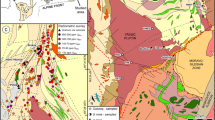
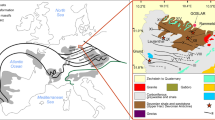
Abstract
Complex (δ18O, δ13C, 87Sr/86Sr, 143Nd/144Nd, and REE composition) data were obtained on quartz-carbonate veins in metasedimentary rocks to elucidate the material sources and to evaluate fluid regime during low-sulfide gold-quartz ore mineralization at the Sukhoi Log deposit. In order to use an oxygen isotopic thermometry for quartz veins, we calibrated empirical dependence of fractionation factors between vein quartz and altered wall rocks. The temperature range of quartz equilibration with wall rocks was evaluated at 380–190°C. Independent temperatures obtained using this thermometer indicate that the vein ankerite can be both earlier and later than vein quartz. The isotopic systematics (δ13C and δ18O) of ankerite in the quartz-carbonate veins, carbonates in the ore-hosting shales of the Khomolkho and Imnyakh formations both within and outside mineralized zones at the deposit indicate that the ore-hosting rocks and veins in the mineralized zone contain incoming carbonate, which was most probably borrowed from the carbonate rocks of the Imnyakh Formation. REE composition of vein ankerite shows that these elements were transported by fluid as carbonate complexes. The behavior of the Eu/Eu* and (La/Yb)n ratios and Mn of the vein ankerite suggest that during carbonate crystallization the system was closed with respect to fluid. Sr-Nd isotope systematics indicates that the isotopic parameters of the vein ankerite were formed with the participation of metasedimentary host rocks of both the Imnyakh and Khomolkho formations, which are contrastingly different in Nd isotopic composition. A fluid/rock ratio during metasomatic processes in the wall rocks was calculated for two scenarios of their thermal history: with a continuously operating heat source beneath the Sukhoi Log structure and with a linear cooling of the structure. The effective integral W/R ratios calculated lie within the range of 0.046–0.226 and suggest that the veins were produced with the metamorphic fluid. Low W/R ratios are inconsistent with the mechanism of vein quartz crystallization due to fluid oversaturation with respect to SiO2 at decreasing temperature. We believe that the main mechanism responsible for the origin of these veins was variations of fluid oversaturation due to pressure variations (pressure solution mechanism). This hypothesis is consistent with the reported isotopic-geochemical characteristics of the wall rocks at the Sukhoi Log deposit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ague, J.J., Fluid flow in the deep crust, in The Crust. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, vol. 3, pp. 195–228.
Bau, M. and Moller, P., Rare-earth element fractionation in metamorphogenic hydrothermal calcite, magnesite and siderite, Mineral. Petrol, 1992, vol. 45, pp. 231–246.
Baumgartner, L.P. and Valley, J.W., Stable isotope transport and contact metamorphic fluid flow, in Stable Isotope Geochemistry, Valley, J.W. and Cole, D.R., Eds., Rev. Mineral. Geochem, 2001, vol. 43, pp. 415–468.
Bottinga, Y., Calculated fractionation factors for carbon and hydrogen isotope exchange in the system calcite-CO2-graphite-methane-hydrogen and water vapor, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1969, vol. 33, pp. 49–64.
Boynton, W.V., Geochemistry of rare earth elements: meteorite studies, in Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984, pp. 63–114.
Buryak, V.A. and Khmelevskaya, N.M., Sukhoi Logodno iz krupneishikh zolotorudnykh mestorozhdenii mira (genezis, zakonomernosti razmeshcheniya orudeneniya, kriterii prognozirovaniya) (Sukhoi Log—One of the World’s Largest Gold Deposits: Genesis, Ore Distribution Patterns, and Forecasting Criteria), Vladivostok: Dal’nauka, 1997.
Buryak, V.A., Metamorfizm i rudoobrazovanie (Metamorphism and Ore-Forming Processes), Moscow: Nedra, 1982.
Cartwright, I. and Oliver, N.H.S., Metamorphic fluids and their relationship to the formation of metamorphosed and metamorphogenic ore deposits, in Metamorphosed and Metamorphogenic Ore Deposits, Spry P., Marshal B., and Vokes, F. M., Eds., Econ. Geol., 2000, vol. 11, pp. 81–96.
Chacko, T., Cole, D.R., and Horita, J., Equilibrium oxygen,hydrogen and carbon isotope fractionation factors applicable to geological systems, in Stable Isotope Geochemistry, Valley, J.W. and Cole, D.R., Eds., Rev. Mineral. Geochem, 2001, vol. 43, pp. 1–81.
Chang, Z., Large, R.R., and Maslennikov, V., Sulfur isotopes in sediment-hosted orogenic gold deposits: evidence for an early timing and a seawater sulfur source, Geology, 2008, vol. 38, pp. 971–974.
Chernyshev, I.V., Chugaev, A.V., Safonov, Yu.G., et al., Lead isotopic composition from data of high-precession MC-ICP-MS and sources of matter in the large-scale Sukhoi Log noble metal deposit, Russia, Geol. Ore Dep., 2009, vol. 51, no. 6, pp. 496–504.
Chumakov, N.M., Semikhatov, M.A., and Sergeev, V.N., Vendian reference section of Southern Middle Siberia, Stratigr. Geol. Correlation, 2013, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 359–382.
Clayton, R.N., O’Neil, J.R., and Mayeda, T.K., Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water, J. Geophys. Res., 1972, vol. 77, pp. 3057–3067.
Criss, R.E. and Taylor, H.P., Stable isotope geochemistry of metamorphic rocks, in Stable Isotopes in High Temperature Geological Processes, Valley, J.W., Taylor, H.P., and O’Neil, J.R., Eds., Rev. Mineral. Geochem., 1986, vol. 16, pp. 373–424.
Diskin, S., Evans, J., Fowler, M.B., and Guion, P.D., Recognising different sediment provenances within a passive margin setting: towards characterising a sediment source to the west of the British Late Carboniferous sedimentary basins, Chem. Geol., 2011, vol. 283, pp. 143–160.
Distler, V.V., Yudovskaya, M.A., Mitrofanov, G.L., et al., Geology, composition, and genesis of the Sukhoi Log noble metals deposit, Russia, Ore Geol. Rev., 2004, vol. 24, pp. 7–44.
Doerffel, K., Statistik in der Analytischen Chemie Leipzig: VEN Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, 1987.
Dubinin, A.V., Geochemistry of Rare-Earth Elements in the Ocean, Moscow: Nauka, 2006.
Dubinina, E.O., Ikonnikova, T.A., and Chugaev, A.V., Heterogeneity of the sulfur isotopic composition of pyrite at the Sukhoi Log deposit and its controlling factors, Dokl. Earth Sci., 2010, vol. 435, no. 6, pp. 1665–1669.
Fisher, D.M. and Brantley, S.L., Models of quartz overgrowth and vein formation: deformation and episodic fluid flow in an ancient subduction zone, J. Geophys. Res., 1992, vol. 97, pp. 20043–20061.
Gregory, R.T., Criss, R.E., and Taylor, H.P., Oxygen isotope exchange kinetics of mineral pairs in closed and open systems: applications to problems of hydrothermal alteration of igneous rocks and Precambrian iron formations, Chem. Geol., 1989, vol. 75, pp. 1–42.
Hu, G.X. and Clayton, R.N., Oxygen isotope salt effects at high pressure and high temperature and the calibration of oxygen isotope geothermometers, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2003, vol. 67, pp. 3227–3246.
Ikonnikova, T.A., Dubinina, E.O., Saroyan, M.R., and Chugaev, A.V., Oxygen isotopic composition of quartz veins and host rocks at the Sukhoi Log Deposit, Russia, Geol. Ore Dep., 2009, vol. 51, no. 6, pp. 505–5011.
Ivanov, A.I., Lifshits, V.I., Perevalov, O.V., et al., Dokembrii Patomskogo nagor’ya (Precambrian of the Patom Highland), Moscow: Nedra, 1995.
Karpenko, I.A., Migachev, I.F., Mikhailov, B.K., and Petrash, N.G., Modern geological-economic assessment of the Sukhoi Log deposit, Rudy Met., 2006, no. 2, pp. 22–27.
Kirschner, D.L., Sharp, Z.D., and Masson, H., Oxygen isotope thermometry of quartz-calcite veins: unraveling the thermal-tectonic history of the subgreenschist facies Morcles nappe (Swiss Alps), Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 1995, vol. 107, pp. 1145–1156.
Korikovsky, S.P. and Fedorovsky, V.S., Rannii dokembrii Patomskogo nagor’ya (Early Precambrian of the Patom Highland), Moscow: Nauka, 1980.
Korol’kov, A.T., Geodinamika zolotorudnykh raionov yuga Vostochnoi Sibiri (Geodynamics of Gold Districts of the Southern East Siberia), Irkutsk: IGU, 2007.
Kryazhev, S.G., Ustinov, V.I., and Grinenko, V.A., Fluid regime at the Sukhoi Log gold deposit: isotopic evidence, Geochem. Int., 2009, vol. 47, no. 10, pp. 1041–1051.
Large, R.R., Maslennikov, V.V., Robert, F., et al., Multistage sedimentary and metamorphic origin of pyrite and gold in the giant Sukhoi Log deposit, Lena gold province, Russia, Econ. Geol., 2007, vol. 102, pp. 1233–1267.
Laverov, N.P., Chernyshev, I.V., Chugaev, A.V., et al., Formation stages of the large-scale noble metal mineralization in the Sukhoi Log Deposit, East Siberia: results of isotopegeochronological study, Dokl. Earth Sci., 2007, vol. 415, no. 2, pp. 810–814.
Luo, Yu-R. and Byrne, R.H., Carbonate complexation of yttrium and rare earth elements in natural waters, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2004, vol. 68, pp. 691–699.
Mook, W.G., Bommerson, J.C., and Staverman, W.H., Carbon isotope fractionation between dissolved bicarbonate and gaseous carbon dioxide, Earth Planet Sci. Lett, 1974, vol. 22, pp. 169–176.
Newton, R.C. and Manning, C.E., Quartz solubility in H2O-NaCl and H2O-CO2 solutions at deep crust-upper mantle pressures and temperatures: 2–15 kbar and 500–900°C, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2000, vol. 64, pp. 2993–3005.
Nothdurft, L.D., Webb, G.E., and Kamber, B.S., Rare earth element geochemistry of Late Devonian reefal carbonates, Canning Basin, Western Australia: confirmation of a seawater REE proxy in ancient limestones, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2004, vol. 68, no. 2, pp. 263–283.
Ohta, A. and Kawabe, I., Rare earth element partitioning between Fe oxyhydroxide precipitates and aqueous NaCl solutions doped with NaHCO3: determinations of rare earth element complexation constants with carbonate ions, Geochem. J., 2000, vol. 34, pp. 439–454.
Pek, A.A., Malkovsky, V.I., and Safonov, Yu.G., Deposition of finely disseminated gold mineralization in black shales: a hypothesis of microstructural control, Geol. Ore Dep., 2011, vol. 53, no. 3, pp. 221–235.
Pokrovskii, B.G., Melezhik, V.A., and Bujakaite, M.I., Carbon, oxygen, strontium, and sulfur isotopic compositions in Late Precambrian rocks of the Patom Complex, Central Siberia: Communication 1. Results, isotope stratigraphy, and dating problems, Lithol. Miner. Resour., 2006, vol. 41, no. 5, pp. 450–474.
Ramsay, J.G., The crack-seal mechanism of rock deformation, Nature, 1980, vol. 284, pp. 135–140.
Razvozzhaeva, E.A., Prokof’ev, V.Yu., Spiridonov, A.M., et al., Precious metals and carbonaceous substance in ores of the Sukhoi Log deposit (Eastern Siberia, Russia), Geol. Ore Dep., 2002, vol. 44, no. 2, pp. 103–110.
Richards, I.J., Connelly, J.B., Gregory, R.T., and Gray, D.R., The importance of diffusion, advection, and host-rock lithology on vein formation: a stable isotope study from the Paleozoic Ouachita orogenic belt, Arkansas and Oklahoma, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 2002, vol. 114, pp. 1343–1355.
Rosenbaum, J. and Sheppard, S.M.F., An isotopic study of siderites, dolomites and ankerites at high temperatures, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1986, vol. 50, pp. 1147–1150.
Rusinov, V.L., Rusinova, O.V., Kryazhev, S.G., et al., Wallrock metasomatism of carbonaceous terrigenous rocks in the Lena gold district, Geol. Ore Dep., 2008, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 1–40.
Sharp, Z.D., A laser-based microanalytical method for the in-situ determination of oxygen isotope ratios of silicates and oxides, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1990, vol. 54, pp. 1353–1357.
Sharp, Z.D., Masson, H., and Luccini, R., Stable isotope geochemistry and formation mechanisms of quartz veins, extreme paleoaltitudes of the central Alps in the Neogene, Am. J. Sci., 2005, vol. 305, pp. 187–219.
Spicuzza, M.J., Valley, J.W., Kohn, M.J., et al., The rapid heating, defocused beam technique: a CO2-laser-based method for highly precise and accurate determination of 18O values of quartz, Chem. Geol., 1998, vol. 144, pp. 195–203.
Strauss, H., Geological evolution from isotope proxy signals-sulfur, Chem. Geol., 1999, vol. 161, pp. 89–101.
Tada, R. and Siever, R., Pressure solution during diagenesis, Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., 1989, vol. 17, pp. 89–118.
Ustinov, V.I., Grinenko, V.A., and Kryazhev, S.G., Physicochemical conditions of metamorphogenic ore formation in the Lena gold district, Vestn. Otd. Nauk Zemle RAN, 2007, no. 1.
Ustinov, V.I., Principles and methods of study of isotope disequilibrium of mineral assemblages, Extended Abstract of Doctoral (Chem) Dissertation, Moscow, 1991.
Uysal, I.T., Zhao, J.X., Golding, S.D., Lawrence, M.G., Glikson, M., and Collerson, K.D., Sm-Nd dating and rare-earth element tracing of calcite: implications for fluid-flow events in the Bowen Basin, Australia, Chem. Geol., 2007, vol. 238, pp. 63–71.
Valley, J.W., Kitchen, N., Kohn, M.J., et al., UWG-2, a garnet standard for oxygen isotope ratios: strategies for high precision and accuracy with laser heating, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1995, vol. 59, pp. 5223–5231.
Wangen, M. and Munz, I.A., Formation of quartz veins by local dissolution and transport of silica, Chem. Geol., 2004, vol. 209, pp. 179–192.
Wood, B.J. and Walther, J.V., Fluid flow during metamorphism and its implications for fluid-rock ratios, in Fluid-Rock Interactions during Metamorphism, New York: Springer-Verlag, 1986, pp. 91–108.
Wood, B.L. and Popov, N.P., The giant Sukhoi Log gold deposit, Siberia Russ. Geol. Geophys., 2006, vol. 47, no. 3, pp. 317–341.
Wood, S.A., The aqueous geochemistry of rare earth elements and yttrium, Chem. Geol., 1990, vol. 82, pp. 159–186.
Yang, X.S., Pressure solution in sedimentary basins: effect of temperature gradient, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2000, vol. 176, pp. 233–243.
Yardley, B.W.D., On some quartz-plagioclase veins in the Connemara schists, Geol. Mag., 1975, vol. 112, pp. 183–190.
Yudovskaya, M.A., Distler, V.V., Rodionov, N.V., et al., Relationship between metamorphism and ore formation at the Sukhoi Log gold deposit hosted in black slates from the data of U-Th-Pb isotopic SHRIMP-dating of accessory minerals, Geol. Ore Dep., 2011, vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 27–57.
Zheng, Y.-F., Calculation of oxygen isotope fractionation in anhydrous silicate minerals, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1993, vol. 57, pp. 1079–1091.
Zheng, Y.-F., On the theoretical calculations of oxygen isotope fractionation factors for carbonate-water systems, Geochem. J., 2011, vol. 45, pp. 341–354.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.O. Dubinina, A.V. Chugaev, T.A. Ikonnikova, A.S. Avdeenko, A.I. Yakushev, 2014, published in Petrologiya, 2014, Vol. 22, No. 4, pp. 347–379.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubinina, E.O., Chugaev, A.V., Ikonnikova, T.A. et al. Sources and fluid regime of quartz-carbonate veins at the Sukhoi Log gold deposit, Baikal-Patom Highland. Petrology 22, 329–358 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869591114040031
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869591114040031