Abstract
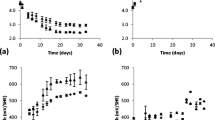
Methods of physicochemical further oxidation of hardly soluble sediment obtained from “wet combustion” of human exometabolites applied to space-purpose Bio Technological Life Support Systems (BTLLS) were studied. Most hardly dissoluble sediment containing Ca, P, Mg, and other essential plant nutrition elements were shown to dissolve in H2O2 and HNO3 aqueous media activated by alternating electric current. Dissolved additional mineral elements allowed (as demonstrated for lettuce) to increase the productivity of BTLLS phototrophic unit plants more than twice, which is comparable to their productivity on standard Knop solution with balanced chemical composition. Thus, dissolved mineral elements can be involved into BTLLS turnover process and increase its closure degree.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tikhomirov, A.A., Ushakova, S.A., Manukovsky, N.S., et al., Adv. Space Res., 2003, vol. 31, no. 7, pp. 1711–1720.
Tikhomirov, A.A., Ushakova, S.A., Velichko, V.V., et al., Acta Astronaut., 2011, vol. 68, nos. 9/10, pp. 1548–1554.
Tikhomirov, A., Kudenko, Yu., Trifonov, S., and Ushakova, S., Adv. Space Res., 2012, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 249–253.
Metody razlozheniya v analiticheskoi khimii (Methods of Degradation in Analytical Chemistry), Moscow: Khimiya, 1984.
Tikhomirov, A.A., Kudenko, Yu.A., Degermendzhi, A.G., et al., Dokl. Biochem. Biophys., 2011, vol. 441, no. 2, pp. 252–254.
Isupova, L.A., Sutormina, E.F., Zakharov, V.P., et al., Catal. Today, 2009, vol. 1475, pp. 5319–5323.
Isupova, L.A., Sutormina, E.F., Kulikovskaya, N.A., et al., Catal. Today, 2005, vol. 105, pp. 429–435.
Zamknutaya sistema: chelovek—vysshie rasteniya (Human–Higher Plants: A Closed System), Lisovskii, G.M., Eds., Novosibirsk Nauka, 1979.
Sutormina, E.F., Trifonov, S.V., Kudenko, Yu.A., et al., Khim. Interesakh Ustoich. Razvit., 2011, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 413–420.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.A. Tikhomirov, S.V. Trifonov, E.A. Morozov, Yu.A. Kudenko, G.S. Kalacheva, S.A. Ushakova, 2016, published in Doklady Akademii Nauk, 2016, Vol. 470, No. 1, pp. 102–104.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tikhomirov, A.A., Trifonov, S.V., Morozov, E.A. et al. Development of human exometabolite deep mineralization method for closed ecosystems. Dokl Biochem Biophys 470, 316–318 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672916050021
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672916050021