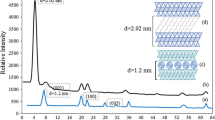
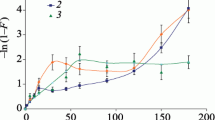
Abstract
The cation exchange process between tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) and Na+ on mont-morillonite was studied by atomic absorption spectrophotometry, X-ray diffraction, differential thermal analysis, and nitrogen sorption at 78°K. The exchange of Co(en)33+ for Na+ was found to be extremely favorable, with a tendency toward segregation of the two kinds of cations in the mixed clays studied. Small amounts of Co(en)3+3 were found to lower the nitrogen sorption capacity of Na+ mont-morillonite while clays with high Co(en)3+3 content had greatly enhanced sorption. An explanation is offered in terms of a dual role of the Co(en)3+3 in determining the kind and amount of nitrogen sorption in the exchanged montmorillonite.
Résumé
Le phénomène d’échange cationique entre le tris (éthylène-diamine) cobalt (III) et le sodium sur la montmorillonite a été étudié par spectrophotométrie d’absorption atomique, diffraction X, analyse thermique différentielle et sorption d’azote à 78°K.
L’échange de Na+ par Co (en)33+ s’est révélé très favorable, avec une tendance vers la ségrégation des deux sortes de cations dans les argiles mixtes étudiées. On a trouvé que de petites quantités de Co (en)33+ abaissent la capacité de sorption pour l’azote de la montmorillonite Na+, tandis que les argiles riches en Co (en)33+ ont une sorption fortement augmentée. On fournit une explication de ce fait sur la base du double rôle que joue le Co (en)33+ dans la détermination de la nature et de l’intensité de la sorption de l’azote dans la montmorillonite ayant subi l’échange d’ion.
Kurzreferat
Der Kationenaustausch zwischen Tri(äthylendiamin)kobalt(III) und Na+ bei Mont-morillonit wurde durch atomische Absorptionsspektrophotometrie, Röntgenbeugung, differentielle Wärmeanalyse und Stickstoffsorption bei 78°K untersucht. Der Austausch von Co(en)3+3 für Na erwies sich als außerordentlich günstig, und es besteht eine Tendenz zur Absonderung der beiden Kationenarten in den untersuchten gemischten Tonsorten. Kleine Mengen Co(en)3+3 senken, wie erwiesen wurde, die Stickstoffsorptionsfähigkeit von Na+ Montmorillonit, während Tonarten mit hohem Co(en)3+3 Gehalt eine stark erhöhte Sorption aufwiesen. Dies wurde dadurch erklärt, daß Co(en)3+3 bei der Bestimmung der Art und des Ausmaßes der Stickstoffsorption in dem ausgetauschten Montmorillonit eine doppelte Rolle spielt.
Резюме
Изучался процесс обмена катионов трис-(этилендиамин) кобальта (III) и Na+ монтмориллонита посредством ядерной абсорбционной спектроскопии, рентгеновской дифракции, дифференциального термического анализа и сорбции азота при 78°К. Нашли, что обмен Со(еп)3+3 для Na+ был очень благоприятный, но с тенденцией сегрегации двух видов катионов в изучаемых смешанных глинах. Заметили, что небольшое количество Со(еп)3+3 понижает способность сорбции азота монтмориллонитом Na+, в то время как высокое содержание Со(еп)3+3 в глинах очень повышает их сорбцию. Объясняется это двойной ролью Со(еп)3+3 в установлении какое количество азота абсорбируется обменным монтмориллонитом.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alymore, L. A. G., Sills, I. D. and Quirk, J. P. (1970) Surface area of homoionic illite and montmorillonite clay minerals as measured by the sorption of nitrogen and carbon dioxide: Clays and Clay Minerals 18, 91–96.
Aylmore, L. A. G. and Quirk, J. P. (1967) The micropore size distributions of clay mineral systems: J. Soil. Sci. 18, 1–17.
Barrer, R. M. and Millington, A. D. (1967) Sorption and intracrystalline porosity in organo-clays: J. Colloid Sci. 25, 359–372.
Barrer, R. M. and Brummer, K. (1963) Relations between partial ion exchange and interlamellar sorption in alkylammonium montmorillonites: Trans. Faraday Soc. 59, 959–968.
Glaeser, R. and Mering, J. (1954) Isotherms d’hydration des montmorillonites bi-ioniques (Na, Ca): Clay Minerals Bull. 2(12), 188–193.
Gregg, S. S. and Sing, K. S. W. (1967) Adsorption Surface Area and Porosity, p. 195. Academic Press. New York.
Grim, R. E. (1968) Clay Mineralogy, p. 193. McGraw-Hill, New York.
MacEwan, D. M. C., Amil, A. R. and Brown, G. (1961) Interstratified clay minerals. In The X-ray Identification and Crystal Structure of Clay Minerals (Edited by Brown, G.). Mineralogical Society, London.
Nelson, F. M. and Eggertson, F. T. (1958) Adsorption measurements by a continuous flow method: Anal. Chem. 30, 1387–1390.
Sawhney, B. L. (1972) Selective sorption and fixation of cations by clay minerals: a review: Clays and Clay Minerals 20, 93–100.
Slabaugh, W. H. (1971) Surface chemistry of thermally decomposed organo-montmorillonite complexes: Clays and Clay Minerals 19, 201–204.
Thomas, J. and Bohor, B. F. (1968) Surface area of mont-morillonite from the dynamic sorption of nitrogen and carbon dioxide: Clays and Clay Minerals 16, 83–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knudson, M.I., McAtee, J.L. The Effect of Cation Exchange of Tris(Ethylenediamine)Cobalt (III) for Sodium on Nitrogen Sorption by Montmorillonite. Clays Clay Miner. 21, 19–26 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1973.0210105
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1973.0210105