Abstract
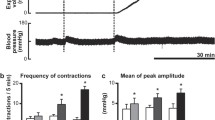
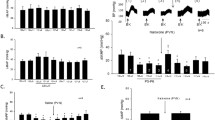
The caudal ventrolateral reticular formation of the medulla oblongata is the first layer of visceral nociceptive processing. In experiments on rats, neuronal responses in this zone to nociceptive stimulation of the large intestine were examined and the effects of selective blockade of 5-HT3 receptors on these responses were assessed. By the character of responses to nociceptive colorectal stimulation (CRS), the recorded medullary neurons were divided into three groups—excited, inhibited and indifferent. Intravenous injection of 5-HT3 antagonist granisetron (1 and 2 mg/kg) as well as local application of this agent on the surface of the medulla oblongata (1.25 and 2.5 nmole) suppressed the background and evoked firing of CRS-excited reticular neurons in a dose-dependent manner but did not exert as pronounced influence on the cells inhibited by visceral nociceptive stimulation. Spike activity in the group of CRS-indifferent neurons under similar conditions was 5-HT3-independent. The results obtained provide evidence that 5-HT3 receptors mediate the facilitating effect of serotonin on supraspinal transmission of the abdominal nociceptive stimulus which, at least in part, is realized via selective activation of visceral medullary nociceptive neurons. A shutdown of this mechanism may underlie the analgesic effect of 5-HT3 antagonists in abdominal pain syndromes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida, T.F., Roizenblatt, S., and Tufik, S., Afferent pain pathways: a neuroanatomical review, Brain Res., 2004, vol. 1000, no. 1–2, pp. 40–56.
Al-Chaer, E.D. and Willis, W.D., Neuroanatomy of visceral pain: pathways and processes, Chronic Abdominal and Visceral Pain. Theory and Practice, Pasricha, P.J., Willis, W.D., and Gebhart, G.F., Eds., New York, 2007, pp. 33–44.
Filippova, L.V. and Nozdrachev, A.D., Modern concepts of coding mechanisms of the visceral pain stimuli, Fiziol. Chel., 2010, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 125–137.
Almeida, A., Leite-Almeida, H., and Tavares, I., Medullary control of nociceptive transmission: Reciprocal dual communication with the spinal cord, Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms, 2006, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 305–312.
Lima, D., Albino-Teixeira, A., and Tavares, I., The caudal medullary ventrolateral reticular formation in nociceptive-cardiovascular integration. An experimental study in the rat, Exp. Physiol., 2002, vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 267–274.
Nozdrachev, A.D. and Chernyshova, M.P., Vistseral’nye refleksy (Visceral Reflexes), Leningrad, 1989.
Ness, T.J., Follett, K.A., Piper, J., and Dirks, B.A., Characterization of neurons in the area of the medullary lateral reticular nucleus responsive to noxious visceral and cutaneous stimuli, Brain Res., 1998, vol. 802, no. 1–2, pp. 163–174.
Ness, T.J., Piper, J.G., and Follett, K.A., The effect of spinal analgesia on visceral nociceptive neurons in caudal medulla of the rat, Anesth. Analg., 1999, vol. 89, no. 3, pp. 721–726.
Robbins, M.T., Uzzell, T.W., Aly, S., and Ness, T.J., Visceral nociceptive input to the area of the medullary lateral reticular nucleus ascends in the lateral spinal cord, Neurosci. Lett., 2005, vol. 381, no. 3, pp. 329–333.
Pinto-Ribeiro, F., Ansah, O.S., Almeida, A., and Pertovaara, A., Response properties of nociceptive neurons in the caudal ventrolateral medulla (CVLM) in monoarthritic and healthy control rats: Modulation of responses by the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN), Brain Res. Bull., 2011, vol. 86, no. 1–2, pp. 82–90.
Bueno, L., de Ponti, F., Fried, M., Kullak-Ublick, G.A., Kwiatek, M.A., Pohl, D., Quigley, E.M., Tack, J., and Talley, N.J., Serotonergic and non-serotonergic targets in the pharmacotherapy of visceral hypersensitivity, Neurogastroenterol. Motil., 2007, vol. 19, suppl. 1, pp. 89–119.
Bannister, K., Bee, L.A., and Dickenson, A.H., Preclinical and early clinical investigations related to monoaminergic pain modulation, Neurotherapeutics, 2009, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 703–712.
Faerber, L., Drechsler, S., Ladenburger, S., Gschaidmeier, H., and Fischer, W., The neuronal 5-HT3 receptor network after 20 years of research—Evolving concepts in management of pain and inflammation, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2007, vol. 560, no. 1, pp. 1–8.
Lummis, S.C.R., 5-HT3 receptors, J. Biol. Chem., 2012, vol. 287, no. 48, pp. 40239–40245.
Fayyaz, M. and Lackner, J.M., Serotonin receptor modulators in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome, Ther. Clin. Risk Manag., 2008, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 41–48.
Mayer, E.A., Berman, S., Derbyshire, S.W., Suyenobu, B., Chang, L., Fitzgerald, L., Mandelkern, M., Hamm, L., Vogt, B., and Naliboff, B.D., The effect of the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, alosetron, on brain responses to visceral stimulation in irritable bowel syndrome patients, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther., 2002, vol. 16, no. 7, pp. 1357–1366.
Kozlowski, C.M., Green, A., Grundy, D., Boissonade, F.M., and Bountra, C., The 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist alosetron inhibits the colorectal distention induced depressor response and spinal c-fos expression in the anaesthetised rat, Gut, 2000, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 474–480.
Miura, M., Lawson, D.C., Clary, E.M., Mangel, A.W., and Pappas, T.N., Central modulation of rectal distension-induced blood pressure changes by alosetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, Dig. Dis. Sci., 1999, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 20–24.
Panteleev, S.S., Busygina, I.I., and Lyubashina, O.A., Effects of selective blockade of 5HT3 receptors on physiological markers of abdominal pain in wakeful dogs, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2013, vol. 99, no. 4, pp. 471–483.
Banner, S.E., Carter, M., and Sanger, G.J., 5-Hydroxytryptamine3 receptor antagonism modulates a noxious visceral pseudoaffective reflex, Neuropharmacol., 1995, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 263–267.
Mazda, T., Yamamoto, H., Fujimura, M., and Fujimiya, M., Gastric distension-induced release of 5-HT stimulates c-fos expression in specific brain nuclei via 5-HT3 receptors in conscious rats, Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol., 2004, vol. 287, no. 1, pp. G228–G235.
Mönnikes, H., Rüter, J., König, M., Grote, C., Grote, C., Kobelt, P., Klapp, B.F., Arnold, R., Wiedenmann, B., and Tebbe, J.J., Differential induction of c-fos expression in brain nuclei by noxious and non-noxious colonic distension: role of afferent C-fibers and 5-HT3 receptors, Brain Res., 2003, vol. 966, no. 2, pp. 253–264.
Panteleev, S.S., Martseva, A.A., and Lyubashina, O.A., Responses of solitary tract nucleus neurons to nociceptive stimuli of the large intestine in rats, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2011, vol. 97, no. 12, pp. 1336–1345.
Paxinos, G. and Watson, C., The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, New York, 1998.
Wang, G., Tang, B., and Traub, R.J., Differential processing of noxious colonic input by thoracolumbar and lumbosacral dorsal horn neurons in the rat, J. Neurophysiol., 2005, vol. 94, no. 6, pp. 3788–3794.
Brink, T.S. and Mason, P., Raphe magnus neurons respond to noxious colorectal distension, J. Neurophysiol., 2003, vol. 89, no. 5, pp. 2506–2015.
Zhang, H.Q., Al-Chaer, E.D., and Willis, W.D., Effect of tactile inputs on thalamic responses to noxious colorectal distension in rat, J. Neurophysiol., 2002, vol. 88, no. 3, pp. 1185–1196.
Hicks, G.A., Coldwell, J.R., Schindler, M., Ward, P.A., Jenkins, D., Lynn, P.A., Humphrey, P.P., and Blackshaw, L.A., Excitation of rat colonic afferent fibres by 5-HT3 receptors, J. Physiol., 2002, vol. 544, pt. 3, pp. 861–869.
Coldwell, J.R., Phillis, B.D., Sutherland, K., Howarth, G.S., and Blackshaw, L.A., Increased responsiveness of rat colonic splanchnic afferents to 5-HT after inflammation and recovery, J. Physiol., 2007, vol. 579, pt. 1, pp. 203–213.
Conte, D., Legg, E.D., McCourt, A.C., Silajdzic, E., Nagy, G.G., and Maxwell, D.J., Transmitter content, origins and connections of axons in the spinal cord that possess the serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) 3 receptor, Neurosci., 2005, vol. 134, no. 1, pp. 165–173.
Suzuki, R., Rygh, L.J., and Dickenson, A.H., Bad news from the brain: descending 5-HT pathways that control spinal pain processing, Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 2004, vol. 25, no. 12, pp. 613–617.
Fonseca, M.I., Ni, Y.G., Dunning, D.D., and Miledi, R., Distribution of serotonin 2A,2C and 3 receptor mRNA in spinal cord and medulla oblongata, Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res., 2001, vol. 89, no. 1–2, pp. 11–19.
Lyubashina, O., Atanasova, D., Panteleev, S., Itzev, D., and Lazarov, N., Differential c-fos expression in nuclei of the caudal medulla oblongata following noxious colorectal distension in anaesthetized rats, Comp. Rend. Acad. Bg. Sci., 2012, vol. 65, no. 5, pp. 709–716.
Nosjean, A., Carella, J.C., Bonahama, L., Machado, B., Hamon, M., and Laguzzi, R., Serotonin(3) receptor stimulation in the nucleus tractus solitarii activates non-catecholaminergic neurons in the rat ventrolateral medulla, Neurosci., 2002, vol. 112, no. 4, pp. 935–949.
Sikandar, S., Bannister, K., and Dickenson, A.H., Brainstem facilitations and descending serotonergic controls contribute to visceral nociception but not pregabalin analgesia in rats, Neurosci. Lett., 2012, vol. 519, pp. 31–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.A. Lyubashina, I.B. Sivachenko, S.S. Panteleev, A.D. Nozdrachev, 2016, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2016, Vol. 52, No. 4, pp. 281—291.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyubashina, O.A., Sivachenko, I.B., Panteleev, S.S. et al. Effects of 5-HT3 receptor blockade on visceral nociceptive neurons in the ventrolateral reticular field of the rat medulla oblongata. J Evol Biochem Phys 52, 313–325 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093016040062
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093016040062