Abstract
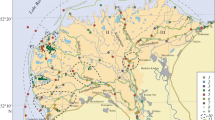
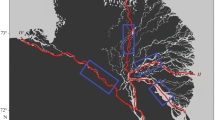
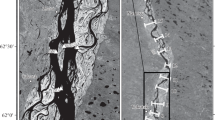
Adaptation of the technology of water turbidity simulation by satellite image data for the delta of the Selenga R., the largest Baikal tributary is given. The results of processing a series of 82 Landsat images are used to assess the seasonal variability of suspended sediment balance in the Selenga delta in period from 1989 up to the present time. It is shown that, at higher water discharges (>1500 m3/s), suspended material will accumulate in the delta (on the average 15% of the total sediment transport at the delta head), governed by material precipitation within inundated floodplain area and lakes in the lower part of the delta. At lower water discharges (<1500 m3/s), a longitudinal increase in suspended sediment transport may take place, caused by setups from Baikal side and channel erosion in the branches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alekseevskii, N.I., Formirovanie i dvizhenie rechnykh nanosov (Formatioin and Motion of River Sediments), Moscow: Geograf. fak. MGU, 1998.
Alekseevskii, N.I., Bezozerova, E.V., Kasimov, N.S., and Chalov, S.R, Spatial variability of suspended sediment transport characteristics in the Selenga Basin during rain floods, Vestn. Mosk. Univ., Ser. Geogr., 2013, no. 3, pp. 60–65.
Alekseevskii, N.I. and Chalov, S.R., Gidrologicheskie funktsii razvetvlennogo rusla (Hydrological Functions of a Branching Channel), Moscow: Geograf. fak. MGU, 2009.
Atlas “Deshifrirovanie mnogozonal’nykh aerokosmicheskikh snimkov. Metodika i rezul’taty” (Interpretation of Polyzonal Aerospace Photographs), Moscow: Nauka, 1982.
Il’icheva, E.I., Gagarinova, O.V., and Pavlov, M.V., Hydrologo-geomorphological analysis of landscape formation within the Selenga river delta, Geogr. Nat. Resour., 2015, no. 3, 263–270.
Korytnyi, L.M., Il’icheva, E.A., Pavlov, M.V., and Amosova, I.Yu., Hydrologo-morphological approach to regionalization of the Selenga River Basin, Geogr. Nat. Resour., 2012, no. 3, pp. 212–217.
Kravtsova, V.I. and Antonova, S.Yu., Applying polyzonal surveying to studying and mapping of shallows: case study of Northeastern Caspian Sea, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Geol. Razved., 1974, no. 1, pp. 78–88.
Labutina, I.A. and Saf’yanov, G.A., Studying sediment transport in rivers by aerospace images in the Kodor and Selenga, in Kosmicheskaya s"emka i tematicheskoe kartografirovanie (Space Surveying and Thematic Mapping), Moscow: Mock. Gos. Univ., 1980, pp. 118–125.
Labutina, I.A., Saf’yanov, G.A., and Sharlai, T.G, Studying Suspended Sediment Transport in Seas by Polyzonal Images, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1976, vol. 230, no. 2, pp. 861–864.
Lisitsyn, A.P, Marginal filter of oceans, Okeanologiya, 1994, vol. 34, no. 5, pp. 735–747.
Perel’man, A.I., Geokhimiya landshafta (Landscape Geochemistry), Moscow: Vyssh. shk, 1966.
Potemkina, T.G, Hydrological–morphological zoning of the mouth zone of the Selenga River, Water Resour., 2004, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 11–16.
Rossinskii, K.I. and Kuz’min, I.A., Balance method for calculating stream bed deformations, Tr. Gidroproekta (Transactions of Gidroproekt), vol. 12, 1964.
Chalov, S.R., Assessing river water turbidity by space images, Dvadtsat’ Chetvertoe plenarnoe mezhvuzovskoe koordinatsionnoe soveshchanie po probleme erozionnykh, ruslovykh i ust’evykh protsessov (Twenty Fourth Plenary Interuniversity Coordination Meeting on the Problem of Erosion, Channel, and Mouth Processes), Barnaul, 2009, pp. 218–220.
Chalov, S.R., Belozerova, E.V., and Gladkova, M.V., Monitoring surface water turbidity with the use of remote sensing methods, Resursy i kachestvo vod sushi: otsenka, prognoz i upravlenie (Resources and Quality of Continental Waters: Assessment, Prediction, and Management), Moscow: Inst. Vodn. Probl., Ross. Akad. Nauk, Geograf. Fak. MGU, 2012, pp. 260–273.
Carlson, P, Mapping surface current flow in turbid near-shore waters of the northeast Pasific, Geol. Surv. Profess., 1976, no. 929, pp. 328–329.
Chalov, S, Jarsjö, J., Kasimov, N., Romanchenko, A., Pietron, J., Thorslund, J., and Belozerova, E., Spatiotemporal variation of sediment transport in the Selenga River Basin, Mongolia and Russia, Environ. Earth Sci., 2015, vol. 73, no. 2, pp. 663–680.
Chalov, S., Thorslund, J., Kasimov, N.S., Nittrouer, J., Iliyecheva, E., Pavlov, M., Pietron, J., Shinkareva, G., Lychagin, M., Aybullatov, D., Kositsky, A., Tarasov, M., Akhtman, Y., Garmaev, E., Karthe, D., and Jarsjö, J, The Selenga River delta: a geochemical barrier protecting Lake Baikal waters, Regional Environ. Change, 2016, pp. 1–15.
Chavez, P.S., Image-based atmospheric correctionsrevisited and improved, Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 1996, vol. 62, no. 9, pp. 1025–1035.
Chen, Z., Muller-Karger, F., and Hu, C, Remote sensing of water clarity in Tampa Bay, Remote Sensing of Environ., 2007, vol. 109, no. 2, pp. 249–259.
Curran, P.J. and Novo, E.M.M, The relationship between suspended sediment concentration and remotely sensed spectral radiance: a review, J. Coastal Res., 1988, pp. 351–368.
Harmä, P., Vepsäläinen, J., Hannonen, T., Pyhälahti, T., Kämäri, J., Kallio, K., Eloheimo, K., and Koponen, S, Detection of water quality using simulated satellite data and semi-empirical algorithms in Finland, Sci. Total Environ., 2001, vol. 268, no. 1, pp. 107–121.
Heim, B., Oberhaensli, H., Fietz, S., and Kaufmann, H, Variation in Lake Baikal’s phytoplankton distribution and fluvial input assessed by SeaWiFS satellite data, Glob. Planet. Change, 2005, no. 46, pp. 9–27.
Hellweger, F.L., Schlosser, P., Lall, U., and Weissel, J.K, Use of satellite imagery for water quality studies in New York Harbor. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Sci., 2004, vol. 61, no. 3, pp. 437–448.
Lavender, S., NagurCherukuru R.C., and Doxaran D. High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing of the Plymouth Coastal Waters, CIMEL, 2001, vol. 2, pp. 438–442.
Nduaguba, D.C, Use of Landsat-1 standard data products for multispectral radiometric analysis of sedimentation in Kainji reservoir, Int. Sci.-Technol. Conf. Space, 1976, vol. 16, pp. 45–52.
Nutchanart, S., Surakit, K., and Thianpopirug, S, Influence of atmospheric correction and number of sampling points on the accuracy of water clarity assessment using remote sensing application, J. Hydrol., 2011, vol. 401, nos. 3–4, pp. 203–220.
Pavelsky, T.M. and Smith, L.C, Remote sensing of suspended sediment concentration, flow velocity and lake recharge in the Peace-Athabaska delta. Canada, Water Resour. Res., 2009, no. 45, pp. 110–126.
Ruddick, K., Nechad, B., Neukermans, G., Park, Y., Doxaran, D., Sirjacobs, D., and Beckers, J.M, Remote sensing of suspended particulate matter in turbid waters: state of the art and future perspectives, in Proc. Ocean Optics XIX Conf. Barga, 2008, pp. 6–10.
Sawaya, K.E., Olmanson, L.G., Heinert, N.J., Brezonik, P.L., and Bauer, M.E, Extending satellite remote sensing to local scales: land and water resource monitoring using high-resolution imagery, Remote Sensing of Environ, 2003, vol. 88, no. 1, pp. 144–156.
Wang, J.J., Lu, X.X., Liew, S.C., and Zhou, Y, Retrieval of suspended sediment concentrations in large turbid rivers using Landsat ETM+: An example from the Yangtze River, China, Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2009, vol. 34, no. 8, pp. 1082–1092.
Zhou, W., Wang, S., Zhou, Y., and Troy, A, Mapping the concentrations of total suspended matter in Lake Taihu, China, using Landsat-5 TM data, Int. J. Remote Sensing, 2006, vol. 27, no. 6, pp. 1177–1191.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.R. Chalov, V.O. Bazilova, M.K. Tarasov, 2017, published in Vodnye Resursy, 2017, Vol. 44, No. 3, pp. 332–339.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chalov, S.R., Bazilova, V.O. & Tarasov, M.K. Suspended sediment balance in Selenga delta at the late XX–early XXI century: Simulation by LANDSAT satellite images. Water Resour 44, 463–470 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807817030071
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807817030071