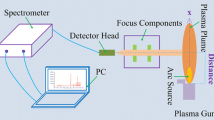
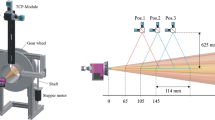
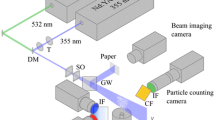
Abstract
Advances in digital imaging technology have enabled the development of sensors that can measure the temperature and velocity of individual thermal spray particles over a large volume of the spray plume simultaneously using imaging pyrometry (IP) and particle streak velocimetry (PSV). This paper describes calibration, uncertainty analysis, and particle measurements with a commercial IP-PSV particle sensor designed for measuring particles in an air plasma spray (APS) process. Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) and molybdenum powders were sprayed in the experiments. An energy balance model of the spray torch was used to manipulate the average particle velocity and temperature in desired ways to test the response of the sensor to changes in the spray characteristics. Time-resolved particle data were obtained by averaging particle streaks in each successive image acquired by the sensor. Frame average particle velocity and temperature were found to fluctuate by 10% during 6 s acquisition periods. These fluctuations, caused by some combination of arc instability, turbulence, and unsteady powder feeding, contribute substantially to the overall particle variability in the spray plume.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Gougeon, C. Moreau, and F. Richard: “On-Line Control of Plasma Sprayed Particles in the Aerospace Industry” in Advances in Thermal Spray Science and Technology, C.C. Berndt and S. Sampath, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1995, pp. 149–55.
M. Prystay, P. Gougeon, and C. Moreau: “Correlation between Particle Temperature and Velocity and the Structure of Plasma Sprayed Zirconia Coatings” in Thermal Spray: Practical Solutions for Engineering Problems, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1996, pp. 517–23.
R.N. Wright, J.R. Fincke, W.D. Swank, and D.C. Haggard: “Particle Velocity and Temperature Influences on the Microstructure of Plasma Sprayed Nickel” in Thermal Spray: Practical Solutions for Engineering Problems, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1996, pp. 511–16.
X. Jiang, J. Matejicek, A. Kulkarni, H. Herman, S. Sampath, D.L. Gilmore, and R.A. Neiser: “Process Maps for Plasma Spray Part II: Deposition and Properties” in Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering via Applied Research, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2000, pp. 157–63.
R.L. Williamson, J.R. Fincke, and C.H. Chang: “A Computational Examination of the Sources of Statistical Variance in Particle Parameters During Thermal Plasma Spraying” in Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering via Applied Research, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2000, pp. 115–24.
J.R. Fincke, W.D. Swank, D.C. Haggard, T.M. Demeny, S.M. Pandit, and A.R. Kashani: “Feedback Control of the Subsonic Plasma Spray Process: System Model” in Advances in Thermal Spray Science and Technology, C.C. Berndt and S. Sampath, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1995, pp. 117–22.
G. Bourque, M. Lamontagne, and C. Moreau: “A New Sensor for On-Line Monitoring the Temperature and Velocity of Thermal Spray Particles” in Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering via Applied Research, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2000, pp. 45–50.
J. Zierhut, K.D. Landes, W. Krömmer, and P. Heinrich: “Particle Flux Imaging (PFI) In-Situ Diagnostics for Thermal Coating Process” in Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering via Applied Research, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2000, pp. 63–66.
J.R. Fincke and W.D. Swank: “Air-Plasma Spraying of Zirconia: Spray Characteristics and Standoff Distance Effect on Deposition Efficiency and Porosity” in Thermal Spray: International Advances in Coatings Technology, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1992, pp. 513–18.
C.M. Hackett and G.S. Settles: “Independent Control of HVOF Particle Velocity and Temperature” in Thermal Spray: Practical Solutions for Engineering Problems, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1996, pp. 665–73.
B.M. Cetegen and W. Yu: “In-Situ Particle Temperature, Velocity, and Size Measurements in DC Arc Plasma Thermal Sprays,” J. Thermal Spray Technol., 1999, 8(1), pp. 57–67.
K. Hollis and R. Neiser: “Particle Temperature and Flux Measurement Utilizing a Nonthermal Signal Correction Process,” J. Thermal Spray Technol., 1998, 7(3), pp. 392–402.
J.R. Fincke, C.L. Jeffery, and S.B. Englert, “In-Flight Measurement of Particle Size and Temperature,” J. Phys. E: Sci. Instrum., 1988, 21, pp. 367–70.
J.E. Craig, R.A. Parker, D.Y. Lee, F.S. Biancaniello, and S.D. Ridder: “A Two-Wavelength Imaging Pyrometer for Measuring Particle Temperature, Velocity and Size in Thermal Spray Processes” in Proceedings of the International Symposium on Advanced Sensors for Metal Processing, Industrial Materials Institute, NRC Canada, 1999, pp. 369–80.
J.E. Craig, R.A. Parker, D.Y. Lee, F.S. Biancaniello, S.D. Ridder, and S.P. Mates: “Particle Temperature Measurements by Spectroscopic and Two-Wavelength Streak Imaging” in Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering via Applied Research, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2000, pp. 51–56.
A. Cezairliyan, “Design and Operational Characteristics of a High-Speed (Millisecond) System for the Measurement of Thermophysical Properties at High Temperatures,” J. Res. Nat. Bur. Stand. (U.S.), 1971, 75C(1), p. 7.
A. Cezairliyan, S. Krishnan, and J.L. McClure: “Simultaneous Measurements of Normal Spectral Emissivity by Spectral Radiometry and Laser Polarimetry at High Temperatures in Millisecond-Resolution Pulse-Heating Experiments: Application to Molybdenum and Tungsten,” Int. J. Thermophys., 1996, 17(6), pp. 1455–73.
D. Basak, U.R. Kattner, J.L. McClure, D. Josell, and A. Cezairliyan: “Application of Laser Polarimetry to the Measurement of Specific Heat Capacity and Enthalpy of the Alloy 53Nb-47Ti (Mass%) in the Temperature Range 1600 to 2000 K by a Millisecond-Resolution Pulse Heating Technique,” Int. J. Thermophys., 2000, 21(4), pp. 913–26.
D.P. Dewitt and G.D. Nutter: Theory and Practice of Radiation Thermometry, John Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1988.
F.A. Graybill and H.K. Iyer: Regression Analysis: Concepts and Applications, Duxbury Press, Belmont, CA, 1994.
P. Gougeon and C. Moreau: “In-Flight Particle Surface Temperature Measurement: Influence of the Plasma Light Scattered by the Particles” in Thermal Spray Coatings: Research, Design and Applications, C.C. Berndt and T.F. Bernecki, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1993, pp. 13–18.
L. Leblanc and C. Moreau: “Study on the Long-Term Stability of Plasma Spraying” in Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering via Applied Research, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2000, pp. 1233–39.
E. Pfender: “Heat and Momentum Transfer to Particles in Thermal Plasma Flows,” Pure Appl. Chem., 1985, 57(9), pp. 1179–95.
C.M. Hackett, G.S. Settles, and J.D. Miller: “On the Gas Dynamics of HVOF Thermal Sprays,” J. Thermal Spray Technol., 1994, 3(3), pp. 299–304.
E. Pfender: “Plasma Jet Behavior and Modeling Associated with the Plasma Spray Process,” Thin Solid Films, 1994, 238, pp. 228–41.
C.H. Chang and J.D. Ramshaw: “Modeling of Non-Equilibrium Effects in a High-Velocity Nitrogen-Hydrogen Plasma Jet,” Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 1996, 16, pp. 5S-17S.
M.I. Boulos, P. Fauchais, and E. Pfender: Thermal Plasmas, Fundamentals and Applications, Vol. 1, Plenum, New York, 1994.
A. Vardelle, P. Fauchais, B. Dussoubs, and N.J. Themelis: “Heat Generation and Particle Injection in a Thermal Plasma Torch,” Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 1998, 18(4), pp. 551–74.
F.S. Biancaniello, J.J. Conway, P.I. Espina, G.E. Mattingly, and S.D. Ridder: “Particle Size Measurement of Inert-Gas-Atomized Powder,” Mater. Sci. Eng., 1990, A124, pp. 9–14.
A.H. Lefevbre: Atomization and Sprays, Hemisphere, New York, 1989.
D.P.H. Hasselman, L.F. Johnson, L.D. Bentsen, R. Syed, H.L. Lee, and M.V. Swain: “Thermal Diffusivity and Conductivity of Dense Polycrystalline ZrO2 Ceramics: A Survey,” Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull., 1987, 66(5), pp. 799–806.
M. Vardelle, A. Vardelle, A.C. Leger, P. Fauchais, and D. Gobin: “Influence of Particle Parameters at Impact on Splat Formation and Solidification in Plasma Spraying Processes,” J. Thermal Spray Technol., 1995, 4(1), pp. 50–58.
F.M. White: Heat and Mass Transfer, Addison-Wesley, New York, 1991.
M. Vardelle, A. Vardelle, B. Dussoubs, P. Fauchais, T.J. Roemer, R.A. Neiser, and M.F. Smith: “Influence of Injector Geometry on Particle Trajectories: Analysis of Particle Dynamics in the Injector and Plasma Jet” in Thermal Spray: Meeting the Challenges of the 21st Century, C. Coddet, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1998, pp. 887–94.
D.L. Gilmore, R.A. Neiser, Y. Wan, and S. Sampath: “Process Maps for Plasma Spray Part I: Plasma-Particle Interactions” in Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering via Applied Research, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2000, pp. 149–55.
J.R. Fincke, R.L. Williamson, and C.H. Chang: “Plasma Spraying of Functionally Graded Materials: Measured and Simulated Results” in Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering via Applied Research, C.C. Berndt, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2000, pp. 141–48.
J.R. Fincke and R.A. Neiser: “Advanced Diagnostics and Modeling of Spray Processes,” MRS Bulletin, Materials Research Society, 2000, 25(7), pp. 26–31.
I. Ahmed and T.L. Bergman: “Three-Dimensional Simulation of Thermal Plasma Spraying of Partially Molten Ceramic Agglomerates,” J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2000, 9(2), pp. 215–24.
Z. Duan, L. Beall, J. Schein, J. Heberlein, and M. Stachowicz: “Diagnostics and Modeling of an Argon/Helium Plasma Spray Process,” J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2000, 9(2), pp. 225–34.
J.T. Walker, “Advances in Coriolis Technology for Precision Flow and Density Measurements of Industrial Fluids” in Proceedings of the Annual Symposium on Instrumentation for the Process Industries, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, 1992, pp. 69–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mates, S.P., Basak, D., Biancaniello, F.S. et al. Calibration of a two-color imaging pyrometer and its use for particle measurements in controlled air plasma spray experiments. J Therm Spray Tech 11, 195–205 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1361/105996302770348853
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105996302770348853