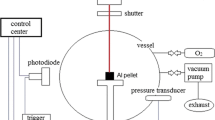
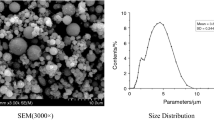
Abstract
Nano aluminum particles have received considerable attention in the combustion community; their physicochemical properties are quite favorable as compared with those of their micron-sized counterparts. The present work provides a comprehensive review of recent advances in the field of combustion of nano aluminum particles. The effect of the Knudsen number on heat and mass transfer properties of particles is first examined. Deficiencies of the currently available continuum models for combustion of nano aluminum particles are highlighted. Key physicochemical processes of particle combustion are identified and their respective time scales are compared to determine the combustion mechanisms for different particle sizes and pressures. Experimental data from several sources are gathered to elucidate the effect of the particle size on the flame temperature of aluminum particles. The flame structure and the combustion modes of aluminum particles are examined for wide ranges of pressures, particle sizes, and oxidizers. Key mechanisms that dictate the combustion behaviors are discussed. Measured burning times of nano aluminum particles are surveyed. The effects of the pressure, temperature, particle size, and type and concentration of the oxidizer on the burning time are discussed. A new correlation for the burning time of nano aluminum particles is established. Major outstanding issues to be addressed in the future work are identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. W. Price and R. K. Sigman, “Combustion of Aluminized Solid Propellants,” in AIAA Progress in Aeronautics and Astronautics, Vol. 185: Solid Propellant Chemistry, Combustion, and Motor Interior Ballistics, Eds. by V. Yang, T. B. Brill, and W. Z. Ren (AIAA, New York, 2000), pp. 663–687.
M. K. Berner, V. E. Zarko, and M. B. Talawar, “Nanoparticles of Energetic Materials: Synthesis and Properties (Review),” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 49(6) 3–30 (2013) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 49 (6), 625–647 (2013).
J. P. Foote, B. R. Thompson, and J. T. Lineberry, “Combustion of Aluminum with Steam for Underwater Propulsion,” in Advances in Chemical Propulsion, Ed. by G. D. Roy (CRC Press, 2002), pp. 133–145.
P. Brousseau and C. J. Anderson, “Nanometric Aluminum in Explosives,” Propell., Explos., Pyrotech. 27(5), 300–306 (2002).
E. Shafirovich, V. Diakov, and A. Varma, “Combustion of Novel Chemical Mixtures for Hydrogen Generation,” Combust. Flame 144(1/2), 415–418 (2006).
C. L. Yeh and K. K. Kuo, “Ignition and Combustion of Boron Particles,” Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 22(6), 511–541 (1996).
G. Young, K. Sullivan, M. R. Zachariah, and K. Yu, “Combustion Characteristics of Boron Nanoparticles,” Combust. Flame 156(2), 322–333 (2009).
A. Ulas, K. K. Kuo, and C. Gotzmer, “Ignition and Combustion of Boron Particles in Fluorine-Containing Environmentsm,” Combust. Flame 127(1–2), 1935–1957 (2001).
G. P. Sutton and O. Biblarz, Rocket Propulsion Elements (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 2010), p. 517.
Y. Huang, G. A. Risha, V. Yang, and R. A. Yetter, “Effect of Particle Size on Combustion of Aluminum Particle Dust in Air,” Combust. Flame 156(1), 5–13 (2009).
D. S. Sundaram, P. Puri, and V. Yang, “Thermochemical Behavior of Nano-Sized Aluminum-Coated Nickel Particles,” J. Nanopart. Res. 16, 1–16 (2014).
P. Puri and V. Yang, “Effect of Particle Size on Melting of Aluminum at Nano Scales,” J. Phys. Chem. C 111(32), 11776–11783 (2007).
J. Eckert, J. C. Holzer, C. C. Ahn, Z. Fu, and W. L. Johnson, “Melting Behavior of Nanocrystalline Aluminum Powders,” Nanostruct. Mater. 2(4), 407–413 (1993).
S. L. Lai, J. R. A. Carlsson, and L. H. Allen, “Melting Point Depression of Al Clusters Generated During the Early Stages of Film Growth: Nanocalorimetry Measurements,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 72(9), 1098–1100 (1998).
V. I. Levitas and K. Samani, “Size and Mechanics Effects in Surface-InducedMelting of Nanoparticles,” Nature Commun. 2, 1–6 (2011).
V. I. Levitas, M. L. Pantoya, G. Chauhan, and I. Rivero, “Effect of the Alumina Shell on the Melting Temperature Depression for Aluminum Nanoparticles,” J. Phys. Chem. C 113(32), 14088–14096 (2009).
C. Q. Sun, Y. Wang, B. K. Yay, S. Li, H. Huang, and Y. B. Zhang, “Correlation between the Melting Point of a Nanosolid and the Cohesive Energy of a Surface Atom,” J. Phys. Chem. B 106(41), 10701–10705 (2002).
C. Brossard, A. Ulas, C. L. Yeh, and K. K. Kuo, “Ignition and Combustion of Isolated Aluminium Particles in the Post-Flame Region of a Flat-Flame Burner,” in 16th Int. Colloquium on the Dynamics of Explosions and Reactive Systems, Krakow, Poland, 1997.
T. P. Parr, C. Johnson, D. Hanson-Parr, K. Higa, and K. Wilson, “Evaluation of Advanced Fuels for Underwater Propulsion,” in 39th JANNAF Combustion Subcommittee Meeting, 2003.
I. G. Assovskiy, O. M. Zhigalina, and V. I. Kolesnikov-Svinarev, “Gravity Effect in Aluminum Droplet Ignition and Combustion,” in Fifth Int. Microgravity Combustion Workshop, Cleveland, 1999.
R. Friedman and A. Macek, “Ignition and Combustion of Aluminium Particles in Hot Ambient Gases,” Combust. Flame 6, 9–19 (1962).
C. J. Bulian, T. T. Kerr, and Puszynski J. A. “Ignition Studies of Aluminum and Metal Oxide Nanopowders,” in 31st Int. Pyrotechnics Seminar, Fort Collins, Colarado, 2004.
M. E. Derevyaga, L. N. Stesik, and E. A. Fedorin, “Ignition and Combustion of Aluminum and Zinc in Air,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 13(6), 852–857 (1977) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 13 (6), 722–726 (1977)].
V. A. Ermakov, A. A. Razdobreev, A. I. Skorik, V. V. Pozdeev, and S. S. Smolyakov, “Temperature of Aluminum Particles at the Time of Ignition and Combustion,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 18(2), 141–143 (1982) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 18 (2), 256–257 (1982)].
D. K. Kuehl, “Ignition and Combustion of Aluminum and Beryllium,” AIAA J. 3(12), 2239–2247 (1965).
S. Yuasa, Y. Zhu, and S. Sogo, “Ignition and Combustion of Aluminum in Oxygen/Nitrogen Mixture Streams,” Combust. Flame 108(4), 387–390 (1997).
M. A. Gurevich, K. I. Lapkina, and E. S. Ozerov, “Limiting Conditions of Ignition of an Aluminum Particle,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 6(2), 172–176 (1970).
M. Schoenitz, C. Chen, and E. L. Dreizin, “Oxidation of Aluminum Particles in the Presence of Water,” J. Phys. Chem. B 113(15), 5136–5140 (2009).
T. G. Theofanous, X. Chen, P. Di Piazza, M. Epstein, and H. K. Fauske, “Ignition of Aluminum Droplets Behind Shock Waves in Water,” Phys. Fluids 6(11), 3513–3515 (1994).
M. A. Trunov, M. Schoenitz, and E. L. Dreizin, “Effect of Polymorphic Phase Transformations in Alumina Layer on Ignition of Aluminum Particles,” Combust. Theory Model. 10(4), 603–623 (2006).
A. Rai, D. Lee, K. Park, and M. R. Zachariah, “Importance of Phase Change of Aluminum in Oxidation of Aluminum Nanoparticles,” J. Phys. Chem. B 108(39), 14793–14795 (2004).
H. Tyagi, P. E. Phelan, R. Prasher, R. Peck, T. Lee, J. R. Pacheco, and P. Arentzen, “Increased Hot-Plate Ignition Probability for Nanoparticle-Laden Disel Fuel,” Nano Lett. 8(5), 1410–1416 (2008).
Y. Gan and L. Qiao, “Combustion Characteristics of Fuel Droplets with Addition of Nano and Micron-Sized Aluminum Particles,” Combust. Flame 158(2), 354–368 (2011).
J. L. Sabourin, R. A. Yetter, B.W. Asay, J. M. Lloyd, V. E. Sanders, G. A. Risha, and S. F. Son, “Effect of Nanoaluminum and Fumed Silica Particles on Deflagration and Detonation of Nitromethane,” Propell., Explos., Pyrotech. 34(5), 385–393 (2009).
R. W. Armstrong, B. Baschung, D. W. Booth, and M. Samirant, “Enhanced Propellant Combustion with Nanoparticles,” Nano Lett. 3(2), 253–255 (2003).
L. Meda, G. Marra, L. Galfetti, S. Inchingalo, F. Severini, and L. De Luca, “Nano-Composites for Rocket Solid Propellants,” Compos. Sci. Technol. 65(5), 769–773 (2005).
A. Dokhan, E. W. Price, J. M. Seitzman, and R. K. Sigman, “The Effects of Bimodal Aluminum with Ultrafine Aluminum on the Burning Rates of Solid Propellants,” Proc. Combust. Inst. 29(2), 2939–2946 (2002).
K. Jayaraman, K. V. Anand, S. R. Chakravarthy, and R. Sarathi, “Effect of Nano-Aluminum in Plateau-Burning and Catalyzed Composite Solid Propellant Combustion,” Combust. Flame 156(8), 1662–1673 (2009).
M. L. Pantoya and J. J. Granier, “Combustion Behavior of Highly Energetic Thermites: Nano versus Micron Composites,” Propell., Explos., Pyrotech. 30(1), 53–62 (2005).
M. Schoenitz, T. S. Ward, and E. L. Dreizin, “Fully Dense Nano-Composite Energetic Powders Prepared by Aarrested Reactive Milling,” Proc. Combust. Inst. 30(2), 2071–2078 (2005).
S. F. Son, B. W. Asay, T. J. Foley, R. A. Yetter, M. H. Wu, and G. A. Risha, “Combustion of Nanoscale Al-MoO3 Thermite in Microchannels,” J. Propul. Power 23(4), 715–721 (2007).
M. R. Weismiller, J. Y. Malchi, R. A. Yetter, and T. J. Foley, “Dependence of Flame Propagation on Pressure and Pressurizing Gas for an Al/CuO Nanoscale Thermite,” Proc. Combust. Inst. 32(2), 1895–1903 (2009).
K. Sullivan and M. R. Zachariah, “Simultaneous Pressure and Optical Measurements of Nanoaluminum Thermites: Investigating the Reaction Mechanism,” J. Propul. Power 26(3), 467–472 (2010).
R. A. Yetter, G. A. Risha, and S. F. Son, “Metal Particle Combustion and Nanotechnology,” Proc. Combust. Inst. 32(2), 1819–1838 (2009).
M. R. Weismiller, J. Y. Malchi, J. G. Lee, R. A. Yetter, and T. J. Foley, “Effects of Fuel and Oxidizer Particle Dimensions on the Propagation of Aluminum Containing Thermites,” Proc. Combust. Inst. 33(2), 1989–1996 (2011).
G. A. Risha, S. F. Son, R. A. Yetter, V. Yang, and B. C. Tappan, “Combustion of Nano-Aluminum and LiquidWater,” Proc. Combust. Inst. 31(2), 2029–2036 (2007).
G. A. Risha, T. L. Connell, Jr, R. A. Yetter, D. S. Sundaram, and V. Yang, “Combustion of Frozen Nanoaluminum and Water Mixtures,” J. Propul. Power 30(1), 133–142 (2014).
D. S. Sundaram, V. Yang, T. L. Connell, Jr, G. A. Risha, and R. A. Yetter, “Flame Propagation of Nano/Micron-Sized Aluminum Particles and Ice (ALICE) Mixtures,” Proc. Combust. Inst. 34(2), 2221–2228 (2013).
V. G. Ivanov, O. V. Gavrilyuk, O. V. Glazkov, and M. N. Safronov, “Specific Features of the Reaction between Ultrafine Aluminum and Water in a Combustion Regime,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 36(2), 60–66 (2000) [Combus., Expl., ShockWaves 36 (2), 213–219 (2000)].
E. Shafirovich, V. Diakov, and A. Varma, “Combustion of Novel Chemical Mixtures for Hydrogen Generation,” Combust. Flame 144(1/2), 415–418 (2006).
M. W. Beckstead, K. Puduppakkam, P. Thakre, and V. Yang, “Modeling of Combustion and Ignition of Solid-Propellant Ingredients,” Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 33(6), 497–551 (2007).
T. J. Foley, C. E. Johnson, and K. T. Higa, “Inhibition of Oxide Formation on Aluminum Nanoparticles by Transition Metal Coating,” Chem. Mater. 17(16), 4086–4091 (2005).
R. J. Jouet, A. D. Warren, D. M. Rosenberg, V. J. Bellitto, K. Park, and M. R. Zachariah, “Surface Passivation of Bare Aluminum Nanoparticles using Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acids,” Chem. Mater. 17(11), 2987–2996 (2005).
R. J. Jouet, J. R. Carney, R. H. Granholm, H. W. Sandusky, and A. D. Warren, “Preparation and Reactivity Analysis of Novel Perfluoroalkyl Coated Aluminum Nanocomposites,” Mater. Sci. Technol. 22(4), 422–429 (2006).
Y. Cui, S. Zhao, D. Tao, Z. Liang, D. Huang, and Z. Xu, “Synthesis of Size-Controlled and Discrete Core-Shell Aluminum Nanoparticles with a Wet Chemical Process,” Mater. Lett. 121, 54–57 (2014).
Y. Kwon, A. A. Gromov, and J. I. Strokova, “Passivation of the Surface of Aluminum Nanopowders by Protective Coatings of the Different Chemical Origin,” Appl. Surface Sci. 253(12), 5558–5564 (2007).
D. S. Sundaram, P. Puri, and V. Yang, “Pyrophoricity of Nascent and Passivated Aluminum Particles at Nano-Scales,” Combust. Flame 160(9), 1870–1875 (2013).
A. V. Fedorov and Yu. V. Kharlamova, “Ignition of an Aluminum Particle,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 39(5), 65–68 (2003) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 39 (5), 544–547 (2003)].
A. V. Fedorov and A. V. Shul’gin, “Point Model of Combustion of Aluminum Nanoparticles in the Reflected Shock Wave,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 47(3), 47–51 (2011) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 47 (3), 289–293 (2011)].
M. W. Beackstead, Y. Liang, and K. V. Pudduppakkam, “Numerical Simulation of Single ALuminum Particle Combustion (Review),” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 41(6), 15–33 (2005) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 41 (6), 622–638 (2005)
F. Liu, K. J. Daun, D. R. Snelling, and G. J. Smallwood, “Heat Conduction from a Spherical Nano-Particle: Status of Modeling Heat Conduction in Laser-Induced Incandescence,” Appl. Phys. B 83(3), 355–382 (2006).
S. Mohan, M. A. Trunov, and E. L. Dreizin, “Heating and Ignition of Metal Particles in the Transition Heat Transfer Regime,” J. Heat Transfer 130(10), 104505 (2008).
P. Puri, “Multi Scale Modeling of Ignition and Combustion of Micro and Nano Aluminum Particles,” Ph. D. Thesis, Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering (The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, 2008).
A. V. Filippov and D. E. Rosner, “Energy Transfer between an Aerosol Particle and Gas at High Temperature Ratios in the Knudsen Transition Regime,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 43(1), 127–138 (2000).
A. Ermoline, D. Yildiz, and E. L. Dreizin, “Model of Heterogeneous Combustion of Small Particles,” Combust. Flame 160(12), 2982–2989 (2013).
D. Allen, H. Krier, and N. Glumac, “Heat Transfer Effects in Nano-Aluminum Combustion at High Temperatures,” Combust. Flame 161(1), 295–302 (2014).
O. Levenspiel, Chemical Reaction Engineering (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1962).
T. R. Marrero and E. A. Mason, “Gaseous Diffusion Coefficients,” J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1(1), 3–118 (1972).
T. Bazyn, H. Krier, and N. Glumac, “Combustion of Nanoaluminum at Elevated Pressure and Temperature Behind Reflected Shock Wavesm,” Combust. Flame 145(4), 703–713 (2006).
K. Park, D. Lee, A. Rai, D. Mukherjee, and M. R. Zachariah, “Size-Resolved Kinetic Measurements of Aluminum Nanoparticle Oxidation with Single Particle Mass Spectrometry,” J. Phys. Chem. B 109(15), 7290–7299 (2005).
B. J. Henz, T. Hawa, and M. R. Zachariah, “On the Role of Built-in Electric Fields on the Ignition of Oxide Coated Nanoaluminum: Ion Mobility Versus Fickian Diffusion,” J. Appl. Phys. 107(2), 024901 (2010).
N. Eisenreich, H. Fietzek, M. Del Mar Juez-Lorenzo, V. Kolarik, A. Koleczko, and V. Weiser, “On the Mechanism of Low Temperature Oxidation for Aluminum Particles Down to the Nano-Scale,” Propell., Explos., Pyrotech. 29(3), 137–145 (2004).
K. Aita, N. Glumac, S. P. Vanka, and H. Krier, “Modeling the Combustion of Nano-Sized Aluminum Particles,” in 44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, Nevada, 2006.
V. I. Levitas, “Burning Time of Aluminum Nanoparticles: Strong Effect of the Heating Rate and Melt-Dispersion Mechanism,” Combust. Flame 156(2), 543–546 (2009).
V. I. Levitas, M. L. Pantoya, and B. Dikici, “Melt Dispersion Versus Diffusive Oxidation Mechanism for Aluminum Nanoparticles: Critical Experiments and Controlling Parmeters,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 92(1), 011921 (2008).
P. Lynch, G. Fiore, H. Krier, and N. Glumac, “Gas-Phase Reaction in Nanoaluminum Combustion,” Combust. Sci. Technol. 182(7), 842–857 (2010).
Y. Li, R. Clark, A. Nakano, R. K. Kalia, and P. Vashishta, “Molecular Dynamics Study of Size Dependence of Combustion of Aluminum Nanoparticles,” Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. (2012).
Y. Li, R. K. Kalia, A. Nakano, and P. Vashishta, “Size Effect on the Oxidation of Aluminum Nanoparticle: Multimillion-Atom Reactive Molecular Dynamics Simulations,” J. Appl. Phys. 114(13), 134312 (2013).
A. V. Grosse and J. B. Conway, “Combustion of Metals in Oxygen,” Ind. Eng. Chem. 50(4), 663–672 (1958).
I. Glassman, “Combustion of Metals: Physical Considerations. Solid Propellant Rocket Research,” in ARS Progress in Astronautics and Rocketry (Academic Press, New York, 1960), Vol. 1, pp. 253–258.
B. J. Mcbride and S. Gordon, “Computer Program for Calculation of Complex Chemical Equilibrium Compositions,” National Aeronautics and Space Administration (1996).
P. Bucher, R. A. Yetter, F. L. Dryer, T. P. Parr, D. M. Hanson-Parr, and E. P. Vicenzi, “Flame Structure Measurement of Single Isolated Aluminum Particles Burning in Air,” Symp. (Int.) on Combustion 26(2), 1899–1908 (1996).
E. L. Dreizin, “Experimental Study of Stages in Aluminum Particle Combustion in Air,” Combust. Flame 105(4), 541–556 (1996).
R. A. Yetter and F. L. Dryer, “Metal Particle Combustion and Classification,” in Micro-Gravity Combustion: Fire in Free Fall, Ed. by H. D. Ross (Academic Press, 2001), pp. 419–478.
R. P. Wilson (Jr.), and F. A. Williams, “Experimental Study of the Combustion of Single Aluminum Particles in O2/Air,” Symp. (Int.) on Combust. 13(1), 833–845 (1971).
B. Legrand, M. Marion, C. Chauveau, I. Gokalp, and E. Shafirovich, “Ignition and Combustion of Levitated Magnesium and Aluminum Particles in Carbon Dioxide,” Combust. Sci. Technol. 165(1), 151–174 (2001).
N. Glumac, H. Krier, T. Bazyn, and R. Eyer, “Temperature Measurements of Aluminum Particles Burning in Carbon Dioxide,” Combust. Sci. Technol. 177(3), 485–511 (2005).
E. L. Dreizin, “On the Mechanism of Asymmetric Aluminum Particle Combustion,” Combust. Flame. 117(4), 841–850 (1999).
P. Bucher, R. A. Yetter, F. L. Dryer, T. Parr, and D. M. Hanson-Parr, “PLIF Species and Ratiometric Temperature Measurements of Aluminum Particle Combustion in O2, CO2 and N2O Oxidizers and Comparison with Model Calculations,” Symp. (Int.) on Combust. 27(2), 2421–2429 (1998).
S. Rossi, E. L. Dreizin, and C. K. Law, “Combustion of Aluminum Particles in Carbon Dioxide,” Combust. Sci. Technol. 164(1), 209–237 (2001).
P. F. Pokhil, A. F. Belyaev, Yu. V. Frolov, V. S. Logachev, and A. I. Korotkov, Combustion of Powdered Metals in Active Media (Nauka, Moscow, 1972) [in Russian].
T. Bazyn, H. Krier, and N. Glumacm, “Evidence for the Transition from the Diffusion-Limit in Aluminum Particle Combustion,” Proc. Combust. Inst. 31(2), 2021–2028 (2007).
C. Badiola, R. J. Gill, and E. L. Dreizin, “Combustion Characteristics of Micron-Sized Aluminum Particles in Oxygenated Environments,” Combust. Flame 158(10), 2064–2070 (2011).
I. S. Altman, “On Heat Transfer between Nanoparticles and Gas at High Temperatures,” J. Aerosol Sci. 30(1), S423–S424 (1999).
S. Mohan, M. A. Trunov, and E. L. Dreizin, “On Possibility of Vapor Phase Combustion for Fine Aluminum Particles,” Combust. Flame 156(11), 2213–2216 (2009).
A. F. Belyaev, Yu. V. Frolov, and A. I. Korotkov, “On Combustion and Ignition of Fine Aluminum Particles,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 4(3), 323–329 (1968).
R. Friedman and A. Macek, “Combustion Studies of Single Aluminum Particles,” Symp. (Int.) on Combust. 9(1), 703–709 (1963).
A. Davis, “Solid Propellants: The Combustion of Particles of Metal Ingredients,” Combust. Flame 7, 359–367 (1963).
A. Zenin, G. Kusnezov, and V. Kolesnikov, “Physics of Aluminum Particle Combustion at Zero-Gravity,” in AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, Nevada, 1999.
J. C. Melcher, R. L. Burton, and H. Krier, “Combustion of Aluminum Particles in Solid Rocket Motor Flows,” in AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Los Angeles, 1999.
R. O. Foelsche, R. L. Burton, and H. Krier, “Ignition and Combustion of Aluminum Particles in H2/O2/N2 Combustion Products,” J. Propul. Power 14(6), 1001–1008 (1998).
M. Marion, C. Chauveau, and I. Gokalp, “Studies on the Ignition and Burning of Levitated Aluminum Particles,” Combust. Sci. Technol. 115(4–6), 369–390 (1996).
M. W. Beakstead, “Correlating Aluminum Burning Times,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 41(5), 55–69 (2005) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 41 (5), 533–546 (2005)].
P. Lynch, H. Krier, and N. Glumac, “A Correlation for Burn time of Aluminum Particles in the Transition Regime,” Proc. Combust. Inst. 32(2), 1887–1893 (2009).
P. Chakraborty and M. R. Zachariah, “Do Nanoenergetic Particles Remain Nano-Sized during Combustion?” Combust. Flame 161(5), 1408–1416 (2014).
J. Buckmaster and T. L. Jackson, “An Examination of the Shrinking-Core Model of Sub-Micron Aluminum Combustion,” Combust. Theory Model. 17(2), 335–353 (2013).
P. Puri and V. Yang, “Thermo-Mechanical Behavior of Nano Aluminum Particles with Oxide Layers During Melting,” J. Nanopart. Res. 12(8), 2989–3002 (2010).
K. O. Hartman, “Ignition and Combustion of Aluminum Particles in Propellant Flame Gases,” in Proc. of 8th JANNAF Combustion Meeting, 1971.
S. E. Olsen and M. W. Beckstead, “Burn Time Measurements of Single Aluminum Particles in Steam and CO2 Mixtures,” J. Propul. Power 12(4), 662–671 (1996).
J. L. Prentice, “Combustion of Laser-Ignited Aluminum Droplets in Wet and Dry Oxidizers,” in 12th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Washington, 1974.
R. J. Gill, C. Badiola, and E. L. Dreizin, “Combustion Times and Emission Profiles of Micron-Sized Aluminum Particles Burning in Different Environments,” Combust. Flame 157(11), 2015–2023 (2010).
S. C. Wong and S. R. Turns, “Ignition of Aluminum Slurry Droplets,” Combust. Sci. Technol. 52(4–6), 221–242 (1987).
T. Bazyn, H. Krier, and N. Glumac, “Oxidizer and Pressure Effects on the Combustion of 10-µm Aluminum Particles,” J. Propul. Power 21(4), 577–582 (2005).
B. Bockmon, M. Pantoya, S. Son, B. Asay, and J. Mang, “Combustion Vlocities and Propagation Mechanisms of Metastable Interstitial Composites,” J. Appl. Phys. 98, 064903 (2005).
V. I. Levitas, B. W. Asay, S. F. Son, and M. Pantoya, “Melt Dispersion Mechanism for Fast Reaction of Nanothermites,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 071909 (2006).
Y. Ohkura, P. M. Rao, and X. Zheng, “Flash Ignition of Al Nanoparticles: Mechanism and Applications,” Combust. Flame 158, 2544–2548 (2011).
V. I. Levitas, “Mechanochemical Mechanism for Reaction of Aluminium Nano- and Micrometre-Scale Particles,” Phil. Trans. Roy Soc. A 371, 20120215 (2013).
V. I. Levitas, M. L. Pantoya, and B. Dikici, “Melt Dispersion Mechanism Versus Diffusive Oxidation Mechanism for Aluminum Nanoparticles: Critical Experiments and Controlling Parameters,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 011921 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.S. Sundaram, V. Yang, V.E. Zarko.
__________
Translated from Fizika Goreniya i Vzryva, Vol. 51, No. 2, pp. 37–64, March–April, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundaram, D.S., Yang, V. & Zarko, V.E. Combustion of nano aluminum particles (Review). Combust Explos Shock Waves 51, 173–196 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508215020045
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508215020045