Abstract
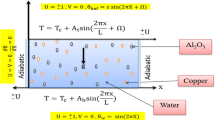
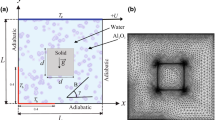
The present paper focuses on the problem of a mixed convection fluid flow and heat transfer of an Al2O3–water nanofluid with the thermal conductivity and effective viscosity dependent on temperature and nanoparticle concentration inside a lid-driven cavity having a hot rectangular obstacle. The governing equations are discretized by using the finite volume method, and the SIMPLE algorithm is employed to couple the velocity and pressure fields. By using the developed code, the effects of the Richardson number and the diameter and volume fraction of Al2O3 nanoparticles on the flow, thermal fields, and heat transfer inside the cavity are studied. The obtained results show that the average Nusselt number for the entire range of the solid volume fraction decreases with an increase in the Richardson number and the nanoparticle diameter. The results also clearly indicate that addition of Al2O3 nanoparticles produces a remarkable enhancement on heat transfer with respect to that of the pure fluid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. U. S. Choi, “Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles,” Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows, Ed. by D. A. Siginer, and H. P. Wang (ASME, New York, 1995), FED-V. 231/MDV. 66, pp. 99–105.
Y. Xuan and Q. Li, “Investigation on Convective Heat Transfer and Flow Features of Nanofluids,” J. Heat Transfer 125, 151–155 (2003).
S. Lee, S. U. S. Choi, S. Li, and J. A. Eastman, “Measuring Thermal Conductivity of Fluids Containing Oxide Nanoparticles,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 121, 280–289 (2001).
H. Q. Xie, J. C. Wang, T. G. Xi, et al., “Dependence of the Thermal Conductivity of Nanoparticle–Fluid Mixture on the Base Fluid,” J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 21, 1469–1471 (2002).
H. E. Patel, T. Pradeep, T. Sundararajan, et al., “A Micro Convection Model for Thermal Conductivity of Nanofluid,” Pramana-J. Phys. 65, 863–869 (2005).
H. Chang, C. S. Jwo, C. H. Lo, et al., “Rheology of CuO Nanoparticle Suspension Prepared by ASNSS,” Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 10, 128–132 (2005).
J. Imberger and P. F. Hamblin, “Dynamics of Lakes, Reservoirs, and Cooling Ponds,” Annual Rev. Fluid Mech. 14, 153–187 (1982).
M. K. Moallemi and K. S. Jang, “Prandtl Number Effects on Laminar Mixed Convection Heat Transfer in a Lid-Driven Cavity,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 35, 1881–1892 (1992).
C. K. Cha and Y. Jaluria, “Recirculating Mixed Convection Flow for Energy Extraction,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 27, 1801–1810 (1984).
F. J. K. Ideriah, “Prediction of Turbulent Cavity Flow Driven by Buoyancy and Shear,” J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 22, 287–295 (1980).
L. A. B. Pilkington, “Review Lecture: The Float Glass Process,” Proc. Roy. Soc. London, Ser. A 314, 1–25 (1969).
F. Talebi, A. H. Mahmoudi, and M. Shahi, “Numerical Study of Mixed Convection Flows in a Square Lid-Driven Cavity Utilizing Nanofluid,” Int. Comm. Heat Mass 37, 79–90 (2010).
E. Abu-Nada and A. J. Chamkha, “Mixed Convection Flow in a Lid Driven Square Enclosure Filled with a Nanofluid,” Eur. J. Mech. B. Fluid 29, 472–482 (2010).
M. Mahmoodi, “Mixed Convection Inside Nanofluid Filled Rectangular Enclosures with Moving Bottom Wall,” Thermal Sci. 15, 889–903 (2011).
A. Arefmanesh and M. Mahmoodi, “Effects of Uncertainties of Viscosity Models for Al2O3–Water Nanofluid on Mixed Convection Numerical Simulations,” Int. J. Thermal Sci. 50, 1706–1719 (2011).
Hemmat M. Esfe, F. Ghadak, A. Haghiri, and S. Mirtalebi, “Numerical Study of Mixed Convection Flows in a Two-Sided Inclined Lid-Driven Cavity Utilizing Nano-Fluid with Various Inclination Angles and Ununiformed Temperature,” Aerospace Mech. J. 8 (2), 69–83 (2012).
A. Fereidoon, S. Saedodin, Hemmat M. Esfe, and M. J. Noroozi, “Evaluation of Mixed Convection in Inclined Square Lid Driven Cavity Filled with Al2O3/Water Nanofluid,” Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 7, 55–65 (2013).
H. Zarei, S. H. Rostamian, and Hemmat M. Esfe, “Heat Transfer Behavior of Mixed Convection Flow in Lid Driven Cavity Containing Hot Obstacle Subjected to Nanofluid with Variable Properties,” J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res. 3, 713–721 (2013).
A. Z. Ghadi, M. J. Noroozi, and Hemmat M. Esfe, “Nanofluid Implementation for Heat Transfer Augmentation of Magneto Hydrodynamic Flows in a Lid-Driven Cavity using Experimental-Based Correlations,” Int. J. Appl. Electromagnetics Mech. 42 (4), 589–602 (2013).
M. R. Heidari, Hemmat M. Esfe, H. Hajmohammad, and M. Akbari, “Mixed Convection Heat Transfer in a Double Lid-Driven Inclined Square Enclosure Subjected to Cu–Water Nanofluid with Particle Diameter of 90 nm,” Heat Transfer Res. 45 (1), 75–95 (2014).
M. Nikfar and M. Mahmoodi, “Meshless Local Petrov — Galerkin Analysis of Free Convection of Nanofluid in a Cavity with Wavy Side Walls,” Eng. Anal. Boundary Elements 36, 433–445 (2012).
M. Mahmoodi and S. Mazrouei Sebdani, “Natural Convection in a Square Cavity Containing a Nanofluid and an Adiabatic Square Block at the Center,” Superlattices Microstruct. 52, 261–275 (2012).
M. Mahmoodi, “Mixed Convection Inside Nanofluid Filled Rectangular Enclosures with Moving Bottom Wall,” Thermal Sci. 15 (3), 889–903 (2011).
Mazrouei S. Sebdani, M. Mahmoodi, and S. M. Hashemi, “Effect of Nanofluid Variable Properties on Mixed Convection in a Square Cavity,” Int. J. Thermal Sci. 52, 112–126 (2012).
S. P. Jang, J. H. Lee, K. S. Hwang, and S. U. S. Choi, “Particle Concentration and Tube Size Dependence of Viscosities of Al2O3–Water Nanofluids Flowing Through Micro- and Minitubes,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 24–31 (2007).
R. L. Hamilton and O. K. Crosser, “Thermal Conductivity of Heterogeneous Two Component Systems,” Indust. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1, 187–191 (1962).
J. Xu, B. Yu, M. Zou, and P. Xu, “A New Model for Heat Conduction of Nanofluids Based on Fractal Distributions of Nanoparticles,” J. Phys. D 39, 4486–4490 (2006).
K. C. Lin and A. Violi, “Natural Convection Heat Transfer of Nanofluids in a Vertical Cavity: Effects of Non- Uniform Particle Diameter and Temperature on Thermal Conductivity,” Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 31, 236–245 (2010).
R. K. Tiwari and M. K. Das, “Heat Transfer Augmentation in a Two-Sided Lid-Driven Differentially Heated Square Cavity Utilizing Nanofluids,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 50, 2002–2018 (2007).
G. V. Hadjisophocleous, A. C. M. Sousaand, and J. E. S. Venart, “Predicting the Transient Natural Convection in Enclosures of Arbitrary Geometry using a Nonorthogonal Numerical Model,” Numer. Heat Transfer. A 13, 373–392 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M. Hemmat Esfe, M. Akbari, A. Karimipour.
Translated from Prikladnaya Mekhanika i Tekhnicheskaya Fizika, Vol. 56, No. 3, pp. 116–127, May–June, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemmat Esfe, M., Akbari, M. & Karimipour, A. Mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with an inside hot obstacle filled by an Al2O3–water nanofluid. J Appl Mech Tech Phy 56, 443–453 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894415030141
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894415030141