Abstract
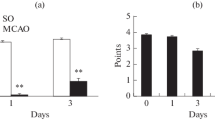
Most ischemic strokes are caused by the occlusion of the middle cerebral artery (MCAO), which results in focal brain lesions in different areas of the neocortex. Secondary damage develops in brain regions located out of the infarct area, including the hippocampus. Hippocampal lesion may lead to cognitive impairments and post-stroke depression. Here, we studied the time course of changes in the levels of corticosterone and proinflammatory cytokine interleukine-1β (IL-1β) in the blood and hippocampus of rats after transient focal brain ischemia. Activation of the hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenal axis, which causes a release of corticosterone into blood, was observed at the early stage after MCAO and was accompanied by the presence of the stress hormone in the hippocampi of both the ischemic and contralateral hemispheres. We show for the first time that this effect was observed only in the ventral hippocampus (VH) but not in the dorsal hippocampus (DH). MCAO induced accumulation of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1β, which coexisted with the elevated level of corticosterone at the early and delayed stages after reperfusion and was also observed in the VH of both hemispheres. Our data show that the VH is more vulnerable to remote damage induced by MCAO compared to the DH and corticosteroid response and neuroinflammation may be detected in the VH of both ischemic and contralateral hemispheres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dirnagl, U., Iadecola, C., and Moskowitz, M.A., Trends Neurosci., 1999, vol. 22, pp. 391–397.
Butler, T.L., Kassed, C.A., Sanberg, P.R., Willing, A.E., and Pennypacker, K.R., Brain Res., 2002, vol. 929, pp. 252–260.
Block, F., Dihné, M., and Loos, M., Prog. Neurobiol., 2005, vol. 75, pp. 342–365.
Lambertsen, K., Biber, K., and Finsen, B., J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 2012, vol. 32, pp. 1677–1698.
Dunn, A.J., Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 2000, vol. 917, pp. 608–617.
John, C.D. and Buckingham, J.C., Curr. Opin. Pharmacol., 2003, vol. 3, pp. 78–84.
Fassbender, K., Schmidt, R., Mössner, R., Daffertshofer, M., and Hennerici, M., Stroke, 1994, vol. 25, pp. 1105–1108.
Johansson, A., Olsson, T., Carlberg, B., Karlsson, K., and Fagerlund, M., J. Neurol. Sci., 1997, vol. 147, pp. 43–47.
Sapolsky, R.M., Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 2000, vol. 57, pp. 925–935.
Jacobson, L. and Sapolsky, R., Endocr. Rev., 1991, vol. 12, pp. 118–134.
Sarabdjitsingh, R.A., Meijer, O.C., Schaaf, M.J., and de Kloet, E.R., Brain Res., 2009, vol. 1249, pp. 43–53.
Segal, M., Richter-Levin, G., and Maggio, N., Hippocampus, 2010, vol. 20, pp. 1332–1338.
Gulyaeva, N.V., Ross. Fiziol. Zhurn. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2013, vol. 99, pp. 3–16.
Longa, E., Weinstein, P., Carlson, S., and Cummins, R., Stroke, 1989, vol. 20, pp. 84–91.
Lin, T.N., He, Y.Y., Wu, G., Khan, M., and Hsu, C.Y., Stroke, 1993, vol. 24, pp. 117–121.
Quast, M.J., Huang, N.C., Hillman, G.R., and Kent, T.A., Magn. Reson. Imaging, 1993, vol. 11, pp. 465–471.
Popp, A., Jaenisch, N., Witte, O.W., and Frahm, C., PLoS One, 2009, vol. 4: e4764.
Smith-Swintosky, V.L., Pettigrew, L.C., Sapolsky, R.M., Phares, C., Craddock, S.D., Brooke, S.M., and Mattson, M.P., J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 1996, vol. 16, pp. 585–598.
Dorey, R., Pierard, C., Chauveau, F., David, V., and Beracochea, D., Neuropsychopharmacology, 2012, vol. 37, pp. 2870–2880.
Higo, S., Hojo, Y., Ishii, H., Komatsuzaki, Y., Ooishi, Y., Murakami, G., Mukai, H., Yamazaki, T., Nakahara, D., Barron, A., Kimoto, T., and Kawato, S., PLoS One, 2011, vol. 6: e21631.
Maggio, N. and Segal, M., Scientific World J., 2010, vol. 10, pp. 462–469.
Sopala, M., Frankiewicz, T., Parsons, C., and Danysz, W., Neurosci. Lett., 2000, vol. 281, pp. 143–146.
Miyashita, K., Abe, H., Nakajima, T., Ishikawa, A., Nishiura-Suzuki, M., Naritomi, H., Tanaka, R., and Sawada, T., Neuroreport, 1994, vol. 5, pp. 945–948.
Robertson, D.A., Beattie, J.E., Reid, I.C., and Balfour, D.J., Eur. J. Neurosci., 2005, vol. 21, pp. 1511–1520.
Lambertsen, K.L., Biber, K., and Finsen, B., J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 2012, vol. 32, pp. 1677–1698.
Doll, D.N., Barr, T.L., and Simpkins, J.W., Aging Dis., 2014, vol. 5, pp. 294–306.
Davies, C.A., Loddick, S.A., Toulmond, S., Stroemer, R.P., Hunt, J., and Rothwell, N.J., J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 1999, vol. 19, pp. 87–98.
Nolden-Koch, M., Breuer, E., and Block, F., J. Neurol., 2000, vol. 247 (Suppl. 3), p. 129.
Uchida, H., Fujita, Y., Matsueda, M., Umeda, M., Matsuda, S., Kato, H., Kasahara, J., and Araki, T., Cell Mol. Neurobiol., 2010, vol. 30, pp. 1125–1134.
Jander, S., Schroeter, M., and Stoll, G., J. Neuroimmunol., 2000, vol. 109, pp. 181–187.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.V. Onufriev, S.V. Freiman, Yu.V. Moiseeva, M.Yu. Stepanichev, N.A. Lazareva, N.V. Gulyaeva, 2017, published in Neirokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 34, No. 3, pp. 235–241.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onufriev, M.V., Freiman, S.V., Moiseeva, Y.V. et al. Accumulation of corticosterone and interleukin-1β in the hippocampus after focal ischemic damage of the neocortex: Selective vulnerability of the ventral hippocampus. Neurochem. J. 11, 236–241 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712417030084
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712417030084