Abstract
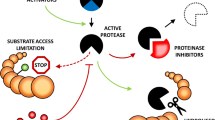
This review considers the main groups of hydrolytic enzymes associated with plant pathogens, as well as proteinaceous inhibitors of these enzymes, acting as the components of plant defense system. The role of hydrolases is described in the development of a pathological process in plant tissues. Significance of hydrolase inhibitors in the development of plant resistance to pathogens is analyzed. It is proposed that specific interactions in the “host plant–pathogen” system, involving hydrolytic enzymes and their proteinaceous inhibitors, depend on the nutritional specialization of fungi.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAI:
-
knottin-like inhibitors of α-amylases
- BFI:
-
bifunctional inhibitors
- CM-proteins:
-
chloroform–methanol proteins
- ISR:
-
induced systemic resistance
- JA:
-
jasmonic acid
- LRR:
-
leucine-rich repeats
- PG:
-
polygalacturonase
- PGIP:
-
polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins
- SA:
-
salicylic acid
- SAR:
-
acquired resistance
- SBBI:
-
soybean-derived Bowman–Birk inhibitor
- SBTI:
-
soybean trypsin inhibitor
References
Protsenko, M.A., Bulantseva, E.A., and Korableva, N.P., Polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins in plant fleshy fruits during their ripening and infections, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2010, vol. 57, pp. 356–362.
Kudryavtseva, N.N., Sof’in, A.V., Revina, T.A., Gvozdeva, E.L., Ievleva, E.V., and Valueva, T.A., Secretion of proteolytic enzymes by three phytopathogenic microorganisms, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 49, pp. 514–520.
Silva, T.M., Damasio, A.R., Maller, A., Michelin, M., Squina, F.M., Jorge, J.A., and Polizeli M. de L., Purification, partial characterization, and covalent immobilization- stabilization of an extracellular a-amylase from Aspergillus niveus, Folia Microbiol., 2013, vol. 58, pp. 495–502.
Mosolov, V.V. and Valueva, T.A., Participation of proteolytic enzymes in the interaction of plants with phytopathogenic microorganisms, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2006, vol. 71, pp. 838–845.
Revina, T.A., Kladnitskaya, G.V., Gerasimova, N.G., Gvozdeva, E.L., and Valueva, T.A., Protein trypsin inhibitor from potato tubers, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2010, vol. 75, pp. 36–40.
Kalve, N.D., Lomate, P.R., and Hivrale, V.K., A proteinaceous thermo labile a-amylase inhibitor from Albizia lebbeck with inhibitory potential toward insect amylases, Arthropod Plant Interact., 2012, vol. 6, pp. 213–220.
Valencia-Jimenez, A., Arboleda, V., and Grossi de Se, M.F., Activity of a-amylase inhibitors from Phaseolus coccineus on digestive a-amylases of the coffee berry borer, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2008, vol. 56, pp. 2315–2320.
Gatehouse, J.A., Prospects for using proteinase inhibitors to protect transgenic plants against attack by herbivorous insects, Curr. Protein Pept. Sci., 2011, vol. 12, pp. 409–416.
Dunaevskii, Ya.E., Matveeva, A.R., Fatkhullina, G.N., Belyakova, G.A., Kolomiets, T.M., Kovalenko, E.D., and Belozerskii, M.A., Extracellular proteases of mycelial fungi as participants of pathogenic processes, Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem., 2008, vol. 34, pp. 286–289.
Protsenko, M.A., Buza, N.L., Krinitsina, A.A., Bulantseva, E.A., and Korableva, N.P., Polygalacturonase- inhibiting protein is a structural component of plant cell wall, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2008, vol. 73, pp. 1053–1062.
Arunachalam, C. and Asha, S., Pectinolytic enzyme–a review of new studies, Adv. Biotech. J. Online, 2010, vol. 9, pp. 1–5. http://wwwadvancedbiotechin/online
Van den Brink, J. and de Vries, R., Fungal enzyme sets for plant polysaccharide degradation, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 91, pp. 1477–1492.
Sinitsyna, O.A., Fedorova, E.A., Semenova, M.V., Gusanov, A.V., Sokolova, L.M., Bubnova, T.M., and Okunev, O.N., Isolation and characterization of extracellular pectin lyase from Penicillium canescens, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2007, vol. 72, pp. 565–571.
Federici, L., di Matteo, A., Fernandez-Recio, J., Tsernoglou, D., and Cervone, F., Polygalacturonase inhibiting proteins: players in plant innate immunity? Trends Plant Sci., 2006, vol. 11, pp. 65–70.
Niture, K., Comparative biochemical and structural characterizations of fungal polygalacturonases, Biologia, 2008, vol. 63, pp. 1–19.
Maulik, A., Ghosh, H., and Basu, S., Comparative study of protein–protein interaction observed in polygalacturonase- inhibiting proteins from Phaseolus vulgaris and Glycine max and polygalacturonase from Fusarium moniliforme, BMC Genomics, 2009, vol. 10, pp. 1–12.
Kars, I. and van Kan, J.A.L., Extracellular enzymes and metabolites involved in pathogenesis of Botrytis, in Botrytis: Biology, Pathology and Control, Elad, Y., Williamson, B., Tudzynski, P., and Delen, N., Eds., Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer-Verlag, 2007, pp. 99–118.
Basaran, P., Ozcan, M., Denisov, Y., and Freeman, S., Elucidation of pectinolytic enzyme activities of a nonpathogenic watermelon pathogen mutant, Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum m87, Aust. Plant Pathol., 2007, vol. 36, pp. 135–141.
Manjurul Md., Haque, Md. and Tsuyumu, S., Virulence, resistance to magainin II,and expression of pectate lyase are controlled by the PhoP-PhoQ two-component regulatory system responding to pH and magnesium in Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937, J. Gen. Plant Pathol., 2005, vol. 71, pp. 47–50.
Payasi, A., Sanwal, R., and Sanwal, G.G., Microbial pectate lyases: characterization and enzymological properties, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2009, vol. 25, pp. 1–14.
Creze, C., Castang, S., Derivery, E., and Haser, R., The crystal structure of pectate lyase Pell from soft rot pathogen Erwinia chrysanthemi in complex with its substrate, J. Biol. Chem., 2008, vol. 283, pp. 18260–18268.
Mohidul, M., Vivek, K., and Hyun K., Baek, K., Production of a major stilbene phytoalexin, resveratrol in peanut (Arachis hypogaea) and peanut products: a mini review, Environ. Sci. Biotechnol., 2013, vol. 12, pp. 209–221.
Mosolov, V.V. and Valueva, T.A., Proteinase inhibitors and their function in plants: a review, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 41, pp. 227–246.
Kreslavski, V.D., Los, D.A., Allakhverdiev, S.I., and Kuznetsov, Vl.V., Signaling role of reactive oxygen species in plants under stress, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2012, vol. 59, pp. 141–154.
Ferrari, S., Savatin, D.V., Sicilia, F., Gramegna, G., Cervone, F., and Lorenzo, G., Oligogalacturonides: plant damage-associated molecular patterns and regulators of growth and development, Front. Plant Sci., 2013, vol. 4, no. 49, doi doi 10.3389/fpls.2013.00049
Vu, B.V., Itoh, K., Nguyen, Q.B., Tosa, Y., and Nakayashiki, H., Cellulases belonging to glycoside hydrolase families 6 and 7 contribute to the virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae, Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact., 2012, vol. 25, pp. 1135–1141.
Zhang, J., Bruton, B.D., and Biles, C.L., Cell walldegrading enzymes of Didymella bryoniae in relation to fungal growth and virulence in cantaloupe fruit, Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2014, vol. 139, pp. 749–761.
Baldrian, P., Voriskova, J., Dobiasova, P., Merhautova, V., Lisa, L., and Valaskova, V., Production of extracellular enzymes and degradation of biopolymers by saprotrophic microfungi from the upper layers of forest soil, Plant Sci., 2011, vol. 338, pp. 111–125.
Yan, S. and Wu, G., Secretory pathway of cellulase: a mini-review, Biotechnol. Biofuels, 2013, vol. 6, no. 177, doi 10.1186/1754-6834-6-177
King, B.C., Waxman, K.D., Nenni, N.V., Walker, L.P., Bergstrom, G.C., and Gibson, D.M., Arsenal of plant cell wall degrading enzymes reflects host preference among plant pathogenic fungi, Biotechnol. Biofuels, 2011, vol. 4, no. 4, doi 10.1186/1754-6834-4-4
Ramanathan, S., Banupriya, S., and Abirami, D., Production and optimization of cellulose from Fusarium oxysporum by submerged fermentation, J. Sci. Ind. Res., 2010, vol. 69, pp. 454–459.
Keinath, A.P., From native plants in central Europe to cultivated crops worldwide: the emergence of Didymella bryoniae as a cucurbit pathogen, HortScience, 2011, vol. 46, pp. 532–535.
Zamani, M., Tehrani, A., Ahmadzadeh, M., Hosseininaveh, V., and Mostofy, Y., Control of Penicillium digitatum on orange fruit combining Pantoea agglomerans with hot sodium bicarbonate dipping, J. Plant Pathol., 2009, vol. 91, pp. 437–442.
Ievleva, E.V., Revina, T.A., Kudryavtseva, N.N., Sof’in, A.V., and Valueva, T.A., Extracellular proteinases from the phytopathogenic fungus Fusarium culmorum, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 42, pp. 298–303.
Geethu, C., Resna, A.K., and Nair, R., Characterization of major hydrolytic enzymes secreted by Pythium myriotylum, causative agent for soft rot disease, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2013, vol. 104, pp. 749–757.
Huma, H. and Khalid, M.F., Plant protease inhibitors: a defense strategy in plants, Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2007, vol. 2, pp. 068–085.
Chand, R., Kumar, M., Kushwaha, C., Shah, K., and Joshi, A., Role of melanin in release of extracellular enzymes and selection of aggressive isolates of Bipolaris sorokiniana in barley, Curr. Microbiol., 2014, vol. 69, pp. 202–211.
Feng, T., Nyffenegger, C., Hojrup, P., Vidal-Melgosa, S., Yan, K., Ulrik, Fangel, J., Meyer, A.S., and Kirpekar, F., Characterization of an extension-modifying metalloprotease: N-terminal processing and substrate cleavage pattern of Pectobacterium carotovorum Prt1, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 98, pp. 10 077–10 089.
Ibragimov, R.I., Yarullina, L.G., Shpirnaya, I.A., Umarov, I.A., Tsvetkov, V.O., and Maksimov, I.V., Biochemical factors of plant resistance to pathogens, Sovrem. Naukoemkie Tekhnol., 2010, no. 4, pp. 46–48.
Gomes, M.T.R., Oliva, M.L., Lopes, M.T.P., and Salas, C.E., Plant proteinases and inhibitors: an overview of biological function and pharmacological activity, Curr. Protein Pept. Sci., 2011, vol. 12, pp. 417–436.
Volpicella, M., Leoni, C., Costanza, A., de Leo, F., Gallerani, R., and Ceci, L.R., Cystatins, serpins and other families of protease inhibitors in plants, Curr. Protein Pept. Sci., 2011, vol. 12, pp. 386–398.
Carlile, A., Bindschedler, L., Bailey, A.M., Bowyer, P., Clarkson, J.M., and Cooper, R.M., Characterization of SNP1, a cell wall degrading trypsin, produced during infection by Stagonospora nodorum, Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact., 2000, vol. 13, pp. 538–550.
Poloni, A., Pessi, I.S., Frazzon, P.G., and van der Sand, S.T., Morphology, physiology, and virulence of Bipolaris sorokiniana isolates, Curr. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 59, pp. 267–273.
Olivieri, F., Zanetti, M.E., Oliva, C.R., Covarruibias, A., and Casalongue, C., Characterization of a novel extracellular serine protease of Fusarium eumartii and its action on pathogenesis related proteins, Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2002, vol. 108, pp. 63–72.
Facincani, A.P., Moreira, L.M., Soares, M.R., Ferreira, C.B., Ferreira, R.M., Ferro, M.I.T., Ferro, J.A., Gozzo, F.C., and de Oliveira, J.C.F., Comparative proteomic analysis reveals that T3SS, Tfp, and xanthan gum are key factors in initial stages of Citrus sinensis infection by Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri, Funct. Integr. Genomics, 2014, vol. 14, pp. 205–217.
Abramovitch, R. and Martin, G., Strategies used by bacterial pathogens to suppress plant defenses, Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2004, vol. 7, pp. 356–364.
Alfano, J.R. and Collmer, A., Type III secretion system effector proteins: double agents in bacterial disease and plant defense, Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2004, vol. 42, pp. 385–414.
Gazi, A., Sarris, P.F., Fadouloglou, V.E., Charova, S.N., Mathioudakis, N., Panopoulos, N.J., and Kokkinidis, M., Phylogenetic analysis of a gene cluster encoding an additional, rhizobial-like type III secretion system that is narrowly distributed among Pseudomonas syringae strains, BMC Microbiology, 2012, vol. 12, no. 188. doi 10.1186/1471-2180-12-188
Kubrak, O.I. and Lushchak, V.I., Production and patterns of a-amylase from Bacillus sp. BKL40, Biotekhnologiya (Kiev), 2009, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 69–79.
Avdiyuk, E.V., Varbanets, L.D., Safronova, L.A., and Kharkevich, E.S., Purification and patterns of a-amylases from Aspergillus flavus var. oryzae and Bacillus subtilis, Biotekhnologiya (Kiev), 2012, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 91–99.
Gappa-Adachi, R., Yano, K., Takeuchi, S., Morita, Y., and Uematsu, S., Phytophthora blight of southern star (Oxypetalum caeruleum) caused by Phytophthora palmivora in Japan, J. Gen. Plant Pathol., 2012, vol. 78, pp. 39–42.
Morkunas, I., Formela, M., Marczak, L., Stobiecki, M., and Bednarski, W., The mobilization of defence mechanisms in the early stages of pea seed germination against Ascochyta pisi, Protoplasma, 2013, vol. 250, pp. 63–75.
Avdiyuk, E.V. and Varbanets, L.D., a-Amylases from Aspergillus flavus var. oryzae and Bacillus subtilis: substrate specificity and resistance to some chemical active substances, Biotekhnologiya (Kiev), 2013, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 36–45.
Varbanets, L.D., Avdiyuk, E.V., and Borzova, N.V., Microbial a-amylases: isolation, purification and practical usage, Biotechnologia Acta, 2008, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 39–51.
Sailas, R.B., Smitha, V.N., Jisha, S., Pradeep, S., Sajith, S., Sreedevi, K.N., Unni, M.K., and Josh, S., A monograph on amylases from Bacillus spp., Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol., 2013, vol. 4, pp. 227–241.
Konarev, A.V., Proteinase inhibitors and resistance to Leptinotarsa decemlineata in potato, in Sovremennye sistemy zashchity i novye napravleniya v povyshenii ustoichivosti kartofelya k koloradskomu zhuku, ser. Geneticheskaya inzheneriya i ekologiya (Current Systems of Defense and New Concept in Increase of Resistance to Leptinotarsa decemlineata in Potato. Ser. Genetic Engineering and Ecology), 2000, vol. 1, pp. 35–40.
Khadeeva, N.V., Kochieva, E.Z., Cherednichenko, M.Yu., Yakovleva, E.Yu., Sidoruk, K.V., Bogush, V.G., Dunaevskii, Ya.E., and Belozerskii, M.A., Use of buckwheat seed protease inhibitor gene for improvement of tobacco and potato plant resistance to biotic stress, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2009, vol. 74, pp. 260–267.
Abdeen, A., Virgos, A., Olivella, E., Villnueva, J., Aviles, X., Gabarra, R., and Prat, S., Multiple insect resistance in transgenic tomato plants overexpressing two families of plant proteinase inhibitors, Plant Mol. Biol., 2005, vol. 57, pp. 189–202.
Charity, J.A., Hughes, P., Anderson, M.A., Bittisnich, D.J., Whitecroßs, M., and Higgins, T.J.V., Pest and disease protection conferred by expression of barley ß-hordothionin and Nicotiana alata proteinase inhibitor genes in transgenic tobacco, Funct. Plant Biol., 2005, vol. 32, pp. 35–44.
Islamov, R.A. and Furusov, O.V., Bifunctional inhibitor of alpha-amylase/trypsin from wheat grain, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 43, pp. 379–382.
Kandelinskaya, O.L., Grishchenko, E.R., Domash, V.I., and Topunov, A.F., Influence of epibrassinolide on the activity of lupine lectin-like proteins and proteinaseinhibitory systems under the sodium chloride salinization, Agrochemistry, 2008, no. 9, pp. 45–49.
Ryan, C.A., Kuo, T., Pearce, G., and Kunkel, R., Variability in the concentration of three heat stable proteinase inhibitor proteins in potato tubers, Am. Potato J., 1976, vol. 53, no. 12, pp. 433–455.
Bode, W. and Huber, R., Structural basis of the endoproteinase–protein inhibitor interaction, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2000, vol. 1477, pp. 241–252.
Jamal, F., Pandey, P.K., Singh, D., and Khan, M.Y., Serine protease inhibitors in plants: nature’s arsenal crafted for insect predators, Phytochem. Rev., 2013, vol. 12, pp. 1–34.
Capocchi, A., Muccilli, V., Cunsolo, V., Saletti, R., Foti, S., and Fontanini, D., Heterotetrameric a-amylase inhibitor from emmer (Triticum dicoccon Schrank) seeds, Phytochemistry, 2013, vol. 88, pp. 6–14.
Zemke, K.J., Muller-Fahrnow, A., and Jany, K., The three-dimensional structure of the bifunctional proteinase K/a-amylase inhibitor from wheat (PKI3) at 2.5 Å resolution, FEBS Lett., 1991, vol. 397, pp. 240–242.
Nesterenko, M.V., Gvozdeva, E.L., Mitskevich, L.G., and Mosolov, V.V., Subtilisin-binding site localization in the molecule of bifunctional wheat inhibitor, Biokhimiya, 1989, vol. 54, pp. 838–845.
Mehrabadi, M., Bandani, A.R., and Saadati, F., Inhibition of Sunn pest, Eurygaster integriceps, a-amylases by a-amylase inhibitors (T-aAI) from Triticale, J. Insect. Sci., 2010, vol. 10, pp. 1–13.
Franco, L., Rigden, D., Melo, F., and Grossi de Sa M., Plant a-amylase inhibitors and their interaction with insect a-amylases, Eur. J. Biochem., 2002, vol. 269, pp. 397–412.
Svensson, B., Fukuda, K., Nielsen, P.K., and Bonsager, B.C., Proteinaceous a-amylase inhibitors, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2004, vol. 1696, pp. 145–156.
Alves, D.T., Vasconcelos, I.M., Oliveira, J.T., Farias, L.R., Dias, S.C., and Chiarello, M.D., Identification of four novel members of Kunitz-like a-amylase inhibitors family from Delonix regia with activity toward coleopteran insects, Pestic. Biochem. Phys., 2009, vol. 95, pp. 166–172.
Nitti, G., Orru, S., Bloch, C., Morhy, L., Marino, G., and Pucci, P., Amino acid sequence and disulphidebridge pattern of three gamma-thionins from Sorghum bicolor, Eur. J. Biochem., 1995, vol. 228, pp. 250–256.
Campos, F. and Richardson, M., The complete amino acid sequence of the bifunctional a-amylase/trypsin inhibitor from seeds of ragi (Indian finger millet, Eleusine coracana Gaertn.), FEBS Lett., 1983, vol. 152, pp. 300–304.
Iulek, J., Franco, O.L., Silva, M., Slivinski, C.T., Bloch, C., Rigden, D.J., and Grossi de Sa, M.F., Purification, biochemical characterization and partial primary structure of a new alpha-amylase inhibitor from Secale cereale (rye), Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 32, pp. 1195–1204.
Khaliluev, M.R. and Shpakovskii, G.V., Genetic engineering strategies for enhancing tomato resistance to fungal and bacterial pathogens, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2013, vol. 60, pp. 721–732.
Radhajeyalakshmi, R., Velazhahan, R., Balasubramanian, P., and Doraiswamy, S., Overexpression of thaumatin-like protein in transgenic tomato plants confers enhanced resistance to Alternaria solani, Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Protect., 2005, vol. 38, pp. 257–266.
Korneeva, I.V., Varlamova, N.V., Pushin, A.S., Firsov, A.P., Dolgov, S.V., Monakhos, G.F., Shalamzari, A., and Dzhalilov, F.S., Transgenic tomato plants expressing PR-5 protein genes demonstrated resistance against Phytophthora infestans and Xanthomonas vesicatoria, Acta Hortic., 2011, vol. 914, pp. 415–418.
Hwang, B.H., Bae, H., Lim, H.S., Kim, K.B., Kim, S.J., Im, M.H., Park, B.S., Kim, D.S., and Kim, J., Overexpression of polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein 2 (PGIP2) of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis) increased resistance to the bacterial pathogen Pectobacterium carotovorum ssp. carotovorum, Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult., 2010, vol. 103, pp. 293–305.
Golba, B., Treutter, D., and Kollar, A., Effects of apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) phenolic compounds on proteins and cell wall-degrading enzymes of Venturia inaequalis, Trees, 2011, vol. 26, pp. 131–139.
Sami, A.J. and Shakoori, A.R., Cellulase activity inhibition and growth retardation of associated bacterial strains of Aulacophora foviecollis by two glycosylated flavonoids isolated from Mangifera indica leaves, J. Med. Plants Res., 2011, vol. 5, pp. 184–190.
Kont, R., Kurasin, M., Teugjas, H., and Valjamae, P., Strong cellulase inhibitors from the hydrothermal pretreatment of wheat straw, Biotechnol. Biofuels, 2013, vol. 6, pp. 1–14.
Domash, V.I., Sharpio, T.P., and Zabreiko, S.A., Plant inhibitors of proteolysis and possibility for their use in medicine, Vestn. Akad. Nauk Belorussii, Ser. Med. Nauk, 2008, no. 1, pp. 58–63.
Mosolov, V.V. and Valueva, T.A., Inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes under abiotic stresses in plants (review), Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 47, pp. 453–459.
Yang, D.H., Hettenhausen, C., and Baldwin, I.T., BAK1 regulates the accumulation of jasmonic acid and the levels of trypsin proteinase inhibitors in Nicotiana attenuata’s responses to herbivory, J. Exp. Bot., 2011, vol. 62, pp. 641–652.
Vasyukova, N.I., Chalenko, G.I., Gerasimova, N.G., Valueva, T.A., and Ozeretskovskaya, O.L., Activation of elicitor defensive properties by systemic signal molecules during the interaction between potato and the late blight agent, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 44, pp. 213–217.
Vasyukova, N.I. and Ozeretskovskaya, O.L., Induced plant resistance and salicylic acid: a review, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 43, pp. 367–373.
Vasyukova, N.I. and Ozeretskovskaya, O.L., Jasmonate-dependent defense signaling in plant tissues, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2009, vol. 56, pp. 581–590.
Egger, B. and Koschier, E.H., Behavioural responses of Frankliniella occidentalis Pergande larvae to methyl jasmonate and cis-jasmone, J. Pest Sci., 2014, vol. 87, pp. 53–59.
Yakovleva, V.G., Egorova, A.M., and Tarchevsky, I.A., Proteomic analysis of the effect of methyl jasmonate on pea seedling roots, Dokl. Biochem. Biophys., 2013, vol. 449, pp. 90–93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.G. Yarullina, A.R. Akhatova, R.I. Kasimova, 2016, published in Fiziologiya Rastenii, 2016, Vol. 63, No. 2, pp. 205–217.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yarullina, L.G., Akhatova, A.R. & Kasimova, R.I. Hydrolytic enzymes and their proteinaceous inhibitors in regulation of plant–pathogen interactions. Russ J Plant Physiol 63, 193–203 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443716020151
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443716020151