Abstract
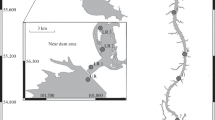
The structure of phytoplankton of the Sea of Japan (Peter the Great Bay), located in the zone influenced by the technical ecosystem of Vladivostok thermal electric power station (VTES-2) (Vladivostok), has been studied throughout the year in the period 2014‒2015. Thermal pollution is two-stage: in the water intake trough, the water temperature rises by 2–3°C compared to background values; directly in the VTES-2 cooling system, by 10–12°C. In the first case, an increase compared to background (reference) areas in the abundance of algae and an extension of the summer–autumn vegetation season of phytoplankton by 1.5–2.0 months were noted. After passing through the cooling system of the power plant, the species composition of phytoplankton changes insignificantly (similarity coefficient value 0.82), but is enriching in benthic diatoms (22 species) from the biofouling of the intake trough. The difference in the values of indices of the total density and biomass of microalgae before and after passing through the cooling system of the power plant during the year did not exceed one order of magnitude. The study revealed that the VTES-2 technical ecosystem significantly affects the quantitative change in phytoplankton at the stage of long-term, but insignificant, thermal effect in the water intake trough, as well as during short-term passage through the cooling system.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Begun, A.A., Phytoplankton of the Zolotoy Rog Cove and the Ussuri Bay (Sea of Japan) in the conditions of anthropogenic pollution, Izv. Tikhook. Inst. Rybn. Khoz. Okeanogr., 2004, vol. 138, pp. 330–344.
Begun, A.A., Orlova, T.Yu., and Zvyagintsev, A.Yu., Phytoplankton of the Amur Bay of the Sea of Japan in the region of Vladivostok City, Algologiya, 2003, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 204–215.
Begun, A.A., Zvyagintsev, A.Yu., and Emel’yanov, A.A., Microalgae od periphyton in the conditions of aquarium complex of FEB RAS (Vladivostok City, Russkii Island), Voda: Khimiya i ekologiya, 2016, no. 3, pp. 42–52.
Belan, T. A., Specific features of abundance and species composition of benthos in the conditions of pollution: Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol) Dissertation, Vladivostok: DVNIGMI, 2001.
Belogurova, L.S. and Zvyagintsev, A.Yu., Dynamics of meio- and macrofauna of fouling in the conditions of chronic anthropogenic pollution (Zolotoy Rog Cove, Seas of Japan), Izv. Tikhook. Inst. Rybn. Khoz. Okeanogr., 2006, vol. 144, pp. 331–350.
Vinokurova, T.T., On the seasonal and short-periodic variability of hydrological characteristics in the Peter the Great Bay, Izv. Tikhook. Inst. Rybn. Khoz. Okeanogr., 1977, vol. 101, pp. 7–12.
Zvyagintsev, A.Yu. and Moshchenko, A.V., Morskie tekhnoekosistemy energeticheskikh stantsii (Marine techno-ecosystems of energetic stations), Vladivostok: Dal’nauka, 2010.
Zvyagintsev, A.Yu., Ivin, V.V., Kashin, I.A., et al., Alien species in the Far-Eastern marine state biosphere reserve, Izv. Tikhook. Inst. Rybn. Khoz. Okeanogr., 2012, vol. 170, pp. 60–81.
Koryakova, M.D., Nikitin, V.M., Zvyagintsev, A. Yu., and Belogurova, L. S., Influence of polluted harbor waters on fouling and corrosion of high alloy steel, Biol. Morya, 2002, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 138–142.
Mileikovskii, S.A., Influence of passing through the system of water colling of coastal electric power stations of industrial enterprises on the reproduction and productivity of marine and estuarine plankton, benthos and nekton, in Obrastanie i biokorroziya v vodnoi srede (Fouling and biocorrosion in aquatic environment), Moscow: Nauka, 1981, pp. 131–137.
Mokievskaya, V.V., Chemical characteristics of water masses, in Osnovnye cherty geologii i gidrologii Yaponskogo morya (Main features of geology and hydrology of the Sea of Japan), Moscow, 1961, part 2, pp. 122–125.
Morozova, T.V., Selina, M.S., and Orlova, T.Yu., Phytoplankton in the region of mariculture farm in the Minonosok Cove of the Sea of Japan Posyet Bay, Biol. Morya, 2002, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 107–112.
Novoselova, T.N. and Protasov, A.A., Phytoplankton of cooling waterbodies of the techno-ecosystems of nuclear and heating power electric stations (Review), Gidrobiol. Zh., 2014, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 40–59.
Ogorodnikova, A.A., Ekologo-ekonomicheskaya otsenka vozdeistviya beregovykh istochnikov zagryazneniya na prirodnuyu sredu i bioresursy zaliva Petra Velikogo (Ecological-economical assessment of the effect of coastal sources of pollution on the environment nad biological resources of the Peter the Great Bay), Vladivostok: TINRO, 2001.
Protasov, A.A., Silaeva, A.A., Yarmoshenko, L.P., et al., Hydrobiological studies of the techno-ecosystem of the Zaporozhskaya nuclear power station, Gidrobiol. Zh., 2013, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 78–94.
Ryabushko, L.I. and Begun, A.A., Diatomovye Vodorosli mikrofitobentosa Yaponskogo morya. T. 1. (Diatom algae of microphytobenthos of the Sea of Japan. V. 1.): Sevastopol’; Simferopol’ N. Orianda, 2015, vol. 288.
Stonik, I.V. and Orlova, T.Yu., Summer–autumn phytoplankton in the Amur Bay of the Sea of Japan, Biol. Morya, 1998, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 205–211.
Shevchenko, O.G., Ponomareva, A.A., and Maslenikov, S.I., Monitoring of the phytoplankton on the area of mariculture farm in the Rifovaya Cove (Peter the Great Bay of the Sea of Japan), Voprosy Rybolovstva, 2014, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 285–294.
Choi, K.H., Kim, Y.O., Lee, J. B., et al., Thermal impacts of a coal power plant on the plankton in an open coastal water environment, J. Mar. Sci. Technol, 2012, vol. 20, pp. 187–194.
Degerlund, M. and Eilertsen, H.C., Main species characteristics of phytoplankton spring blooms in the Atlantic and Arctic waters (68°–80° N), Estuaries and Coasts, 2010, vol. 33, pp. 242–269.
Du, G.Y., Son, M., Yun, M., et al., Microphytobenthic biomass and species composition in intertidal flats of the Nakdong River estuary, Korea, Estuarine, Coastal Shelf Sci, 2009, vol. 82, pp. 663–672.
Guiry, M.D. and Guiry, G.M., http://www.algaebase.org. (data of enquiry: 12.02.2019)
Identifying of marine phytoplankton / Ed. Tomas C.R. St.-Petersburg, USA: Academic Press, 1997. 858 p.
Jiang, Z.B., Zeng, J.N., Chen, Q.Z., et al., Dynamic change of phytoplankton cell density after thermal shock and chlorination in a subtropical bay in china, J. Plant Ecol, 2008, vol. 32, pp. 1386–1396.
Kasim, M. and Mukai, H., Contribution of benthic and epiphytic diatoms to clam and oyster production in the Akkeshi-Ko estuary, J. Oceanogr, 2006, vol. 62, pp. 267–281.
Lee, C.W., The effect of thermal effluent on marine diatoms and bacteria, Malaysian J. Sci, 2003, vol. 22, pp. 23–27.
Lee, S.D., Yun, S.M., Park, J.S., and Lee, J.H., Floristic survey of diatom in the three islands (Baeknyeong, Daecheong, Socheong) from Yellow Sea of Korea, J. Ecol. Environ, 2015.
Liu, S., Huang, H., Huang, L.M., et al., Ecological response of phytoplankton to the operation of Daya Bay nuclear power station, Chinese J. Mar. Environ. Sci, 2006, vol. 25, pp. 9–12.
Liu, J.Y., Checklist of biota of Chinese seas, Beijing: Sci. Press, Acad. Sinica, 2008, p. 1267.
Lo, W.T., Hwang, J.J., Hsu, P.K., et al., Seasonal and spatial distribution of phytoplankton in the waters off nuclear power plants, north of Taiwan, J. Mar. Sci. Technol, 2004, vol. 12, pp. 372–379.
Ma, Z.L., Gao, K.S., Li, W., et al., Impacts of chlorination and heat shocks on growth, pigments and photosynthesis of Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Bacillariophyceae), J. Experimental Mar. Biol. Ecol, 2011, vol. 397, pp. 214–219.
Maestini, S.Y., Robert, J.-M., and Fruguet, A., Simultaneous uptake of ammonium and nitrate by oyster-pond algae, Marin. Biol. Lett, 1982, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 143–153.
Moorthi, S., Caron, D.A., Gast, R.J., and Sanders, R.W., Mixotrophy: a widespread and important ecological strategy for planktonic and sea-ice nanoflagellates in the ross sea, antarctica, Aquatic Microbial Ecol, 2009, vol. 54, pp. 269–277.
Mitra, A., Flynn, K.J., Burkholder, M., et al., The role of mixotrophic protists in the biological carbon pump, Biogeosci, 2014, vol. 11, pp. 995–1005.
Park, J., Khim, J.S., Ohtsuka, T., et al., Diatom assemblages on Nanaura mudflat, Ariake Sea, Japan: with reference to the biogeography of marine benthic diatoms in Northeast Asia, Botanical Studies, 2012, vol. 53, pp. 105–124.
Poornima, E.H., Rajaduraia, M., Rao, T.S., et al., Impact of thermal discharge from a tropical coastal power plant on phytoplankton, J. Thermal Biol, 2005, vol. 30, pp. 307–316.
Rajadurai, M., Poornima, E.H., Narasimhanb, S.V., et al., Phytoplankton growth under temperature stress: laboratory studies using two diatoms from a tropical coastal power station site, J. Thermal Biol, 2005, vol. 30, pp. 299–305.
Saravanane, N., Satpathy, K.K., Nair, K.V.K., and Durairaj, G., Preliminary observations on the recovery of tropical phytoplankton after entrainment, J. Thermal Biol, 1998, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 91–97.
Shevchenko, O.G., Shulkin, V.M., and Ponomareva, A.A., Phytoplankton and hydrochemical parameters near net pens with beluga whales in a shallow bay of the northwestern Sea of Japan, Thalassas: An Int. J. Mar. Sci, 2017.
Skaloud, P., Rezacova, M., and Ellegaard, M., Spatial distribution of phytoplankton in spring 2004 along a transect in the eastern part of the North Sea, J. Oceanography, 2006, vol. 62, pp. 717–729.
Stonik, I.V. and Orlova, T.Yu., Phytoplankton of the coastal waters off Vladivostok City (the north-western part of the East Sea) under eutrophic conditions, Ocean and Polar Res, 2002, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 359–365.
Sun, J. and Liu, D., Geometric models for calculating cell biovolume and surface area for phytoplankton, J. Plankton Res, 2003, no. 25, pp. 1331–1346.
Zhao, L., Sun, J., Gao, Y., et al., Hippodonia fujiannensis sp. nov. (Bacilariophyceae), a new epipsammic diatom from the low intertidal zone, Fujian Province, China, Phytotaxa, 2017, vol. 295, no. 1, pp. 77–85.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to the staff of the Resource Collection of the Center of Collective Use “Marine Biobank” of the Far Eastern branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, that maintains the cultures of microalgae.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Begun, A.A., Maslennikov, S.I. Influence of the Technical Ecosystem of the Electric Power Plant (Vladivostok) on the Phytoplankton of the Japanese Sea. Water Resour 48, 404–412 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807821030052
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807821030052