Abstract.
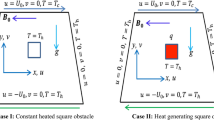
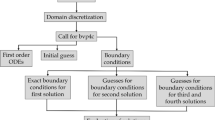
The purpose of this research is the numerical study of turbulent flow field, heat transfer and entropy generation of a Cuo-MWCNT-oil hybrid nanofluid in a trapezoidal enclosure under the influence of a magnetic field in natural convection. The enclosure side walls are insulated, the top wall is cold and the bottom one is hot. The study is done on Rayleigh numbers 107 to 1010, Hartmann numbers 0 to 500, and volume fractions 0 to 1 percent of nanoparticles. The governing equations were solved numerically using a finite volume method and SIMPLER algorithm. According to numerical results, it was observed that the application and increase of a magnetic field increases the flow tendency to vortices. In all Rayleigh numbers and for all the studied Hartmann numbers, the stream function and average Nusselt number reduced by increasing the volume fraction of nanoparticles. It was also observed that for smaller Rayleigh numbers, increasing the Hartmann number will have a more tangible effect on reducing the average Nusselt number. By increasing the Rayleigh number in all the studied Hartmann numbers and volume fractions, the total entropy generated increased. The optimal mode for each Rayleigh number in terms of the minimum value of entropy generation is the least volume fraction and the most Hartmann number.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Togun, M.R. Safaei, Rad Sadri, S.N. Kazi, A. Badarudin, K. Hooman, E. Sadeghinezhad, Appl. Math. Comput. 239, 153 (2014)
M.A. Ahmeda, M.Z. Yusoff, K.C. Ng, N.H. Shuaib, Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 6, 212 (2015)
V. Bianco, F. Scarpa, L.A. Tagliafico, Renew. Energy 116, 9 (2018)
R. Davarnejad, M. Jamshidzadeh, Eng. Sci. Technol. 18, 536 (2014)
R. Choudhary, S. Subudhi, Appl. Therm. Eng. 108, 1095 (2016)
M. Siavashi, M. Jamali, Appl. Therm. Eng. 100, 1149 (2016)
H. Ghodsinezhad, M. Sharifpur, J.P. Meyer, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 76, 1120 (2016)
S. Mosayebidorcheha, M. Sheikholeslami, M. Hatamid, D.D. Ganji, Particuology 13, 20 (2016)
Y. Varol, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 37, 1350 (2010)
H. Saleh, R. Roslan, I. Hashim, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 54, 194 (2011)
R. Nasrin, P. Salma, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 39, 270 (2012)
A. Aghaei, H. Khorasanizadeh, G. Sheikhzadeh, M. Abbaszadeh, J. Magn. & Magn. Mater. 403, 133 (2016)
A. Arefmanesh, A. Aghaei, H. Ehteram, Appl. Math. Modell. 40, 815 (2016)
T.L. Bergman, A.S. Lavine, F.P. Incropera, D.P. DeWitt, Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, fourth edition (Wiley, 2016)
B.E. Launder, D.B. Spalding, Lectures in Mathematical Models of Turbulence (Academic Press, London, 1972)
A.H. Mahmoudi, I. Pop, M. Shahi, F. Talebi, Comput. Fluids 72, 46 (2011)
L. Syam Sundar, K.V. Sharma, Manoj K. Singh, A.C.M. Sousa, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 68, 185 (2017)
J. Buongiorno, J. Heat Transfer 128, 240 (2006)
A. Aghaei, H. Khorasanizadeh, G.A. Sheikhzadeh, Heat Mass Transf. 54, 151 (2018)
S.V. Patankar, Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow (HemispHere, McGraw-Hill, Washington DC, 1980)
M.S. Bohn, A.T. Kirkpatrick, D.A. Olson, J. Heat Transf. 106, 339 (1984)
G. Barakos, E. Mitsoulis, D. Assimacopoulos, Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 18, 695 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
The EPJ Publishers remain neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghaei, A., Khorasanizadeh, H. & Sheikhzadeh, G.A. A numerical study of the effect of the magnetic field on turbulent fluid flow, heat transfer and entropy generation of hybrid nanofluid in a trapezoidal enclosure. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 134, 310 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12681-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12681-3