Summary
Background. Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) has been demonstrated in various human cancers, including colorectal cancer. Thus, overexpression of COX-2 may be involved in the growth and progression of cancer, and this may have prognostic significance.
Aim. The aim of our study is to evaluate the expression of COX-2 in colorectal cancer tissue, and to examine the relationship of its expression to various clinicopathological parameters and patient survival.
Methods. Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue blocks were obtained from 60 patients who underwent surgery for colorectal carcinoma in 1995 at the Chonnam National University Hospital in Gwangju, Korea. We have used an immunohistochemical technique to localize COX-2 in colorectal carcinoma tissues.
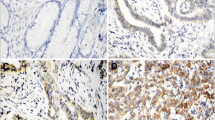
Results. Immunohistochemical staining of the colorectal cancer specimens demonstrated that COX-2 expression was localized to the carcinoma cells and was not detectable in the stromal compartment of the cancers. The COX-2 immunostaining pattern was predominantly homogenous, and perinuclear cytoplasmic within the tumors. Normal colonic epithelium adjacent to the tumor showed no staining for COX-2. The COX-2 protein was detected in 70% (42/60) of colorectal carcinoma tissues. However, no significant correlation was found between COX-2 expression and various clinicopathological parameters, including histologic grade, tumor size, depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, or stage. Furthermore, COX-2 expression did not correlate with patient survival (p=0.401).
Conclusion. These results suggest that COX-2 expression may play an important role in the evolution of colon carcinogenesis. However, further studies are needed to determine the prognostic relevance of COX-2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thun MJ, Namboodiri MM, Heath CW. Aspirin use and reduced risk of fatal colon cancer. N Engl J Med 1991;325:1593–1596.
Thun MJ, Namboodiri MM, Calle EE, et al. Aspirin use and risk of fatal cancer. Cancer Res 1993;53:1322–1327.
Giovannucci E, Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, et al. Aspirin use and the risk for colorectal cancer and adenoma in male health professionals. Ann Intern Med 1994;121:241–246.
Giovannucci E, Egan KM, Hunter DJ, et al. Aspirin and the risk of colorectal cancer in women. N Engl J Med 1995;333:609–612.
Dubois RN, Abramson SB, Crofford L, et al. Cyclooxygenase in biology and disease. FASEB J 1998;12:1063–1073.
Herschman HR, Xie W, Reddy S. Inflammation, reproduction, cancer and all that.… The regulation and role of the inducible prostaglandin synthase. Bioessays 1995;17:1031–1037.
Subbaramaiah K, Zakim D, Weksler BB, et al. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase: a novel approach to cancer prevention. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1997;216:201–210.
Taketo MM. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in tumorigenesis (part I). J Natl Cancer Inst 1998;90:1529–1536.
Taketo MM. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in tumorigenesis (Part II). J Natl Cancer Inst 1998;90:1609–1620.
Herschman HR. Prostaglandin synthase 2. Biochim Biophys Acta 1996;1299:125–140.
Williams CW, DuBois RN. Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase: why two isoforms? Am J Physiol 1996;270:393–400.
Oshima M, Dinchuk JE, Karman SL, et al. Suppression of intestinal polyposis in APC716 knock out mice by inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 (cox-2). Cell 1996;87:803–809.
Kawamori T, Rao CV, Seibert K. Chemopreventive activity of celecoxib, a specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, against colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 1998;58:409–412.
Kargman SL, O’Neill GP, Vickers PJ, et al. Expression of prostaglandin G/H synthase-1 and -2 protein in human colon cancer. Cancer Res 1995;55:2556–2559.
Hwang D, Scollard D, Byrne J, et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 in human breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 1998;90:455–460.
Wolff H, Saukkonen K, Anttila S, et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human lung carcinoma. Cancer Res 1998;58:4997–5001.
Uefuji K, Ichikura T, Mochizuki H, et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 protein in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol 1998;69:168–172.
Zimmermann KC, Sarbia M, Weber AA, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human esophageal carcinoma. Cancer Res 1999;59:198–204.
Tsujii M, DuBois RN. Alterations in cellular adhesion and apoptosis in epithelial cells overexpressing prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2. Cell 1995;83:493–501.
Tsujii M, Kawano S, Tsuji S, et al. Cyclooxygenase regulates angiogenesis induced by colon cancer cells. Cell 1998;93:705–716.
Huang M, Stolina M, Sharma S, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer cyclooxygenase-2-dependent regulation of cytokine balance in lymphocytes and macrophages: up-regulation of interleukin 10 and down-regulation of interleukin 12 production. Cancer Res 1998;58:1208–1216.
Kojima M, Morisaki T, Uchiyama A, et al. Association of enhanced cyclooxygenase-2 expression with possible local immunosuppression in human colorectal carcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol 2001;8:458–465.
Reed JA, Manahan LJ, Park CS, et al. Complete one-hour immunohistochemistry based on capillary action. Biotechniques 1992;13:434–443.
Eberhart CE, Coffey RJ, Radhika A, et al. Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression in human colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas. Gastroenterology 1994;107:1183–1188.
O’Neill GP, Ford-Hutchinson AW. Expression of mRNA for cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 in human tissues. FEBS Lett 1993;330:156–160.
Gustafson-Svard C, Lilja I, Hallbook O, et al. Cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression in human colorectal adenocarcinomas and in azoxymethane induced colonic tumours in rats. Gut 1996;38:79–84.
Dimberg J, Samuelsson A, Hugander A, et al. Differential expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human colorectal cancer. Gut 1999;45:730–732.
Sinicrope FA, Lemoine M, Xi L, et al. Reduced expression of cyclooxygenase 2 proteins in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancers relative to sporadic cancers. Gastroenterology 1999;117:350–358.
Heath CW Jr, Thun MJ, Greenberg ER, et al. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and human cancer. Report of an interdisciplinary research workshop. Cancer 1994;74:2885–2888.
Steinbach G, Lynch PM, Phillips RK, et al. The effect of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1946–1952.
Murata H, Kawano S, Tsuji S, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression enhances lymphatic invasion and metastasis in human gastric carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol 1999;94:451–455.
Lim HY, Joo HJ, Choi JH, et al. Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 protein in human gastric carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:519–525.
Cianchi F, Cortesini C, Bechi P, et al. Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression correlates with tumor angiogenesis in human colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2001;121:1339–1347.
Sheehan KM, Sheahan K, O’Donoghue DP, et al. The relationship between cyclooxygenase-2 expression and colorectal cancer. JAMA 1999;282:1254–1257.
Tomozawa S, Tsuno NH, Sunami E, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression correlates with tumour recurrence, especially haematogenous metastasis, of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2000;83:324–328.
Sheng H, Shao J, Morrow JD, et al. Modulation of apoptosis and Bcl-2 expression by prostaglandin E2 in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 1998;58:362–366.
Tsujii M, Kawano S, DuBois RN. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human colon cancer cells increases metastatic potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94:3336–3340.
Kambayashi T, Alexander AR, Fong M, et al. Potential involvement of IL-10 in suppressing tumour-associated macrophages. Colon-26-derived prostaglandin E2 inhibits TNF-alpha release via a mechanism involving IL-10. J Immunol 1995;154:3383–3390.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joo, YE., Kim, HS., Min, SW. et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 protein in colorectal carcinomas. Int J Gastrointest Canc 31, 147–154 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/IJGC:31:1-3:147
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IJGC:31:1-3:147