Abstract
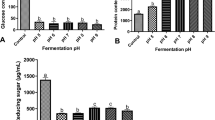
Solid-state fermentation of coconut oil cake has been carried out with Rhizopus oligosporus for the production of phytase. Phytase is used commercially in the animal feed industry to improve animal performance because there is a substantial and growing interest among swine and poultry producers in the application of phytase to improve the nutritional quality in animal feeds. Demonstrated benefits include improved feed yield ratios and reduction in the environmental costs associated with the disposal of animal wastes. We report the production of extracellular phytase by R. oligosporus under solid-state fermentation using coconut oil cake as substrate. Maximal enzyme production (14.29 U/g of dry substrate) occurred at pH 5.3, 30°C, and 54.5% moisture content after 96 h of incubation. The addition of extra nutrients to the substrate resulted in inhibition of product formation. The results indicate the scope for production of phytase using coconut oil cake as solid substrate without additional nutrients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martinez, C., Ros, G., Periago, M. J., Lopez, G., Ortuno, J., and Rincon (1996), Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2(4), 201–209.
Pandey, A. (1992), Process Biochem. 27, 109–117.
Pandey, A. (1994), in Solid State Fermentation, Pandey, A. (ed.), Wiley Eastern Limited, New Delhi, pp. 3–10.
Pandey, A., Soccol, C. R., and Mitchell, D. A. (2000), Process Biochem. 35, 1153–1169.
Pandey, A., Szakacs, G., Soccol, C. R., Rodriguez, A., and Soccol, V. T. (2001), Bioresour. Technol. 77, 203–214.
Tengerdy, R. P., Szakacs, G., and Sicopz, J. (1997), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 57/58, 563–569.
Pandey, A., Selvakumar, P., Soccol, C. R., Soccol, V. T., Krieger, N., and Fontana, J. D. (1999), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 81, 35–52.
Pandey, A., Soccol, C. R., Benjamin, S., Krieger, N., and Soccol, V. T. (1999), Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 29, 119–132.
Harland, B. F. and Harland, J. (1980), Cereal Chem. 57(3), 226–229.
Sailas, B. (1997), PhD thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin, India.
Ramesh, M. V. and Lonsane, B. K. (1987), Biotechnol. Lett. 9(5), 323–328.
Prabhu, G. N. (1996), PhD thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabu, A., Sarita, S., Pandey, A. et al. Solid-state fermentation for production of phytase by Rhizopus oligosporus . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 102, 251–260 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:102-103:1-6:251
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:102-103:1-6:251