Abstract.
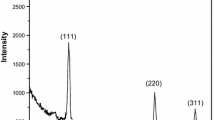
ZnSe thin films have been deposited on high cleaned glass substrate by spray pyrolysis technique within the glass substrate temperature range (400 ○C to 450 ○C). The structural properties of ZnSe thin films have been investigated by (XRD) X-ray diffraction techniques. The X-ray diffraction spectra showed that ZnSe thin films are polycrystalline and have a cubic (zinc blende) structure. The most preferential orientation is along the (111) direction for all spray deposited ZnSe films together with orientations in the (220) and (311) planes also being abundant. The film thickness was determined by an interferometric method. The lattice parameter, grain size, microstrain and dislocation densities were calculated and correlated with the substrate temperature (TS). The optical properties of ZnSe thin films have been investigated by UV/VIS spectrometer and the direct band gap values were found to be in the region of 2.65 eV to 2.70 eV. The electrical properties of ZnSe thin films have been investigated using the Van der Pauw method and the high quality ZnSe thin films were observed to develop at 430 ○C with a resistivity of 56,4×105 ohm cm, a conductivity of 1.77×10-7 (Ω cm)-1 and a hall mobility of 0.53 cm2/Vsec.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Kumar, T.P. Sharma, Optical Mat. 10, 253 (1998)
G. Riveros, H. Gomez, R. Henriguez, R. Schrebler, R.E. Maratti, E.A. Dalchiele, Solar Energy Mat. Solar Cells 70, 255 (2001)
L. Ting Chu, S.C. Shirley, Solid-State Elec. 38, 533 (1995)
S.A. Empedocles, D.J. Norris, M.G. Bawendi, Pyhs. Rev. Lett. 77, 3873 (1996)
C.C. Kim, S. Sivananthan, Phys. Rev. B 53, 1475 (1996)
V.L. Colvin, M.C. Schlamp, A.P. Alivisatos, Nature 370, 354 (1994)
A.D. S, Yan. Y, M.M. Al-Jassim, Progress in Photovoltaics, 10 (5) 309 (2002)
P.K.R. Kalita, B.K. Sarma, H.L. Das., Bull. Mater. Sci. 23, 313 (2000)
A. Schmidth et al., J. Crystal Growth 101, 758 (1990)
S.Y. Wang et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 61, 506 (1992)
H. Goto, T. Ido, A. Takatsuka, J. Crystal Growth 529, 214 (2000)
C.D. Lukhande, P.S. Patil, A. Ennaoui, H. Tributsch, Appl. Surface Sci. 294, 123 (1998)
J.P. Rai, Solar Energy Mat. 30, 376 (1993)
A. Lizzo, M.A. Tagliente, L. Caneve, S. Scaglione, Thin Solid Films 8, 368 (2000)
S.T. Lakshmikumar, A.C. Rastogi, Thin Solid Films 259, 151 (1995)
G.I. Rusu, M.E. Popa, G.G. Rusu, I. Salaoru, Appl. Surface Sci. 218, 222 (2003)
K.L. Chopra, Thin Film Phenomena (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1969)
M. Bedir, Ph.D. Gaziantep University (2002)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction (A.W. Pub. Comp. Inc., 1978), pp. 99–106
K. Reichelt, X. Jiang, Thin Solid Films 191, 91 (1990)
M. Sherif EL et al., J. Matter. Sci. Electron. 7, 391 (1996)
I.A. Ovid’ko, Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 1 61 (2000)
W.D. Nix, Mec. Proper., Thin Films, Nadai Medal Lecture, ASME Congress, New York, 2001
S. Lalitha et al., Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells 82, 187 (2000)
I.M. Khan, in: Handbook of Thin Film Technology, edited by L.I. Maissel, R. Glang (Mc-Graw Hill, New York, 1970), Chap. 10
I.A. Ovid’ko, Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 1, 61 (2000)
F.A. Kröger, The Chemistry of Imperfect Crystals (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1964)
C.F.Rong, G.D. Watkins, Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 1486 (1989)
C.K. De, N.K. Mishra, Indian J. Phys. A 71, 530 (1997)
A. Ashor, N. El-Kadry, M.R. Ebid, M. Farghal, A.A. Ramadan, Thin Solid Films 279, 242 (1996)
N. El-Kadry, M.F. Ahmed, K.A. Hady, Thin Solid Films 274, 120 (1996)
O. Heavens, Optical Properties of Thin Solid Films (Dover, New York, 1965)
J.N. Hodgson, Optical Absorption and Dispersion in Solids (Chapman and Hall, London, 1970)
II-VI Semiconductor Compounds, edited by M. Jain (World Scientific, Singapore, 1993)
S. Adachi, T. Taguchi, Phys. Rev. B 43, 9569 (1991)
T.E. Jenkins, Semiconductor Science Growth and Characterization Techniques (Prentice-Hall, New York, 1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bedir, M., Öztaş, M., Bakkaloğlu, Ö. et al. Investigations on structural, optical and electrical parameters of spray deposited ZnSe thin films with different substrate temperature. Eur. Phys. J. B 45, 465–471 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2005-00207-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2005-00207-3