Abstract
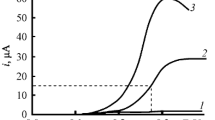
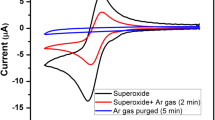
Rate constants for the reaction of superoxide O- 2 with various substrates were obtained through stationary electrode polarography theory and technique. In solvent acetonitrile, the substrate and the rate constants of the reaction O- 2 + AH- k2→Product, are, AH = isopropanol (k2 < 0.01 M-1 s-1); ethanol (k2 = 1.42 × 102 M-1 s-1); methanol (k2 = 1.1 × 107 M-1 s-1), H2O (k2 = 1.0 × 105 M-1 s-1). In MeCN, O-2 was found to be rather unreactive towards glucose and acetone but it reacts with fructose and sucrose catalytically. However, in DMF2, O- 2reacts with glucose and fructose with k2 order of 105 M-1 s-1. The mechanism of the reaction of O- 2 with the substrates (AH) is proposed as O- 3 + AH k2O, AHk2 k-1 k′ [O2H + AH]-, k-2→O2H + A- with k1 = 109 M-1 s-1 and k-1 = 108 -109 s-1. With these values of k-1 and k1, k′ k2(obs). The reversible E1/2 for O2 + e O- 2 in various solvents: MeCN, acetone, isopropanol, methanol, H2O were obtained either directly from the reversible voltammogram or from experimental voltammograms and the rate constants obtained (as above) using stationary electrode polargraphy theory; E1/2 being -0.82 (MeCN),-0.85 (acetone),-0.72 (isopropanol);-0.66 (MeOH),-0.56 (H2O) vs SCE.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
I. Fridovich, in: Pathology of Oxygen, A. P. Autor (Ed.). Academic Press (1982).
(a) A. P. Autor (Ed.), Pathology of Oxygen. Academic Press (1982). (b) D. T. Sawyer, Acc. Chem. Res. 14, 393 (1981). (c) J. S. Valentine, in: Oxygen, Biochemical and Clinical Aspects, W. S. Caughey (Ed.). Academic Press (1980). (d) J. A. Valentine, in: Superoxide and Superoxide Dismutases, A. M. Michelson, J. M. McCord and I. Fridovich (Eds). Academic Press (1977). (e) D. T. Swayer and J. L. Robers, Acc. Chem. Res. 21, 469 (1988).
(a) A. Ledwith, in: Biochemical Mechanism of Paraquat Toxicity, A. P. Autor (Ed.). Academic Press (1977). (b) M. Mohammad, R. Iqbal, A. Y. Khan, K. Zahir and R. Jahan, J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 7, 141 (1985).
(a) G. Bemzi and A. Moretti, Neurobiol. Aging 16, 661 (1995). (b) J. M. McCord, Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 69, 131, 209, 112 (1995). (c) V. Darley-Usmer, H. Wiseman and B. Halliwel, FEBS Lett. (1995). (d) G. Multhoup, T. Rupport, A. Schlicksupp, L. Hesse, D. Beher, C. L. Masters and K. Beyren-ther, Biochem. Biopharmol. 54, 533 (1997). (e) J. F. Grieveau and D. Le Lammon, Int. J. Androl. 20, 61 (1997). (f) J. B. de Haan, E. J. Wolvetang, F. Cristiano, R. Immello, C. Bladier, M. J. Kelner and I. Kola, Adv. Pharmacol. 38, 379 (1997). (g) Z. Sahmoun, K. Jamoussi and K. M. Zeghal, Therapie 52, 251 (1997). (h) B. M. Morrison, J. H. Morrison and J. W. Gordon, J. Expl. Zool. 82, 32 (1988). (i) J. Parvez, R. P. Baldwin, R. M. Buchanan and P. W. Faguy, in: Electrochem. Soc. Meeting Abstracts, Spring Meeting, Montreal Quebec, Canada 1357 (A) (1997). (j) K. Tammeveski, M. Arulepp, T. Tenno, C. Ferrater and J. Claret, Electrochim. Acta 42, 2961 (1997). (k) S. Singh and K. N. Singh, in: Third Natl. Conf. on Electrochemicals, Souvenir & Abstracts, Barc, Mumbai, p. 4 (1997). (l) K. Tammeveski, T. Tenno, J. Claret and C. Ferrater, Electrochim. Acta 42, 893 (1997). (m) C. King, Y. Xie and F. Anson, J. Electroanal. Chem. 413, 165 (1996). (n) S. Billozar, T. Zalewska and A. Lisowska-Olekslak, J. Appl. Electrochem. 26, 1053 (1996).
(a) M. Mohammad, R. Iqbal, A. Y. Khan, K. Zahir and R. Jahan, J. Electroanal. Chem. 124, 139 (1981). (b) M. Mohammad, Anal. Chem. 47, 958 (1975). (c) M. Mohammad, S. U. Sheikh, M. Iqbal, R. Ahmed, M. Razaq and R. Jahan, Electroanal. Chem. 89, 431 (1978). (d) M. Mohammad, R. Iqbal, A. Y. Khan, K. Zahir and R. Jahan, J. Phys. Chem. 85, 2816 (1981).
M. Mohammad, Anal. Chem. 49, 60 (1976), see also ref. [5] above.
(a) M. Mohammad and M. Iqbal, J. Electrochem. Soc. (India) 30, 204 (1981). (b) M. Mohammad, A. Y. Khan, M. Afzal, A. Nisa and R. Ahmed, Aust. J. Chem. 27, 2495 (1974). (c) M. Mohammad, A.Y. Khan, M. S. Subhani, W. Begum, N. Ashraf, R. Qureshi and R. Iqbal, Res. Chem. Intermediate 16, 29 (1991). (d) H. Taube, J. Gen. Physiol. 49, 29 (1965). (e) R. Rainis and M. Szwarc, Proc. Roy. Soc. 339A, 417 (1974). (f) N. Gupta and H. Linschitz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 6384 (1997).
(a) M. E. Peover and B. S. White, Electrochim. Acta 11, 1061 (1966). (b) J. M. Hale, in: Reactions of Molecules at Electrodes, N. S. Hush (Ed.). Wiley-Interscience (1971).
A. J. Bard and L. R. Faulkner, in: Electrochemical Methods, pp. 246, 701. Wiley (1980).
M. Mohammad, A. Y. Khan, M. Iqbal, R. Iqbal and M. Razaq, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 100, 7658 (1978).
E. M. Kosower, in: Introduction to Physical Organic Chemistry, p. 302. Wiley (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammad, M., Khan, A.Y., Subhani, M.S. et al. Kinetics and electrochemical studies on superoxide. Research on Chemical Intermediates 27, 259–267 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1163/156856701300356473
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/156856701300356473