Abstract.
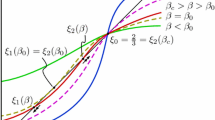
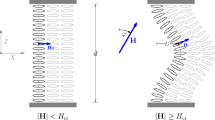
By use of a local stability criterion recently introduced, we predict the existence of a periodic saddle-splay Freedericksz (PSSF) transition that adds to the existing class of classical Freedericksz transitions driven in a nematic cell by an external field. Occurrence of the PSSF transition requires a saddle-splay elastic constant with a large enough magnitude and different anchoring strengths at the plates confining the nematic cell. Otherwise, either the PSSF transition does not occur at all, or it requires a field higher than that associated with the classical aperiodic splay Freedericksz (ASF) transition, in which case it is not observable. Here, we determine the threshold field for which the PSSF precedes the ASF transition, as well as the structure of the destabilizing mode.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Freedericksz, V. Zolina, Trans. Faraday Soc. 29, 919 (1933).
P.G. de Gennes, J. Prost, The Physics of Liquid Crystals (Clarendon Press, Oxford 1993).
E. Guyon, Am. J. Phys. 43, 877 (1975).
A.J. Palangana, M. Simões, L.R. Evangelista, A.A. Arrotéia, Phys. Rev. E 56, 4282 (1997).
F. Lonberg, R.B. Meyer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 55, 718 (1985).
C. Oldano, Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 1098 (1986).
E. Miraldi, C. Oldano, A. Strigazzi, Phys. Rev. A 34, 4348 (1986).
J.L. Ericksen, Phys. Fluids 9, 1205 (1966).
R. Rosso, E.G. Virga, S. Kralj, Phys. Rev. E 70, 011710 (2004).
E.G. Virga, Variational Theories for Liquid Crystals (Chapman & Hall, London, 1994).
O.D. Lavrentovich, V.M. Pergamenshchik, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 9, 2389 (1995).
V.M. Pergamenshchik, Phys. Rev. E 61, 3936 (2000).
D.W. Allender, G.P. Crawford, J.W. Doane, Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 1442 (1991).
S. Kralj, S. Žumer, Phys. Rev. A 45, 2461 (1992).
A. Sparavigna, O.D. Lavrentovich, A. Strigazzi, Phys. Rev. E 49, 1344 (1994).
A.L. Alexe-Ionescu, G. Barbero, I. Lelidis, Phys. Rev. E 66, 061705 (2002).
G. Barbero, V.M. Pergamenshchik, Phys. Rev. E 66, 051706 (2002).
C.M. Bender, S.A. Orszag, Advanced Mathematical Methods for Scientists and Engineers. Asymptotic Methods and Perturbation Theory (Springer, Heidelberg, 1999).
G.P. Crawford, S. Žumer, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 9, 2469 (1995).
J. Nehring, A. Saupe, J. Chem. Phys. 53, 337 (1971).
A.D. Kiselov, Phys. Rev. E 69, 041701 (2004).
H.J. Deuling, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 19, 123 (1972).
G. Barbero, L.R. Evangelista, An Elementary Course on the Continuum Theory for Nematic Liquid Crystals (World Scientific, Singapore, 2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kralj, S., Rosso, R. & Virga, E.G. Periodic saddle-splay Freedericksz transition in nematic liquid crystals. Eur. Phys. J. E 17, 37–44 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2004-10104-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2004-10104-3