Abstract
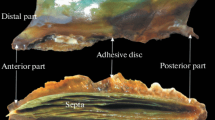
In the commercial Pacific mussel species, Mytilus trossulus, from the Sea of Japan, features of the morphological structure of the byssal apparatus, byssal threads, and pedal groove are studied. Steps in the process of byssal threads formation and characters of the morphological structure of the byssal groove related to this process are described in M. trossulus. The byssal apparatus is shown to consist of a root, a stem, and byssal threads, the latter in cross section being ellipsoid in shape. A byssal thread consists of a corrugated proximal part located immediately behind the cuff and is one-third of its length, and a relatively smooth and flexible distal part taking up two-thirds of the thread length and ending with an attachment disk at the distal end. On the surface of the attachment disk, three reinforcing cords are situated. The morphological features observed in these structures are discussed in terms of the spatial distribution of mytilids in marine coastal zones, a successful habitat of M. trossulus being rocky shores with active wave activities.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Allen, J.A., Cook, M., Jackson, D.J., et al., Observations on the rate of production and mechanical properties of the byssus threads of Mytilus edulis L., J. Mollusc. Stud., 1976, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 279–289.
Bairati, A. and Vitellaro-Zuccarello, L., The ultrastructure of the byssal apparatus of Mytilus galloprovincialis. II. Observations by microdissection and scanning electron microscopy, Mar. Biol., 1974, vol. 28, pp. 145–158.
Banu, A., Shymasundari, K., and Hanumantha Rao, K., The organization and chemistry of the byssus of some bivalves of the Waltair Coast, India, Veliger, 1980, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 77–82.
Bell, E.C. and Gosline, J.M., Mechanical design of mussel byssus material yield enhances attachment strength, J. Exp. Biol., 1996, vol. 199, no. 4, pp. 1005–1017.
Berger, V.Ya., Letunov, V.N., Vshevtsov, G.V., and Saranchova, O.L., Morphofunctional and ecological aspects of byssal thread formation in mussels (Mytilus edulis L.), in Ekologiya obrastaniya v Belom more (Fouling Ecology in the White Sea), Leningrad: Zool. Inst., Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1985, pp. 67–75.
Brown, C.H., Some structural proteins of Mytilus edulis, Quart. J. Microsc. Sci., 1952, vol. 93, pp. 487–502.
Carrington, E. and Gosline, J.M., Mechanical design of mussel byssus: load cycle and strain rate dependence, Am. Malacol. Bull., 2004, vol. 18, pp. 135–142.
Carter, J.G., Harries, P.J., Malchus, N., Sartori, A.F., Anderson, L.C., Bieler, R., Bogan, A.E., Coan, E.V., Cope, J.C.W., Cragg, S.M., Cartia-March, J.R., Hylleberg, J., Kelley, P., Kleemann, K., Kriz, J., et al., Illustrated Glossary of the Bivalvia, Treatise online no. 48, 2012, vol. 1, p. 15.
Denny, M.W., Lift as a mechanism of patch initiation in mussel beds, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 1987, vol. 113, pp. 231–245.
Denny, M., Gaylord, B., Helmuth, B., and Daniel, T., The menace of momentum: dynamic forces of flexible organisms, Limnol. Oceanogr., 1998, vol. 43, no. 5, pp. 955–968.
Eckroat, L.R. and Steel, L.M., Comparative morphology of the byssi of Dreissena polymorpha and Mytilus edulis, Am. Malacol. Bull., 1993, vol. 10, pp. 103–108.
Gosline, J., Lillie, M., Carrington, E., Guerette, P., Ortlepp, C., and Savage, K., Elastic proteins: biological roles and mechanical properties, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., B, 2002, vol. 357, no. 1418, pp. 121–132.
Gosling, E.M., The Mussel Mytilus: Ecology, Physiology, Genetics and Culture, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1992, vol. 25.
Lee, C.Y., Lim, S.S.L., and Owen, M.D., The rate and strength of byssal reattachment by blue mussels (Mytilus edulis L.), Can. J. Zool., 1990, vol. 68, pp. 2005–2009.
Mironov, A.A., Komissarchik, Ya.Yu., and Mironov, V.A., Metody elektronnoi mikroskopii v biologii i meditsine: metodicheskoe rukovodstvo (Methods of Electron Microscopy in Biology and Medicine: a Methodological Guide), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 1994.
Price, H.A., Structure and formation of the byssus complex in Mytilus (Mollusca, Bivalvia), J. Mollusc. Stud., 1983, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 9–17.
Primakov, I.M., Lezin, P.A, Ivanov, M.V., and Kulakovskii., Puti optimizatsii marikul’tury midii v Belom more (Ways to Optimize Mussel Mariculture in the White Sea), Moscow: KMK, 2006.
Pujol, J.P., Rolland, M., Lasry, S., and Vinet, S., Comparative study of the amino acid composition of the byssus in some common bivalve mollusks, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 1970, vol. 34, pp. 193–201.
Qin, X. and Waite, J.H., Exotic collagen gradients in the byssus of mussel M. edulis, J. Exp. Biol., 1995, vol. 198, pp. 633–644.
Skarlato, O.A., Bivalve mollusks of the Far Eastern seas of the USSR (Dysodonta), in Keys to the Fauna of the USSR, Leningrad: Zool. Inst., Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1960, vol. 71.
Skarlato, O.A., Dvustvorchatye mollyuski umerennykh shirot zapadnoi chasti Tikhogo okeana (Bivalves of Temperate Latitudes of the Western Part of the Pacific Ocean), Leningrad: Nauka, 1981.
Skarlato, O.A., Golikov, A.N., Vasilenko, S.V., et al., Composition, structure, and distribution of bottom biocenoses in the coastal waters of Posiet Bay (Sea of Japan), Issled. Fauny Morei, 1967, vol. 5, no. 13.
Smeathers, J.E. and Vincent, J.F.V., Mechanical properties of mussel byssus threads, J. Mollusc. Stud., 1979, vol. 45, pp. 219–230.
Tamarin, A. and Keller, P.J., An ultrastructural study of the byssal thread forming system in Mytilus, J. Ultrastruct. Res., 1972, vol. 40, pp. 401–416.
Vekhova, E.E., Reattachment of certain species of mytilid bivalves to various substrates, Russ. J. Mar. Biol., 2006, vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 308–311.
Vekhova, E.E., Comparative morphology of byssus filaments of three representatives of the family Mytilidae (Bivalvia) from the Sea of Japan, Zool. Zh., 2007, vol. 86, no. 2, pp. 154–162.
Vekhova, E.E., The adaptive morphology of byssus in Mytilus coruscus, Crenomytilus grayanus, and Modiolus modiolus (Mytilidae, Bivalvia) from the Sea of Japan, Biol. Bull. (Moscow), 2019, vol. 46, no. 9, pp. 1030–1044.
Waite, J., Adhesion in byssally attached bivalves, Biol. Rev. Cambridge Philos. Soc., 1983, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 209–231.
Waite, J.H., Marine bioadhesion: unraveling the chemistry, J. Adhesion Soc. Jpn., 1997, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 186–194.
Yonge, C.M., On the primitive significance of the byssus in the Bivalvia and its effects in evolution, J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K., 1962, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 113–125.
Zolotarev, V.N., Sklerokhronologiya morskikh dvustvorchatykh mollyuskov (Sclerochronology of Marine Bivalve Mollusks), Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1989.
NOTATION
Abbreviations for Figs. 3–5: bg, byssal groove of the foot; ff, fine furrows; bt, byssal threads; lc, lateral cord; vl, ventral foot surface; ce, corrugated edge; b, bottom of byssal groove; de, distal end; df, distal fossa; z1, the transition zone from disk to the distal part of byssal thread; z2, transition zone from distal to proximal part of the byssal thread; cf, cuffs; l, mussel foot; os, opposite side of byssal thread; p, pores in groove; ad, attachment disk; pe, proximal end; dp, disk plate; w, longitudinal cord; fc, frontal cord; tf, transverse fold; c, cilia in byssal groove; s, byssal stem; bf, folds of byssal groove; cp, clavate papilla of the byssal groove of the foot.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The author expresses the deep gratitude to D.V. Fomin (Center for Collective Use of the A.V. Zhirmunsky National Scientific Center of Marine Biology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences) for his help in using the Carl Zeiss, Sigma 300 VP scanning electron microscope.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Support Foundation. This work was supported by the Malacological Society of London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vekhova, E.E. The Byssal Apparatus in the Pacific Mussel, Mytilus trossulus (Bivalvia, Mytilidae), from the Sea of Japan. Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 48, 1443–1451 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359021090235
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359021090235