merck, F1804, clone M2) or anti-myc antibody (1:50,000, abcam, ab9106) and Clarity Western ECL substrate (1705061, Bio-Rad). As a loading control, total protein was detected using Stain-Free technology (Bio-Rad).
Purification of the SWI/SNF complex
The SWI/SNF complex was purified from a protease-deficient yeast strain containing 3× Flag tag at the C-terminus of Snf6 (Snf6-3Flag). The tagged yeast strain was grown in 2 L of YPD overnight at 30 °C. Cells were collected by centrifugation and washed with 40 ml of cold PBS. Cells were resuspended in 15 ml of Lysis buffer B (20 mM HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.4, 350 ml NaCl, 10% glycerol, 0.1% Tween 20, 1 mM PMSF, Halt protease and phosphatase inhibitor (11844111, Fisher Scientific)) and lysed in a FastPreP-24 bead beater (MP Biomedicals). Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 16,000 × g at 4 °C for 20 min. The cleared lysate was mixed with anti-FLAG M2 antibody (30 μg, F1804, Merck) bound to Dynabeads Protein G (10765583, Fisher Scientific) and incubated at 4 °C for 2 h. The beads were washed five times in 1 ml of Lysis buffer B. Bound proteins were eluted with 200 μl of Lysis buffer B containing 1 mg/ml 3× FLAG peptide (Merck) by incubating at room temperature for 30 min, with shaking. The elution step was repeated twice, yielding 400 μl of eluate. The SWI/SNF complex was further purified and concentrated using Amicon Ultra centrifugal filter unit (MWCO 100 kDa, UFC5100, Merck), removing smaller proteins including 3× FLAG peptide and exchanging buffer to PBS containing 0.02% Tween 20 and 50% glycerol. The purified proteins were analysed by 4–15% TGX gel (4568085, Bio-Rad) followed by SYPRO Ruby staining (S12000, Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Purification of His-tagged Rtt106
His-Rtt106 was purified from E. coli using Ni-NTA resin (30210, QIAGEN). E. coli cells NiCo21(DE3) (C2529H, NEB) carrying pET28a-ScRTT106 were grown in 100 ml LB-kanamycin at 37 °C to OD600 0.6. Expression of His-Rtt106 was induced by incubating with 0.4 mM IPTG at 37 °C for 3 h. Cells were then collected by centrifugation, resuspended in 2 ml of Lysis buffer C (50 mM NaH2PO4, pH 8.0, 1 M NaCl, 10 mM imidazole, 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 0.1% Triton X-100, 10% glycerol, 1 mM PMSF, 3 μg/ml pepstatin A and Halt protease inhibitor), and lysed by sonicating on ice (Soniprep 150), with four cycles of 10 sec on then 10 sec off, at an amplitude of 8 μm. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 16,000 × g at 4 °C for 20 min. The cleared lysate was mixed with 250 μl of Ni-NTA resin and incubated at 4 °C for 60 min. After washing the resin with Wash buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, pH 8.0, 1 M NaCl, 20 mM imidazole, 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 0.1% Triton X-100, 10% glycerol, 1 mM PMSF, 3 μg/ml pepstatin A), His-Rtt106 was eluted with Elution buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl, 250 mM imidazole, 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 0.1% Triton X-100, 10% glycerol).
GST pull-down assay
E. coli cells NiCo21(DE3) carrying pGEX-6P-1, pGEX-6P-1-ScPDR1, pGEX-6P-1-ScPDR3, and pGEX-6P-1-ScRTT106 were grown in LB-ampicillin at 30 °C until OD600 reaches 0.5. The expression of GST and GST-fusion proteins was induced by incubating with 0.1 mM IPTG at 16 °C for 18 h. Cells were then collected by centrifugation, resuspended in cold Lysis buffer D (PBS containing 1 M NaCl, 0.1% Triton X-100, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM PMSF, Halt protease inhibitor), and lysed by sonicating on ice (Soniprep 150), with four cycles of 10 sec on, 10 sec off, at an amplitude of 8 μm. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 16,000 × g at 4 °C for 20 min. The cleared lysate was mixed with 20 μl of glutathione-Sepharose beads (GE17-0756-01, Merck) and incubated at 4 °C for 30 min. After washing four times with Lysis buffer D, the beads bound to GST or GST fusions were incubated with purified SWI/SNF, purified His-Rtt106 or yeast cell lysate containing HA-tagged Rtt106 in Binding buffer (PBS, 0.1% Triton X-100, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 10% glycerol, 1 mM PMSF, Halt protease inhibitor) at 4 °C for 2 h. After washing four times with binding buffer, bound proteins were eluted in SDS sample buffer, and analysed by SDS-PAGE and western blot. GST and GST fusions were detected using Stain-Free technology (Bio-Rad) or by Amido black staining (A8181, Merck). Snf6-3FLAG, His-Rtt106 and Rtt106-6HA were detected using anti-FLAG M2-HRP (1:5000, A8592, Merck), anti-His (1:5000, 652502, Biolegend), and anti-HA (1:5000, HA.11 clone 16B12, Biolegend) antibodies, respectively.
Spot assay
Yeast cultures grown in YPD at 30 °C overnight were diluted and then spotted on YPD plates containing fluconazole (PHR1160, Merck) or ketoconazole (K1003, Merck). The plates were then incubated at 30 °C for 2–4 days.
Minichromosome isolation
Minichromosomes were isolated essentially as described46. Cells carrying minichromosome plasmids were grown in 1 L of SILAC media70 (Kaiser SC-Arg-Lys-Trp (Formedium), supplemented with 20 mg/L heavy arginine-HCl (Arg10, CK Isotopes) and 30 mg/L lysine-2HCl (Lys6, CK Isotopes) or, for a control, 20 mg/L light arginine-HCl and 30 mg/L light lysine-2HCl) at 30 °C until log phase and harvested. After washing cells in ice-cold water supplemented with 2 mM PMSF, cells were resuspended in buffer H150 (25 mM HEPES-KOH, pH 7.5, 150 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 10% glycerol, 0.02% NP40, 1 mM PMSF, cOmplete Protease Inhibitor cocktail without EDTA (11873580001, Merck), PhosSTOP (4906845001, Merck), 5 mM nicotinamide) and disrupted using a FastPreP-24 bead beater (MP Biomedicals). Clarified lysates were prepared by centrifugation at 20,000 × g for 20 min three times. lacO-containing minichromosomes were isolated by immunoprecipitating LacI-3FLAG with anti-FLAG M2 antibody (12 μg, F1804, Merck) crosslinked to Dynabeads protein G (10765583, Fisher Scientific) by dimethyl pimelimidate. Proteins on purified minichromosomes were eluted in Elution buffer (50 mM ammonium bicarbonate, 0.1% RapiGest SF (186001860, Waters), 1 mM IPTG). The eluted proteins were analysed by SYPRO Ruby staining and western blot analysis.
Mass spectrometry
Peptides digested by trypsin in solution (n = 1 biological sample) were analysed using an Orbitrap Q Exactive Plus mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific) equipped with a Dionex U3000 RSLCnano liquid chromatography system configured for pre-concentration on C18 PepMap 100 (300 µm i.d. × 5 mm) then peptide separation on EASY-Spray PepMap RSLC C18 (75 µm i.d. × 50 cm) over a 245 min elution gradient as described previously71 with minor modifications. Two solvents were formed, solvent A was made from water/formic acid (1000:0.1) and solvent B from water/acetonitrile/formic acid (20:80:0.1). An increasing proportion of solvent B was used to separate peptides along a gradient: 3–40% from 5 to 205 min; 40–90% from 205 to 206 min; 90% from 206 to 216 min; 90–3% from 216 to 217 min, followed by re-equilibration of the column (3% Solvent B from 217–245 min). Mass spectra were acquired using a Top 10 data-dependent method starting at 25 min and lasting 205 min. Full MS scans were conducted between 375 and 1750 m/z at a resolution 70,000 (m/z 200), automatic gain control 3E + 6 and a maximum injection time 50 ms. Following each survey scan the 10 most intense ions of charge state 2–5 were sequentially selected (isolation window 1.6 m/z) and fragmented in the higher-energy collisional dissociation (HCD) cell at a normalized collision energy of 28%. MS/MS scans were conducted at a resolution 17,500, automatic gain control 5E + 4 and a maximum injection time 100 ms. Dynamic exclusion of 40 s prevented ions from triggering subsequent data-dependent scans during that time.
Mass spectrometry data analysis
RAW data obtained from SILAC samples were processed with MaxQuant (version 1.6.5.0)72 using the standard settings for Orbitrap against a S. cerevisiae protein database (UP000002311_559292). Carbamidomethylation of cysteines was set as a fixed modification and oxidation of methionines, deamidation of asparagines and glutamines, and protein N-terminal acetylation as variable modifications. Minimal peptide length was set to seven amino acids and a maximum of two missed Trypsin/P cleavages was allowed. SILAC quantification was performed using standard settings and a Label min ratio count of 5. RAW data obtained from the SWI/SNF-enriched fraction was processed with Proteome Discoverer (version 2.2.0.388, Thermo Fisher Scientific) incorporating Mascot Server (version 2.5) using the standard settings for Orbitrap, against a S. cerevisiae protein database (UP000002311_559292). Carbamidomethylation of cysteines was set as a fixed modification and oxidation of methionines, and phosphorylation of serines, threonines and tyrosines as variable modifications. A maximum of three missed Trypsin cleavages was allowed. A strict target FDR of 0.01 for the decoy database search was used.
Statistics and reproducibility
Statistical analysis was performed by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test, one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD test, or two-sided Mann–Whitney test as described in each figure legend. For Northern blot and GST pull-down analyses and testing protein level of Pdr5 (Fig. 4b), each experiment was repeated three times independently with similar results, and one representative data of the replicates are presented. The experiments for confirming the expression of a series of epitope-tagged Pdr3 (Supplementary Fig. 3b, c) were performed once with at least two different isolates which showed similar results. Minichromosome isolation and purification of the SWI/SNF complex followed by SYPRO Ruby staining (Supplementary Fig. 6a, b) were repeated three times independently with similar results; data from one representative experiment are shown. Mass spectrometry analysis of isolated minichromosome was performed once and therefore proteins quantified at least 5 ratio counts were presented, allowing reliable quantification of proteins in the sample analysed. The binding of SWI/SNF to the PDR5 promoter (found by the minichromosome isolation experiment) was subsequently confirmed by ChIP-qPCR analysis with three biological replicates with similar results. Enrichment of the SWI/SNF complex by immunopurification was assessed by comparing the band pattern on the gel with that in published data48 (n = 3 biological replicates, with similar results), and subsequently confirmed by mass spectrometry (n = 1).
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
The data that support this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. All raw-data files for ChIP-seq and RNA-seq data were uploaded to ArrayExpress under accession numbers: E-MTAB-9787 and E-MTAB-11013. The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD028798. Publicly available datasets used in this study are GSM3452517 (Swi3 ChEC-seq), GSM3177770 (MNase-seq, +Snf2), GSM3177771 (MNase-seq, -Snf2), GSM3452556 (TBP ChIP-seq, +Snf2), GSM3452557 (TBP ChIP-seq, -Snf2), SRX648019 (MNase-seq, WT), SRX648516 (MNase-seq, rtt106Δ), SRX648532 (Yta7 ChIP-seq), GSM1565066 (TSS-seq), Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome (sacCer3, April 2011) (https://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/sacCer3/chromosomes/) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein database (UP000002311_559292). Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Pappas, P. G., Lionakis, M. S., Arendrup, M. C., Ostrosky-Zeichner, L. & Kullberg, B. J. Invasive candidiasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 4, 18026 (2018).
Brown, G. D. et al. Hidden killers: human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 4, 165rv113 (2012).
Wiederhold, N. P. Antifungal resistance: current trends and future strategies to combat. Infect. Drug Resist. 10, 249–259 (2017).
Sipos, G. & Kuchler, K. Fungal ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in drug resistance & detoxification. Curr. Drug Targets 7, 471–481 (2006).
Balzi, E. & Goffeau, A. Yeast multidrug resistance: the PDR network. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 27, 71–76 (1995).
Paul, S. & Moye-Rowley, W. S. Multidrug resistance in fungi: regulation of transporter-encoding gene expression. Front. Physiol. 5, 143 (2014).
Thakur, J. K. et al. A nuclear receptor-like pathway regulating multidrug resistance in fungi. Nature 452, 604–609 (2008).
Golin, J. & Ambudkar, S. V. The multidrug transporter Pdr5 on the 25th anniversary of its discovery: an important model for the study of asymmetric ABC transporters. Biochem. J. 467, 353–363 (2015).
Ferrari, S. et al. Gain of function mutations in CgPDR1 of Candida glabrata not only mediate antifungal resistance but also enhance virulence. PLoS Pathog. 5, e1000268 (2009).
Balzi, E., Wang, M., Leterme, S., Van Dyck, L. & Goffeau, A. PDR5, a novel yeast multidrug resistance conferring transporter controlled by the transcription regulator PDR1. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 2206–2214 (1994).
Katzmann, D. J., Burnett, P. E., Golin, J., Mahe, Y. & Moye-Rowley, W. S. Transcriptional control of the yeast PDR5 gene by the PDR3 gene product. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 4653–4661 (1994).
Mahe, Y. et al. The ATP-binding cassette multidrug transporter Snq2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a novel target for the transcription factors Pdr1 and Pdr3. Mol. Microbiol. 20, 109–117 (1996).
Mamnun, Y. M., Pandjaitan, R., Mahe, Y., Delahodde, A. & Kuchler, K. The yeast zinc finger regulators Pdr1p and Pdr3p control pleiotropic drug resistance (PDR) as homo- and heterodimers in vivo. Mol. Microbiol. 46, 1429–1440 (2002).
Meyers, S. et al. Interaction of the yeast pleiotropic drug resistance genes PDR1 and PDR5. Curr. Genet. 21, 431–436 (1992).
Wolfger, H., Mahe, Y., Parle-McDermott, A., Delahodde, A. & Kuchler, K. The yeast ATP binding cassette (ABC) protein genes PDR10 and PDR15 are novel targets for the Pdr1 and Pdr3 transcriptional regulators. FEBS Lett. 418, 269–274 (1997).
Hallstrom, T. C. & Moye-Rowley, W. S. Multiple signals from dysfunctional mitochondria activate the pleiotropic drug resistance pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 37347–37356 (2000).
Rhee, H. S. & Pugh, B. F. Genome-wide structure and organization of eukaryotic pre-initiation complexes. Nature 483, 295–301 (2012).
Lai, W. K. M. & Pugh, B. F. Understanding nucleosome dynamics and their links to gene expression and DNA replication. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 548–562 (2017).
Kubik, S. et al. Sequence-directed action of RSC remodeler and general regulatory factors modulates +1 nucleosome position to facilitate transcription. Mol. Cell 71, 89–102 e105 (2018).
Kubik, S. et al. Opposing chromatin remodelers control transcription initiation frequency and start site selection. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 26, 744–754 (2019).
Rufiange, A., Jacques, P. E., Bhat, W., Robert, F. & Nourani, A. Genome-wide replication-independent histone H3 exchange occurs predominantly at promoters and implicates H3 K56 acetylation and Asf1. Mol. Cell 27, 393–405 (2007).
Adkins, M. W., Howar, S. R. & Tyler, J. K. Chromatin disassembly mediated by the histone chaperone Asf1 is essential for transcriptional activation of the yeast PHO5 and PHO8 genes. Mol. Cell 14, 657–666 (2004).
Korber, P. et al. The histone chaperone Asf1 increases the rate of histone eviction at the yeast PHO5 and PHO8 promoters. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 5539–5545 (2006).
Su, D. et al. Structural basis for recognition of H3K56-acetylated histone H3-H4 by the chaperone Rtt106. Nature 483, 104–107 (2012).
Li, Q. et al. Acetylation of histone H3 lysine 56 regulates replication-coupled nucleosome assembly. Cell 134, 244–255 (2008).
Imbeault, D., Gamar, L., Rufiange, A., Paquet, E. & Nourani, A. The Rtt106 histone chaperone is functionally linked to transcription elongation and is involved in the regulation of spurious transcription from cryptic promoters in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 27350–27354 (2008).
Zunder, R. M., Antczak, A. J., Berger, J. M. & Rine, J. Two surfaces on the histone chaperone Rtt106 mediate histone binding, replication, and silencing. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, E144–E153 (2012).
Huang, S. et al. Rtt106p is a histone chaperone involved in heterochromatin-mediated silencing. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 13410–13415 (2005).
Lombardi, L. M., Davis, M. D. & Rine, J. Maintenance of nucleosomal balance in cis by conserved AAA-ATPase Yta7. Genetics 199, 105–116 (2015).
Eriksson, P. R., Ganguli, D., Nagarajavel, V. & Clark, D. J. Regulation of histone gene expression in budding yeast. Genetics 191, 7–20 (2012).
Fillingham, J. et al. Two-color cell array screen reveals interdependent roles for histone chaperones and a chromatin boundary regulator in histone gene repression. Mol. Cell 35, 340–351 (2009).
Zunder, R. M. & Rine, J. Direct interplay among histones, histone chaperones, and a chromatin boundary protein in the control of histone gene expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 32, 4337–4349 (2012).
Ferreira, M. E., Flaherty, K. & Prochasson, P. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae histone chaperone Rtt106 Mediates the cell cycle recruitment of SWI/SNF and RSC to the HIR-dependent histone genes. PLoS ONE 6, e21113 (2011).
Dimova, D., Nackerdien, Z., Furgeson, S., Eguchi, S. & Osley, M. A. A role for transcriptional repressors in targeting the yeast Swi/Snf complex. Mol. Cell 4, 75–83 (1999).
Kurat, C. F. et al. Restriction of histone gene transcription to S phase by phosphorylation of a chromatin boundary protein. Genes Dev. 25, 2489–2501 (2011).
Wang, C. et al. Structure of the yeast Swi/Snf complex in a nucleosome free state. Nat. Commun. 11, 3398 (2020).
Sudarsanam, P., Iyer, V. R., Brown, P. O. & Winston, F. Whole-genome expression analysis of snf/swi mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3364–3369 (2000).
Shivaswamy, S. & Iyer, V. R. Stress-dependent dynamics of global chromatin remodeling in yeast: dual role for SWI/SNF in the heat shock stress response. Mol. Cell Biol. 28, 2221–2234 (2008).
Dutta, A. et al. Swi/Snf dynamics on stress-responsive genes is governed by competitive bromodomain interactions. Genes Dev. 28, 2314–2330 (2014).
Gkikopoulos, T., Havas, K. M., Dewar, H. & Owen-Hughes, T. SWI/SNF and Asf1p cooperate to displace histones during induction of the saccharomyces cerevisiae HO promoter. Mol. Cell Biol. 29, 4057–4066 (2009).
Yudkovsky, N., Logie, C., Hahn, S. & Peterson, C. L. Recruitment of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex by transcriptional activators. Genes Dev. 13, 2369–2374 (1999).
Neely, K. E., Hassan, A. H., Brown, C. E., Howe, L. & Workman, J. L. Transcription activator interactions with multiple SWI/SNF subunits. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 1615–1625 (2002).
Scholes, D. T., Banerjee, M., Bowen, B. & Curcio, M. J. Multiple regulators of Ty1 transposition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae have conserved roles in genome maintenance. Genetics 159, 1449–1465 (2001).
Kemmeren, P. et al. Large-scale genetic perturbations reveal regulatory networks and an abundance of gene-specific repressors. Cell 157, 740–752 (2014).
Delahodde, A., Delaveau, T. & Jacq, C. Positive autoregulation of the yeast transcription factor Pdr3p, which is involved in control of drug resistance. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 4043–4051 (1995).
Unnikrishnan, A., Gafken, P. R. & Tsukiyama, T. Dynamic changes in histone acetylation regulate origins of DNA replication. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 430–437 (2010).
Shahi, P., Gulshan, K., Näär, A. M. & Moye-Rowley, W. S. Differential roles of transcriptional mediator subunits in regulation of multidrug resistance gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 21, 2469–2482 (2010).
Kapoor, P. et al. Regulation of Mec1 kinase activity by the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex. Genes Dev. 29, 591–602 (2015).
Malabat, C., Feuerbach, F., Ma, L., Saveanu, C. & Jacquier, A. Quality control of transcription start site selection by nonsense-mediated-mRNA decay. elife 4, e06722 (2015).
Paul, S., Schmidt, J. A. & Moye-Rowley, W. S. Regulation of the CgPdr1 transcription factor from the pathogen Candida glabrata. Eukaryot. Cell 10, 187–197 (2011).
Dion, M. F. et al. Dynamics of replication-independent histone turnover in budding yeast. Science 315, 1405–1408 (2007).
Pchelintsev, N. A. et al. Placing the HIRA histone chaperone complex in the chromatin landscape. Cell Rep. 3, 1012–1019 (2013).
Venkatesh, S. & Workman, J. L. Histone exchange, chromatin structure and the regulation of transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 178–189 (2015).
Tsai, H. F., Krol, A. A., Sarti, K. E. & Bennett, J. E. Candida glabrata PDR1, a transcriptional regulator of a pleiotropic drug resistance network, mediates azole resistance in clinical isolates and petite mutants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50, 1384–1392 (2006).
Liu, Z. & Myers, L. C. Candida albicans Swi/Snf and mediator complexes differentially regulate Mrr1-induced MDR1 expression and fluconazole resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61, e01344–e01317 (2017).
Jenull, S. et al. The Candida albicans HIR histone chaperone regulates the yeast-to-hyphae transition by controlling the sensitivity to morphogenesis signals. Sci. Rep. 7, 8308 (2017).
Mao, X., Cao, F., Nie, X., Liu, H. & Chen, J. The Swi/Snf chromatin remodeling complex is essential for hyphal development in Candida albicans. FEBS Lett. 580, 2615–2622 (2006).
Nishikawa, J. L. et al. Inhibiting fungal multidrug resistance by disrupting an activator-mediator interaction. Nature 530, 485–489 (2016).
Longtine, M. S. et al. Additional modules for versatile and economical PCR-based gene deletion and modification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 14, 953–961 (1998).
Laughery, M. F. et al. New vectors for simple and streamlined CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 32, 711–720 (2015).
Kubota, T., Hiraga, S., Yamada, K., Lamond, A. I. & Donaldson, A. D. Quantitative proteomic analysis of chromatin reveals that Ctf18 acts in the DNA replication checkpoint. Mol. Cell Proteomics 10, M110 005561 (2011).
Katou, Y. et al. S-phase checkpoint proteins Tof1 and Mrc1 form a stable replication-pausing complex. Nature 424, 1078–1083 (2003).
van Bakel, H. et al. A compendium of nucleosome and transcript profiles reveals determinants of chromatin architecture and transcription. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003479 (2013).
Kim, D., Langmead, B. & Salzberg, S. L. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 12, 357–360 (2015).
Li, H. et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25, 2078–2079 (2009).
Liao, Y., Smyth, G. K. & Shi, W. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 30, 923–930 (2014).
Robinson, M. D., McCarthy, D. J. & Smyth, G. K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26, 139–140 (2010).
Mansour, F. H. & Pestov, D. G. Separation of long RNA by agarose-formaldehyde gel electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 441, 18–20 (2013).
Cankorur-Cetinkaya, A. et al. A novel strategy for selection and validation of reference genes in dynamic multidimensional experimental design in yeast. PLoS ONE 7, e38351 (2012).
Kubota, T., Stead, D. A., Hiraga, S.-I., ten Have, S. & Donaldson, A. D. Quantitative proteomic analysis of yeast DNA replication proteins. Methods 57, 196–202 (2012).
Causey, D. R. et al. Proteomic comparison of selective breeding and growth hormone transgenesis in fish: Unique pathways to enhanced growth. J. Proteomics 192, 114–124 (2019).
Cox, J. & Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized ppb-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 1367–1372 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We thank Karl Kuchler, Carol Munro, Donna MacCallum, Delma Childers and Ian Stansfield for plasmids and strains; Ben Rutter, Madeleine Murray and Tom Jayasekara for help with material constructions and homology search; Vamsi Gali, Anne Donaldson, Yuki Katou and Katsuhiko Shirahige for preliminary ChIP-seq data; Shin-ichiro Hiraga for MaxQuant analysis; Stefan Hoppler for access for equipment; Sophie Shaw and Antonio Ribeiro for bioinformatic analysis of the RNA-seq data and also data uploading to ArrayExpress and Anne Donaldson and Alexander Lorenz for careful reading of the manuscript. We are grateful to the core facilities at University of Aberdeen: the CGEBM facility for help with ChIP-seq and RNA-seq (Ewan Campbell and Zeynab Heidari), the Proteomics facility for mass spectrometry (David Stead) and the qPCR facility. Work was supported by Medical Research Council (MRC) Career Development Fellowship L019698/1 to T.K., and Wellcome Trust Strategic Award for Medical Mycology and Fungal Immunology 097377/Z/11/Z to T.K. and D.M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualisation: V.N. and T.K.; Formal analysis: V.N. and T.K.; Investigation: V.N., D.M. and T.K.; Writing—original draft: T.K.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Source data
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolov, V.N., Malavia, D. & Kubota, T. SWI/SNF and the histone chaperone Rtt106 drive expression of the Pleiotropic Drug Resistance network genes. Nat Commun 13, 1968 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29591-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29591-z
This article is cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms governing antifungal drug resistance
npj Antimicrobials and Resistance (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.