Abstract
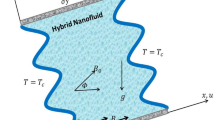
This paper presents a numerical investigation on magneto-hydrodynamics combined convection in a nanofluid-saturated porous 2-D cavity with different tilting angles of applied magnetic field and aspect ratios. The moving upper horizontal wall is heated uniformly. The temperature along the bottom wall is a constant cold temperature while the adiabatic condition is maintained at the vertical sidewalls. The finite volume method is applied to solve the system of non-dimensional equations. The pertinent parameters of the current study are Hartmann number (Ha), solid volume fraction (χ), Richardson number (Ri), the aspect ratio (Ar), Darcy number (Da), and the inclination angle of the magnetic field (γ). The slope of applied magnetic field affects the magnetic field intensity and the overall rate of heat transfer is augmented in the forced convection regime than the mixed convection regime. The mean Nusselt number raises on increasing of Ar for all considered Richardson numbers. In the presence of magnetic field, the rate of heat transfer is almost equal to the amplification of solid volume concentration when Ar = 0.25, whereas, it increases for Ar > 0.25 with the raise in the solid volume concentration. An increase in Hartmann number and Darcy number is insignificant on mean rate of heat transfer in the mixed convection regime at Ar ≤ 0.5.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I.E. Sarris, S.C. Kakarantzas, A.P. Grecos, N.S. Vlachos, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 48, 3443 (2005)
J.M. Jalil, K.A. Al-Tae’y, Numer.Heat Transfer Part A 51, 899 (2007)
G.R. Kefayati, M. Gorji-Bandpy, H. Sajjadi, D.D. Ganji, Sci. Iran. 19, 1053 (2012)
S. Ray, D. Chatterjee, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 57, 200 (2014)
S. Ray, D. Chatterjee, Numer. Heat Transfer Part A 66, 530 (2014)
A. Malleswaran, S. Sivasankaran, J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 9, 311 (2016)
S.U. Choi, J.A. Estman, A.S.M.E. Publ Fed. 48, 99 (1995)
R.K. Tiwari, M.K. Das, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 50, 2002 (2007).
M. Alinia, D.D. Ganji, M. Gorji-Bandpy, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 38, 1428 (2011).
S.M. Aminossadati, A. Kargar, B. Ghasemi, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 52, 102 (2012)
A. Fereidoon, S. Saedodin, M. Hemmat Esfe, M.J. Noroozi, Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 7, 55 (2013)
M.H. Esfe, M. Akbari, D.S. Toghraie, A. Karimipour, M. Afrand, Heat Transfer Res. 45, 409 (2014)
K. Khanafer, K. Vafai, Numer. Heat Transfer Part A 42, 465 (2002)
I.A. Badruddin, Z.A. Zainal, P.A. Aswatha Narayana, K.N. Seetharamu, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 33, 491 (2006)
E. Vishnuvardhanarao, M.K. Das, Numer. Heat Transfer Part A 53, 88 (2007)
T. Basak, P.V. Krishna Pradeep, S. Roy, I. Pop, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 54, 1706 (2011)
L. Agarwal, A. Satheesh, C.G. Mohan, Heat Transfer Asian Res. 44, 305 (2015)
M.M. Rahman, H.F. Öztop, R. Saidur, S. Mekhilef, K. Al-Salem, Therm. Sci. 19, 1761 (2015).
A.J. Chamkha, M.A. Ismael, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 67, 135 (2013)
A.M. Rashad, A.J. Chamkha, C. RamReddy, P.V.S.N. Murthy, Heat Transfer Asian Res. 43, 397 (2014)
A.A. Hassan, M.A. Ismael, Int. J. Therm. Env. Eng. 10, 93 (2015)
S. Sureshkumar, M. Muthtamilselvan, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 131, 95 (2016)
M. Muthtamilselvan, S. Sureshkumar, Nonlinear Eng. 7, 1 (2018)
S. Ergun, Chem. Eng. Prog. 48, 89 (1952)
J.C. Maxwel, in A treatise on electricity and magnetism (Oxford University Press, Cambridge, 1904,) pp. 435–441
W. Yu, S.U. Choi, J. Nanopart. Res. 5, 167 (2003)
S.V. Patankar, inNumerical heat transfer and fluid flow (McGraw Hill book company, New York, 1980,) pp. 126–130
T. Hayase, J.A. Humphrey, R.A. Greif, J. Comput. Phys. 98, 108 (1992)
K.M. Khanafer, A.J. Chamkha, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 42, 2465 (1999)
R. Iwatsu, J.M. Hyun, K. Kuwahara, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 36, 1601 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sureshkumar, S., Muthukumar, S., Muthtamilselvan, M. et al. MHD convection of nanofluid in porous medium influenced by slanted Lorentz force. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 229, 331–346 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2019-900085-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2019-900085-0