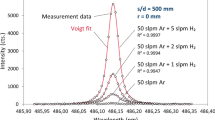
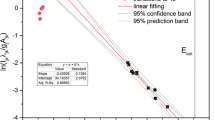
Abstract
Low pressure plasma spraying (LPPS) is a thermal spraying technique that has found a niche for low oxidation products. It uses a low pressure environment (i.e., chamber pressure between 2 and 90 kPa) and yields supersonic plasma jets. The enthalpy probe technique is a common measurement method in plasmas. However LPPS jets are difficult to diagnose as their supersonic nature forces the apparition of a shock wave in front of any measuring device inserted in the jet. Incomplete or erroneous assumptions are usually invoked to overcome the difficulties associated with this shock wave and carry out the LPPS jet diagnosis from enthalpy probe measurements. In this work, a new device is designed to gain access to an additional physical quantity, which is needed to assess the aerodynamic non-equilibrium state of the jet. It is combined with enthalpy probe measurements, and the resulting set of experimental data is used with a numerical procedure based on gas dynamics theory, yielding free-stream supersonic plasma jet values from the measurements behind the induced shock wave. The results agree well with the phenomenology of supersonic jets in aerodynamic nonequilibrium. However this new method is restricted by the local thermodynamic equilibrium assumption, which is directly linked with the pressure and temperature conditions of the plasma jet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Fauchais and M. Vardelle, Plasma Spraying: Present and Future, Pure Appl. Chem., Vol 66 (No. 6), 1994, p 1247–1258
R.W. Smith and R. Novak, Thermal Spraying: Advances and Applications in US Thermal Spray Technology I. Technology and Materials, Powder Metall. Int., Vol 23 (No. 3), 1991, p 147–155
E. Pfender, Thermal Plasma Technology: Where Do We Stand and Where Are We Going?, Plasma Chem. Plasma P., Vol 19 (No. 1), 1999, p 1–31
P. Fauchais, A. Vardelle, and B. Dussoubs, Quo Vadis Thermal Spraying?, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 10(1), 2001, p 44–66
P. Fauchais and A. Vardelle, Thermal Plasmas, IEEE T. Plasma Sci., Vol 25 (No. 6), 1997, p 1258–1280
P. Fauchais, Thermal Plasma Engineering Today in Western Europe, High Temp. Chem. Proc., Vol 1, 1992, p 1–43
L. Prandtl, Essential of Fluid Dynamics, Hafner Publishing Company, New York, NY, 1952, 452 p 268
P.J. Meyer and D. Hawley, Electro-Plasma Inc. LPPS Production Systems, Thermal Spray Coatings: Properties, Processes and Applications, T.F. Benecki, Ed., May 4–10, 1991 (Pittsburgh, PA), ASM International, 1992, p 29–38
J. Grey, Thermodynamic Methods of High-Temperature Measurement, ISA T., Vol 4 (No. 2), 1965, p 102–115
J. Grey, P.F. Jacobs, and M.P. Sherman, Calorimetric Probe for the Measurement of Extremely High Temperatures, Rev. Sci. Instrum., Vol 33 (No. 7), 1962, p 738–741
S. Katta, J.A. Lewis, and W.H. Gauvin, A Plasma Calorimetric Probe, Rev. Sci. Instrum., Vol 44 (No. 10), 1973, p 1519–1523
F.A. Vassallo, “Miniature Enthalpy Probes for High Temperature Gas Streams,” Aerospace Research Laboratories (USAF), Paper ARL 66-0115, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, OH, 1966.
F.J. Huber, “Probes for Measuring Mass Flux, Stagnation Point Heating, and Total Enthalpy of High Temperature Hypersonic Gas Flows,” AIAA Aerodynamic Testing Conference, AIAA Paper No. 66-750, Los Angeles, CA, Sept 1966
F.A. Vassallo, “A Fast Acting Miniature Enthalpy Probe, AIAA Aerodynamic Testing Conference,” AIAA Paper No.68-391, San Francisco, CA, April 1968
J. Grey and P.F. Jacobs, Experiments on Turbulent Mixing in a Partially Ionized Gas, AIAA J., Vol 2 (No. 3), 1964, p 433–438
J. Grey, M.P. Sherman, P.M. Williams, and D.B. Fradkin, Laminar Arc-jet Mixing and Heat Transfer: Theory and Experiments, AIAA J., Vol 4 (No. 6), 1965, p 986–993
T.J. O’Connor, E.H. Comfort, and L.A. Cass, Turbulent Mixing of an Axisymmetric Jet of Partially Dissociated Nitrogen with Ambient Air, AIAA J., Vol 4 (No. 11), 1966, p 2026–2032
L.A. Anderson and R.E. Sheldahl, Experiments with Two Flow-Swallowing Enthalpy Probes in High-Energy Supersonic Streams, AIAA J., Vol 9 (No. 9), 1971, p 1804–1810
M. Brossa and E. Pfender, Probe Measurements in Thermal Plasma Jets, Plasma Chem. Plasma P., Vol 8 (No. 1), 1988, p 75–90
E. Pfender, J.R. Fincke, and R. Spores, Entrainment of Cold Gas into Thermal Plasma Jets, Plasma Chem. Plasma P., Vol 11 (No. 4), 1991, p 529–543
A. Capetti and E. Pfender, Probe Measurements in Argon Plasma Jets Operated in Ambient Argon, Plasma Chem. Plasma P., Vol 9 (No. 2), 1989, p 329–341
W.D. Swank, J.R. Fincke, and D.C. Haggard, Modular Enthalpy Probe and Gas Analyzer for Thermal Plasma Measurements, Rev. Sci. Instrum., Vol 64 (No. 1), 1993, p 56–62
J.R. Fincke, C.H. Chang, W.D. Swank, and D.C. Haggard, Entrainment and Demixing in Subsonic Thermal Plasma Jets: Comparison of Measurements and Predictions, Int. J. Heat Mass Tran., Vol 37, 1994, p 1673–1682
J.R. Fincke, W.D. Swank, S.C. Snyder, and D.C. Haggard, Enthalpy Probe Performance in Compressible Thermal Plasma Jets, Rev. Sci. Instrum., Vol 64 (No. 12), 1993, p 3585–3593
M. Hollenstein, M. Rahmane, and M.I. Boulos, Aerodynamic Study of the Supersonic Induction Plasma Jet, M. Hrabovský, M. Konrád, and V. Kopecký, Ed., Organizing Committee of the 14th International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry, Prague, Czech Republic, 1999, p 257–261
J.R. Fincke, S.C. Snyder, and W.D. Swank, Comparison of Enthalpy Probe and Laser Light Scattering Measurement of Thermal Plasma Temperatures and Velocities, Rev. Sci. Instrum., Vol 64 (No. 3), 1993, p 711–718
M. Rahmane, G. Soucy, and M.I. Boulos, Analysis of the Enthalpy Probe Technique for Thermal Plasma Diagnostics, Rev. Sci. Instrum., Vol 66 (No. 6), 1995, p 3424–3431
J.-L. Dorier, M. Gindrat, C. Hollenstein, M. Loch, A. Refke, A. Salito, and G. Barbezat, Plasma Jet Properties in a New Spraying Process at Low Pressure for Large Area Thin Film Deposition, Thermal Spray 2001: New Surfaces for a New Millenium, C.C. Berndt, K.A. Khor, and E.F. Lugscheider, Ed., May 28–30, 2001 (Singapore), ASM International, 2001, p 759–764
A.H. Shapiro, The Dynamics and Thermodynamics of Compressible Fluid Flow, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1953, 647, p 76–115
R. Henne, M. Müller, E. Proß, G. Schiller, F. Gitzhofer, and M.I. Boulos, Near-Net-Shape Forming of Metallic Bipolar Plates for Planar Solid Oxide Fuel Cells by Induction Plasma Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., Vol 8 (No. 1), 1999, p 110–116
M. Gindrat, J-L. Dorier, C. Hollenstein, M. Loch, A. Refke, A. Salito, and G. Barbezat, Effect of Specific Operating Conditions on the Properties of LPPS Plasma Jets Expanding at Low Pressure, International Thermal Spray Conference, E. Lugscheider and C.C. Berndt, Ed., May 4–6, 2002 (Düsseldorf, Germany), DVS Deutscher Verband für Schweißen, DVS-Verlag GmBH, 2002, p 459–464
B. Jodoin, M. Gindrat, J-L. Dorier, C. Hollenstein, M. Loch, and G. Barbezat, Modelling and Diagnostics of a Supersonic DC Plasma Jet Expanding at Low Pressure, International Thermal Spray Conference, E. Lugscheider and C.C. Berndt, Ed., May 4–6, 2002 (Düsseldorf, Germany), DVS Deutscher Verband für Schweißen, DVS-Verlag GmBH, 2002, p 716–720
J-L. Dorier, B. Jodoin, M. Gindrat, A. Blais, C. Hollenstein, and G. Barbezat, A Novel Approach to Interpret Enthalpy Probe Measurements in Low Pressure Supersonic Plasma Jets, R. D’Agostino, Ed., Organizing Committee of the 16th International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry, Taormina, Italy, 2003
Y. Bartosiewicz, P. Proulx, and Y. Mercadier, A Self-Consistent Two-Temperature Model for the Computation of Supersonic Argon Plasma Jets, J. Phys. D App. Phys., Vol 35, 2002, p 2139–2148
A.B. Murphy and C.J. Arundell, Transport Coefficients of Argon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon-Nitrogen, and Argon-Oxygen Plasmas, Plasma Chem. Plasma P., Vol 14 (No. 4), 1994, p 451–490
M.I. Hoffert and H. Lien, Quasi-One-Dimensional, Nonequilibrium Gas Dynamics of Partially Ionized Two-Temperature Argon, Phys. Fluids, Vol 10 (No. 8), 1967, p 1769–1776
E.P. Muntz, B.B. Hamel, and B.L. Maguire, Some Characteristics of Exhaust Plume Rarefaction, AIAA J., Vol 8 (No. 9), 1970, p 1651–1658
J. Grey, Sensitivity Analysis for the Calorimetric Probe, Rev. Sci. Instrum., Vol 34 (No. 8), 1963, p 857–859
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blais, A., Jodoin, B., Dorier, JL. et al. Inclusion of aerodynamic non-equilibrium effects in supersonic plasma jet enthalpy probe measurements. J Therm Spray Tech 14, 342–353 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1361/105996305X59387
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105996305X59387