Abstract
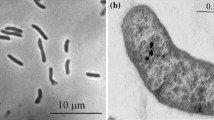
The new mesophilic, chemolithoautotrophic, moderately halophilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium strain 11-6, could grow at a NaCl concentration in the medium of 30–230 g/l, with an optimum at 80–100 g/l. Cells were vibrios motile at the early stages of growth. Lactate, pyruvate, malate, fumarate, succinate, propionate, butyrate, crotonate, ethanol, alanine, formate, and H2/CO2 were used in sulfate reduction. Butyrate was degraded completely, without acetate accumulation. In butyrate-grown cells, a high activity of CO dehydrogenase was detected. Additional growth factors were not required. Autotrophic growth occurred, in the presence of sulfate, on H2/CO2 or formate without other electron donors. Fermentation of pyruvate and fumarate was possible in the absence of sulfate. Apart from sulfate, sulfite, thiosulfate, and elemental sulfur were able to serve as electron acceptors. The optimal growth temperature was 37°C; the optimum pH was 7.2. Desulfoviridin was not detected. Menaquinone MK-7 was present. The DNA G+C content was 55.2 mol %. Phylogenetically, the bacterium represented a separate branch within the cluster formed by representatives of the family Desulfohalobiaceae in the class Deltaproteobacteria. The bacterium was assigned to a new genus and species, Desulfovermiculus halophilus gen. nov., sp. nov. The type strain is 11-6T (= VKM B-2364), isolated from the highly mineralized formation water of an oil field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oren, A., Bioenergetic Aspects of Halophilism, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 1999, vol. 63, no. 2, pp. 334–348.
Ollivier, B., Hatchikian, C.E., Prensier, G., et al., Desulfohalobium retbaense gen. nov., sp. nov., a Halophilic Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium from Sediments of a Hypersaline Lake in Senegal, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1991, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 74–81.
Caumette, P., Cohen, Y., and Matheron, R., Isolation and Characterization of Desulfovibrio halophilus sp. nov., a Halophilic Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from Solar Lake (Sinai), Syst. Appl. Microbiol., 1991, vol. 14, pp. 33–38.
Tardy-Jacquenod, C., Magot, M., Patel, B.K.C., et al., Desulfotomaculum halophilum sp. nov., a Halophilic Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from Oil Production Facilities, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1998, vol. 48, pp. 333–338.
Brandt, K.K., Patel, B.K.C., and Ingvorsen, K., Desulfocella halophila gen. nov., sp. nov., a Halophilic, Fatty-Acid-Oxidizing, Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from Sediments of the Great Salt Lake, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1999, vol. 49, pp. 193–200.
Rabus, R., Hansen, T., and Widdel, F., Dissimilatory Sulfate-and Sulfur-Reducing Prokaryotes, The Prokaryotes, ch. 274, New York: Springer, LLC, 2004.
Widdel, F., Anaerober Abbau von Fettsäuren und Benzoesäure durch neu isolierte Arten Sulfat-reduzierender Bakterien, Thesis, Göttingen, 1980, pp. 29–150.
Rozanova, E.P. and Pivovarova, T.A., Reclassification of Desulfovibrio thermophilus (Rozanova, Khudyakova, 1974), Mikrobiologiya, 1988, vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 102–106 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 85–89].
Belyakova, E.V. and Rozanova, E.P., Newly Discovered Properties of Spore-Forming Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, Desulfotomaculum Strains 435 and 781, Mikrobiologiya, 2004, vol. 73, no. 2, pp. 284–286 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 73, no. 2, pp. 237–239].
Postgate, J.R., A Diagnostic Reaction of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans, Nature, 1959, vol. 183, pp. 481–482.
Belyaev, S.S., Borzenkov, I.A., Milekhina, E.I., Charakhch’yan, I.A., and Ivanov, M.V., Development of Microbial Processes in Exploited Strata of the Romashkinskoe Oil Field, Mikrobiologiya, 1990, vol. 59, no. 6, pp. 1118–1126.
Collins, M.D. and Jones, D., Analysis of Isoprenoid Quinones, Methods Microbiol., 1985, vol. 18, pp. 329–354.
Pusheva, M.A. and Sokolova, T.G., Distribution of CO-Dehydrogenase Activity in the Anaerobic Thermophilic Carboxydotrophic Bacterium Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans Grown at the Expense of CO or Pyruvate, Mikrobiologiya, 1995, vol. 64, no. 5, pp. 581–586 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 64, no. 5, pp. 491–495].
Edwards, U., Rogall, T., Bloeker, H., Ende, M.D., and Boeettge, E.C., Isolation and Direct Complete Nucleotide Determination of Entire Genes, Characterization of Gene Coding for 16S Ribosomal RNA, Nucleic Acids Res., 1989, vol. 17, pp. 7843–7853.
Widdel, F. and Pfennig, N., Sporulation and Further Nutritional Characteristics of Desulfotomaculum acetoxidans, Arch. Microbiol., 1981, vol. 129, no. 5, pp. 401–402.
Tazaki, M., Kamagata, Y., Nakamura, K., and Mikami, E., Isolation and Characterization of Thermophilic Benzoate-Degrading, Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium, Desulfotomaculum thermobenzoicum sp. nov., Arch. Microbiol., 1991, vol. 155, pp. 348–352.
Spormann, A.M. and Thauer, R.K., Anaerobic Acetate Oxidation to CO2 by Desulfotomaculum acetoxidans. Demonstration of Enzymes Required for the Operation of an Oxidative Acetyl-CoA/Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenase Pathway, Arch. Microbiol., 1988, vol. 150, pp. 374–380.
Tarasov, A.L., Borzenkov, I.A., Milekhina, E.I., Belyaev, S.S., and Ivanov, M.V., Dynamics of Microbial Processes in the Stratal Waters of the Romashkinskoe Oil Field, Mikrobiologiya, 2002, vol. 71, no. 6, pp. 849–857 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 71, no. 6, pp. 735–742].
Collins, M.D. and Widdel, F., Respiratory Quinones of Sulfate-Reducing and Sulfur-Reducing Bacteria: A Systematic Investigation, Syst. Appl. Microbiol., 1986, vol. 8, nos. 1–2, pp. 8–18.
Zhilina, T.N., Zavarzin, G.A., Rayney, F.A., et al., Desulfonatronovibrio hydrogenovorans gen. nov., sp. nov., an Alkaliphilic, Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1997, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 144–149.
Kuever, J., Rainey, F.A., and Widdel, F., Family Desulfohalobiaceae, Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed., vol. 2, part C, pp. 948–955, Garryty, G.M., Ed., New York: Springer, 2005.
Audiffrin, C., Cayol, J.-L., Joulian, C., et al., Desulfonauticus submarinus gen. nov., sp. nov., a Novel Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from a Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 53 C, pp. 1585–1590.
Brandt, K.K. and Ingvorsen, K., Desulfobacter halotolerance sp. nov., a Halotolerant Acetate-Oxidizing Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from Sediments of Great Salt Lake, Utah, Syst. Appl. Microbiol., 1997, vol. 20, pp. 366–373.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.V. Belyakova, E.P. Rozanova, I.A. Borzenkov, T. P. Tourova, M.A. Pusheva, A.M. Lysenko, T.V. Kolganova, 2006, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2006, Vol. 75, No. 2, pp. 201–211.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belyakova, E.V., Rozanova, E.P., Borzenkov, I.A. et al. The new facultatively chemolithoautotrophic, moderately halophilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovermiculus halophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from an oil field. Microbiology 75, 161–171 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261706020093
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261706020093