Abstract
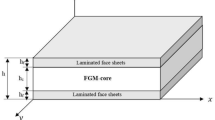
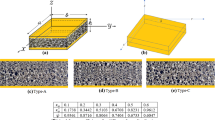
This paper investigates damped vibrational behavior of a lightweight sandwich plate subjected to a periodic load within a limited time. The lightweight sandwich structure includes a thick polymeric porous core with either functionally graded or uniformly distributions of voids which is sandwiched by two thin layers of laminate composites. To investigate the effect of void distribution properly, the same void volume fraction has been considered while different types of core have been analyzed. Using the first-order shear deformation theory of plates, the governing equations for the free and forced vibrations have been developed. By involving structural damping, these equations which are able to treat thin to moderately thick plates have been solved by developing a computationally cost-effective finite element approach. An extensive sensitivity analysis has been performed to examine the effects of fiber orientation in composite layers, void’s volume and dispersion in core, and geometrical dimensions on the vibrational behavior of such porous composite sandwich plates (PCSPs). The results show that the use of foam in PCSPs considerably reduces the amplitude of vibrations and improves the fundamental frequency. Furthermore, it was found that the use of [45, −45]2 composite layers offers PCSPs with the highest natural frequency and the lowest amplitude of vibrations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Xie, S. Sahmani, B. Safaei, B. Xu, Nonlinear secondary resonance of FG porous silicon nanobeams under periodic hard excitations based on surface elasticity theory. Eng. Comput. 37, 1611–1634 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00931-w
S.-X. Chen, S. Sahmani, B. Safaei, Size-dependent nonlinear bending behavior of porous FGM quasi-3D microplates with a central cutout based on nonlocal strain gradient isogeometric finite element modelling. Eng. Comput. 37, 1657–1678 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01303-z
X. Yang, S. Sahmani, B. Safaei, Postbuckling analysis of hydrostatic pressurized FGM microsized shells including strain gradient and stress-driven nonlocal effects. Eng. Comput. 37, 1549–1564 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00901-2
D.X. Hung, T.M. Tu, L.N. Van, P.H. Anh, Nonlinear buckling and postbuckling of FG porous variable thickness toroidal shell segments surrounded by elastic foundation subjected to compressive loads. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 107, 106253 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2020.106253
R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, K. Behdinan. Layer arrangement impact on the electromechanical performance of a five-layer multifunctional smart sandwich plate. In: K. Behdinan, R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, (eds.) Adv. Multifunct. Light. Aerostructures Des. Dev. Implement. 1st ed., Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Ltd; (2021), p. 3–24
H. Lin, D. Cao, Y. Xu, Vibration characteristics and flutter analysis of a composite laminated plate with a store. Appl Math Mech English Ed 9, 241–260 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-018-2297-6
M. Alhijazi, Q. Zeeshan, Z. Qin, B. Safaei, M. Asmael, Finite element analysis of natural fibers composites: a review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 9, 853–875 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2020-0069
R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, G. Payganeh, Thermoelastic dynamic analysis of wavy carbon nanotube reinforced cylinders under thermal loads. Steel Compos. Struct. 25, 315–326 (2017). https://doi.org/10.12989/scs.2017.25.3.315
A.M. Fattahi, B. Safaei, Z. Qin, F. Chu, Experimental studies on elastic properties of high density polyethylene-multi walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Steel Compos. Struct. 38, 187 (2021). https://doi.org/10.12989/scs.2021.38.2.177
S. Karimzadeh, B. Safaei, T.C. Jen, Investigate the importance of mechanical properties of SWCNT on doxorubicin anti-cancer drug adsorption for medical application: A molecular dynamic study. J. Mol. Graph. Model 101, 107745 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2020.107745
E. Magnucka-Blandzi, K. Wisniewska-Mleczko, M.J. Smyczynski, P. Kedzia, Buckling of a sandwich symmetrical circular plate with varying mechanical properties of the core. Appl. Math. Mech. English Ed 39, 981–992 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-018-2347-8
J.R. Vinson, Sandwich structures. Appl. Mech. Rev. 54, 201 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3097295
R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, S.A. Meguid, S. Rashahmadi, Electro-dynamic analysis of smart nanoclay-reinforced plates with integrated piezoelectric layers. Appl. Math. Model 75, 267–278 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.05.033
M. Shaban, H. Mazaheri, Bending analysis of five-layer curved functionally graded sandwich panel in magnetic field: closed-form solution. Appl. Math. Mech. English Ed 42, 251–274 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2675-7
Y. Feng, H. Qiu, Y. Gao, H. Zheng, J. Tan, Creative design for sandwich structures: a review. Int. J. Adv. Robot Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/1729881420921327
L. Wu, X. Zhang, J. Ban, Q. Jiang, T. Li, J. Lin, Design and optimization of multi-scale porous sandwich composites with excellent sound absorption and cushioning properties. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636221993903
T. Liu, S. Hou, X. Nguyen, X. Han, Energy absorption characteristics of sandwich structures with composite sheets and bio coconut core. Compos Part B 114, 328–338 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.01.035
R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, K. Behdinan, Thermo-electro-mechanical behavior of an advanced smart lightweight sandwich plate. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 106, 106142 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2020.106142
M.-C. Trinh, D.-D. Nguyen, S.-E. Kim, T.M. Chien, N.D. Duc, S.K. Eock, Effects of porosity and thermomechanical loading on free vibration and nonlinear dynamic response of functionally graded sandwich shells with double curvature. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 87, 119–132 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2019.02.010
M. Esmaeilzadeh, M. Kadkhodayan, Dynamic analysis of stiffened bi-directional functionally graded plates with porosities under a moving load by dynamic relaxation method with kinetic damping. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 93, 105333 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2019.105333
W. Gao, Z. Qin, F. Chu, Wave propagation in functionally graded porous plates reinforced with graphene platelets. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 102, 105860 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2020.105860
Y. Liu, Z. Qin, F. Chu, Nonlinear forced vibrations of FGM sandwich cylindrical shells with porosities on an elastic substrate. Nonlinear Dyn. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06358-7
Y. Liu, Z. Qin, F. Chu, Analytical study of the impact response of shear deformable sandwich cylindrical shell with a functionally graded porous core. Mech. Adv. Mater Struct. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2020.1818904
F. Fan, Y. Xu, S. Sahmani, B. Safaei, Modified couple stress-based geometrically nonlinear oscillations of porous functionally graded microplates using NURBS-based isogeometric approach. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 372, 113400 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113400
J.L. Mantari, A.S. Oktem, S.C. Guedes, A new trigonometric shear deformation theory for isotropic, laminated composite and sandwich plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 49, 43–53 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2011.09.008
P. Malekzadeh, A.R. Fiouz, H. Razi, Three-dimensional dynamic analysis of laminated composite plates subjected to moving load. Compos. Struct. 90, 105–114 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2009.02.008
A.R. Setoodeh, P. Malekzadeh, K. Nikbin, Low velocity impact analysis of laminated composite plates using a 3D elasticity based layerwise FEM. Mater Des. 30, 3795–3801 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.01.031
C.H. Thai, A.J.M. Ferreira, E. Carrera, H. Nguyen-Xuan, Isogeometric analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates using a layerwise deformation theory. Compos. Struct. 104, 196–214 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPSTRUCT.2013.04.002
T. Yu, S. Yin, T.Q. Bui, S. Xia, S. Tanaka, S. Hirose, NURBS-based isogeometric analysis of buckling and free vibration problems for laminated composites plates with complicated cutouts using a new simple FSDT theory and level set method. Thin. Walled Struct. 101, 141–156 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2015.12.008
F. Tornabene, N. Fantuzzi, M. Bacciocchi, J.N. Reddy, A posteriori stress and strain recovery procedure for the static analysis of laminated shells resting on nonlinear elastic foundation. Compos. Part B Eng. 126, 162–191 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPOSITESB.2017.06.012
R. Xiaohui, W. Zhen, J. Bin, A refined sinusoidal theory for laminated composite and sandwich plates. Mech. Adv. Mater Struct. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2018.1538469
M. Sehoul, M. Benguediab, A. Bakora, A. Tounsi, Free vibrations of laminated composite plates using a novel four variable refined plate theory. Steel Compos. Struct. 24, 603–613 (2017). https://doi.org/10.12989/scs.2017.24.5.603
H.K. Bisheh, N. Wu, Wave propagation characteristics in a piezoelectric coupled laminated composite cylindrical shell by considering transverse shear effects and rotary inertia. Compos. Struct. 191, 123–144 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.02.010
Z. Wang, T. Yu, T.Q. Bui, N.A. Trinh, N.T.H. Luong, N.D. Duc et al., Numerical modeling of 3-D inclusions and voids by a novel adaptive XFEM. Adv. Eng. Softw. 102, 105–122 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.09.007
N.V. Nguyen, H.X. Nguyen, S. Lee, H. Nguyen-xuan, Geometrically nonlinear polygonal finite element analysis of functionally graded porous plates. Adv. Eng. Softw. 126, 110–126 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2018.11.005
J. Yang, D. Chen, S. Kitipornchai, Buckling and free vibration analyses of functionally graded graphene reinforced porous nanocomposite plates based on Chebyshev-Ritz method. Compos Struct 193, 281–294 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPSTRUCT.2018.03.090
Y.H. Dong, Y.H. Li, D. Chen, J. Yang, Vibration characteristics of functionally graded graphene reinforced porous nanocomposite cylindrical shells with spinning motion. Compos. Part B Eng. 145, 1–13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.03.009
M.R. Barati, A.M. Zenkour, Electro-thermoelastic vibration of plates made of porous functionally graded piezoelectric materials under various boundary conditions. J. Vib. Control. 24, 1910–1926 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546316672788
M. Askari, A.R. Saidi, A.S. Rezaei, An investigation over the effect of piezoelectricity and porosity distribution on natural frequencies of porous smart plates. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636218791092
M. Mohammadi, M. Bamdad, K. Alambeigi, R. Dimitri, F. Tornabene, Electro-elastic response of cylindrical sandwich pressure vessels with porous core and piezoelectric face-sheets. Compos. Struct. 225, 111119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPSTRUCT.2019.111119
R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, K. Behdinan, B. Safaei, Z. Qin, Static performance of agglomerated CNT-reinforced porous plates bonded with piezoceramic faces. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 188, 105966 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105966
R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, K. Behdinan, B. Safaei, Z. Qin, Buckling behavior of porous CNT-reinforced plates integrated between active piezoelectric layers. Eng. Struct. 222, 111141 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2020.111141
R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, K. Behdinan, Free vibration response of smart sandwich plates with porous CNT-reinforced and piezoelectric layers. Appl. Math. Model (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2021.03.013
N.V. Nguyen, J. Lee, H. Nguyen-Xuan, Active vibration control of GPLs-reinforced FG metal foam plates with piezoelectric sensor and actuator layers. Compos. Part B Eng. 172, 769–784 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPOSITESB.2019.05.060
J. Zhao, F. Xie, A. Wang, C. Shuai, J. Tang, Q. Wang, Vibration behavior of the functionally graded porous (FGP ) doubly-curved panels and shells of revolution by using a semi-analytical method. Compos. Part B 157, 219–238 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.08.087
O. Zargar, M. Mollaghaee-Roozbahani, M. Bashirpour, M. Baghani, The application of homotopy analysis method to determine the thermal response of convective-radiative porous fins with temperature-dependent properties. Int. J. Appl. Mech. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1758825119500893
M. Babaei, M. Hadi, K. Asemi, Natural frequency and dynamic analyses of functionally graded saturated porous annular sector plate and cylindrical panel based on 3D elasticity. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 96, 105524 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2019.105524
B. Sobhani Aragh, M.H. Yas, Effect of continuously grading fiber orientation face sheets on vibration of sandwich panels with FGM core. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 53, 628–638 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJMECSCI.2011.05.009
R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, K. Behdinan, Temperature effect on free vibration response of a smart multifunctional sandwich plate. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636220908707
R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, A. Radhi, K. Behdinan, Damped dynamic behavior of an advanced piezoelectric sandwich plate. Compos. Struct. 243, 112243 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112243
A.R. Setoodeh, M. Shojaee, P. Malekzadeh, Vibrational behavior of doubly curved smart sandwich shells with FG-CNTRC face sheets and FG porous core. Compos. Part B Eng. 165, 798–822 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPOSITESB.2019.01.022
B. Safaei, R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, Z. Qin, K. Behdinan, F. Chu, Determination of thermoelastic stress wave propagation in nanocomposite sandwich plates reinforced by clusters of carbon nanotubes. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636219848282
A. Amiri, M. Mohammadimehr, M. Anvari, Stress and buckling analysis of a thick-walled micro sandwich panel with a flexible foam core and carbon nanotube reinforced composite (CNTRC) face sheets. Appl. Math. Mech. English Ed. 41, 1027–1038 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2627-7
Q. Li, D. Wu, X. Chen, L. Liu, Y. Yu, W. Gao, Nonlinear vibration and dynamic buckling analyses of sandwich functionally graded porous plate with graphene platelet reinforcement resting on Winkler-Pasternak elastic foundation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 148, 596–610 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJMECSCI.2018.09.020
R. Moradi-Dastjerdi, K. Behdinan, Stress waves in thick porous graphene-reinforced cylinders under thermal gradient environments. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 110, 106476 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2020.106476
B. Safaei, The effect of embedding a porous core on the free vibration behavior of laminated composite plates. Steel Compos. Struct. 35, 659–670 (2020). https://doi.org/10.12989/SCS.2020.35.5.659
Reddy JN. Mechanics of Laminated Composite Plates and Shells: Theory and Analysis. CRC press; 2004.
M. Mohammadsalehi, O. Zargar, M. Baghani, Study of non-uniform viscoelastic nanoplates vibration based on nonlocal first-order shear deformation theory. Meccanica 52, 1063–1077 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-016-0432-0
R. Talebitooti, K. Daneshjoo, S.A.M. Jafari, Optimal control of laminated plate integrated with piezoelectric sensor and actuator considering TSDT and meshfree method. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 55, 199–211 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2015.09.004
A.H. Baferani, A.R. Saidi, H. Ehteshami, Accurate solution for free vibration analysis of functionally graded thick rectangular plates resting on elastic foundation. Compos. Struct. 93, 1842–1853 (2011)
H. Thai, D. Choi, A refined plate theory for functionally graded plates resting on elastic foundation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 71, 1850–1858 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2011.08.016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safaei, B. Frequency-dependent damped vibrations of multifunctional foam plates sandwiched and integrated by composite faces. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136, 646 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01632-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01632-4