Abstract
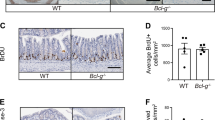
The potential role of the bcl-2 relative bcl-w as a physiological regulator of apoptosis in intestinal epithelia has been investigated. Immunoblots for bcl-w with new monoclonal antibodies revealed that it was expressed in the small intestine and colon, among other murine tissues, as well as in six human tumour cell lines of epithelial origin, including two colon carcinoma lines. To assess whether bcl-w regulates either spontaneous or damage-induced apoptosis in the small intestine or colon, apoptosis in intestinal crypts of bcl-w −/− and wild-type mice was quantified microscopically on a cell positional basis. Spontaneous apoptosis within crypt epithelia was not significantly increased by loss ofbcl-w, in either the small intestine or midcolon. However, after treatment with the cytotoxic drug 5-fluorouracil or with γ-radiation, the bcl-w-null animals exhibited substantially more apoptosis than their wild-type counterparts in both tissues. The greatest enhancement of apoptosis attributable to the absence of bcl-w (up to sixfold) occurred in the small intestine. Hence, bcl-w is an important determinant of damage-induced apoptosis in intestinal epithelia, and unlike bcl-2, which regulates only colonic apoptosis, plays a major role in small intestinal epithelium.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5-FU:
-
5-fluorouracil
References
Adams JM and Cory S. . 1998 Science 281: 1322–1326.
Dive C and Hickman JA. . 1991 Br. J. Cancer 64: 192–196.
Gibson L, Holmgreen SP, Huang DCS, Bernard O, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Sutherland GR, Baker E, Adams JM and Cory S. . 1996 Oncogene 13: 665–675.
Manne U, Myers RB, Moron C, Poczatek RB, Dillard S, Weiss H, Brown D, Srivastava S and Grizzle WE. . 1997 Int. J. Cancer 74: 346–358.
Merritt AJ, Jones LS and Potten CS. . 1996 Techniques in Apoptosis. Cotter and Martin (eds), Portland Press Ltd., London pp. 269–300.
Merritt AJ, Potten CS, Kemp CJ, Hickman JA, Ballmain A, Lane DP and Hall PA. . 1994 Cancer Res. 54: 614–617.
Merritt AJ, Potten CS, Watson AJM, Loh DY, Nakayama K, Nakayama K and Hickman JA. . 1995 J. Cell Sci. 108: 2261–2271.
Potten CS. . 1977 Nature 269: 518–521.
Potten CS. . 1992 Cancer Metast. Rev., 11: 179–195.
Potten CS and Grant HK. . 1998 Br. J. Cancer 78: 993–1003.
Potten CS, Owen G and Roberts SA. . 1990 Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 57: 185–199.
Print CG, Loveland KL, Gibson L, Meehan T, Stylianou A, Wreford N, DeKretser D, Metcalf D, Kontgen F, Adams JM and Cory S. . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 12424–12431.
Pritchard DM, Potten CS and Hickman JA. . 1998 Cancer Res. 58: 5453–5465.
Pritchard DM, Potten CS, Korsmeyer SJ, Roberts S and Hickman JA. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 7287–7293.
Pritchard DM, Watson AJ, Potten CS, Jackman AL and Hickman JA. . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94: 1795–1799.
Reed JC. . 1999 Apoptosis and Cancer Chemotherapy, Hickman JA and Dive C. (eds). Humana Press, Totowa, NJ pp. 99–116.
Ross AI, Waymire KG, Moss JE, Parlow AF, Skinner MK, Russell LD and MacGregor G. . 1998 Nature Genetics 18: 251–256.
Veis DJ, Sorenson CM, Shutter JR and Korsmeyer SJ. . 1993 Cell 75: 229–239.
Watson AJM, Merritt AJ, Jones LS, Askew JN, Anderson E, Becciolini A, Balzi M, Potten CS and Hickman JA. . 1996 Br. J. Cancer 73: 889–895.
Acknowledgements
We thank Susanna Novakovi, Leonie Cullen and Evette Shomali for technical assistance and for research support, the Medical Research Council (UK), the Cancer Research Campaign (UK), AMRAD Biotech, the National Health and Medical Research Council (Australia), the US National Cancer Institute (CA 43540 and CA80188) and the Dr Josef Steiner Cancer Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pritchard, D., Print, C., O'Reilly, L. et al. Bcl-w is an important determinant of damage-induced apoptosis in epithelia of small and large intestine. Oncogene 19, 3955–3959 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203729
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203729
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
BCL-w: apoptotic and non-apoptotic role in health and disease
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
MiR-133b regulates bladder cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting Bcl-w and Akt1
Cancer Cell International (2014)
-
A functional genomics screen identifies PCAF and ADA3 as regulators of human granzyme B-mediated apoptosis and Bid cleavage
Cell Death & Differentiation (2014)
-
Genetic unraveling of colorectal cancer
Tumor Biology (2014)
-
Acetylation of p53 stimulates miRNA processing and determines cell survival following genotoxic stress
The EMBO Journal (2013)