Abstract
A 5 ton/d pilot scale two-phase anaerobic digester was constructed and tested to treat Korean food wastes in Anyang city near Seoul.
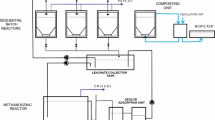
The easily degradable presorted food waste was efficiently treated in the two-phase anaerobic digestion process. The waste contained in plastic bags was shredded and then screened for the removal of inert materials such as fabrics and plastics, and subsequently put into the two-stage reactors. Heavy and light inerts such as bones, shells, spoons, and plastic pieces were again removed by gravity differences. The residual organic component was effectively hydrolyzed and acidified in the first reactor with 5 d space time at pH of about 6.5. The second, methanization reactor converted the acids into methane with pH between 7.4 and 7.8. The space time for the second reactor was 15 d. The effluent from the second reactor was recycled to the first reactor to provide alkalinities.
The process showed stable steady-state operation with the maximum organic loading rate of 7.9 kg volatile solid (VS)/m3/d and the volatile solid reduction efficiency of about 70%. The total of 3.6 tons presorted MSW containing 2.9 tons of food organic was treated to produce about 230 m3 of biogas with 70% (v/v) of methane and 80 kg of humus.
This process is extended to full-scale treating 15 tons of food waste a day in Euiwang city and the produced biogas is utilized for the heating/cooling of adjacent buildings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korea Ministry of Environment (KMOE) (1998), White Book of Environment, pp. 710–712.
Fouhy, K. (1993), Chemical Engineering/May 1993, 45–48.
International Energy Agency (IEA) (1994), Biogas from municipal solid waste, Technical Brochure (IEA Bio-energy Agreement Task XI; MSW conversion, to energy ed.)
Cho, J. K., Park, S. C., and Chang, H.N. (1995), Biores. Technol. 52, 245–253.
Ghosh, S., Henry, M. P., and Sajjad, A. (1983), Novel two-phase anaerobic gasification with solid-bed acid digestion in tandem with fixed-film methane fermentation. Proc. Int. Gas Res. Conf., London, June 13–16, 1983.
Anderson, G. K. and Saw, C. B. (1992), Proceedings of the Symposium on Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Waste, Venice, April 14–17, 1992, pp. 171–179.
Chanakya, H. N., Borgaonkar, S., Meena, G., and Jagadish, K. S. (1993), Biores. Technol 46, 227–231.
Pavan, P., Mussaco, A., Battistoni, P., Mata-Alvarez, J., and Cecchi, F. (1996), in Management of Urban Biodegradable Wastes, Hansen, J.-A., ed., James & James Ltd., London, pp. 125–131.
Cho, J. K., Kim, B. S., Park, S. C., Choi, Y. S., and Chang, H. N. (1996), Biomass Bioenergy 10, 1, 25–35.
Brinkmann, J. and Hack, P. J. F. M. (1996), in Management of Urban Biodegradable Wastes, Hansen, J.-A., ed., James & James Ltd., London, pp. 181–192.
Cho, J. K., Lee, J. P., Lee, J. S., Park, S. C., and Chang, H. N. (1996), J. Korean Solid Waste Eng. Soc. 13, 5, 616–624.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author to whom all correspondence and reprint requests should be addressed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.P., Lee, J.S. & Park, S.C. Two-phase methanization of food wastes in pilot scale. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 79, 585–593 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:79:1-3:585
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:79:1-3:585