Abstract
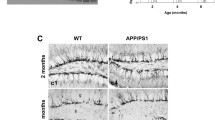
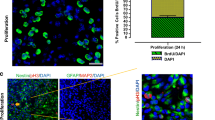
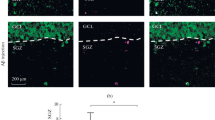
The adult mammalian brain contains populations of stem cells that can proliferate and then differentiate into neurons or glia. The highest concentration of such neural progenitor cells (NPC) is located in the subventricular zone (SVZ) and these cells can produce new olfactory bulb and cerebral cortical neurons. NPC may provide a cellular reservoir for replacement of cells lost during normal cell turnover and after brain injury. However, neurogenesis does not compensate for neuronal loss in age-related neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), suggesting the possibility that impaired neurogenesis contributes to the pathogenesis of such disorders. We now report that amyloid β-peptide (Aβ), a self-aggregating neurotoxic protein thought to cause AD, can impair neurogenesis in the SVZ/cerebral cortex of adult mice and in human cortical NPC in culture. The proliferation and migration of NPC in the SVZ of amyloid precursor protein (APP) mutant mice, and in mice receiving an intraventricular infusion of Aβ, were greatly decreased compared to control mice. Studies of NPC neurosphere cultures derived from human embryonic cerebral cortex showed that Aβ can suppress NPC proliferation and differentiation, and can induce apoptosis. The adverse effects of Aβ on neurogenesis were associated with a disruption of calcium regulation in the NPC. Our data show that Aβ can impair cortical neurogenesis, and suggest that this adverse effect of Aβ contributes to the depletion of neurons and the resulting olfactory and cognitive deficits in AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson S. A., Marin O., Horn C, Jennings K., and Rubenstein J. L. (2001) Distinct cortical migrations from the medial and lateral ganglionic eminences. Development 128, 353–363.
Begley J. G., Duan W., Chan S., Duff K., and Mattson M. P. (2001) Altered calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial dysfunction in cortical synaptic compartments of presenilin-1 mutant mice. J. Neurochem. 72, 1030–1039.
Buxbaum J. D., Thinakaran G., Koliatsos V., O’Callahan J., Slunt H. H., Price D. L., and Sisodia S. S. (1998) Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor in the rathippocampus: transport and processing through the perforant path. J. Neurosci. 18, 9629–9637.
Caldwell M. A., He X., Wilkie N., Pollack S., Marshall G., Wafford K. A., and Svendsen C. N. (2001) Growth factors regulate the survival and fate of cells derived from human neurospheres. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 475–479.
Chapman P. F., White G. L., Jones M. W., Cooper-Blacketer D., Marshall V. J., Irizarry M., et al. (1999) Impaired synaptic plasticity and learning in aged amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 271–276.
Chen G., Chen K. S., Knox J., Inglis J., Bernard A., Martin S. J., et al. (2000) A learning deficit related to age and beta-amyloid plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 408, 975–979.
Cheng B. and Mattson M. P. (1994) NT-3 and BDNF protect CNS neurons against metabolic/excitotoxic insults. Brain Res. 640, 56–67.
Devanand D. P., Michaels-Marston K. S., Liu X., Pelton G. H., Padilla M., Marder K., et al. (2000) Olfactory deficits in patients with mild cognitive impairment predict Alzheimer’s disease at follow-up. Am. J. Psychiatry 157, 1399–1405.
Duan W., Guo Z., and Mattson M. P. (2001) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediates an excitoprotective effect of dietary restriction in mice. J. Neurochem. 76, 619–626.
Gage F. H. (2000) Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 287, 1433–1438.
Gould E., Beylin A., Tanapat P., Reeves A., and Shors T. J. (1999) Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 260–265.
Guo Q., Fu W., Xie J., Luo H., Sells S. F., Geddes J. W., et al. (1998) Par-4 is a mediator of neuronal degeneration associated with the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. Nat. Med. 4, 957–962.
Guo Z. H. and Mattson M. P. (2000) Neurotrophic factors protect cortical synaptic terminals against amyloid and oxidative stress-induced impairment of glucose transport, glutamate transport and mitochondrial function. Cereb. Cortex 10, 50–57.
Haughey N. J., Nath A., Liu D., Chan S. L., Borchard A. C., Rao M. S., and Mattson M. P. (2001) Disruption of neurogenesis by amyloid β-peptide and perturbed calcium homeostasis in models of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Submitted.
Hauser K. F., Houdi A. A., Turbek C. S., Elde R. P., and Maxson W. III. (2000) Opioids intrinsically inhibit the genesis of mouse cerebellar granule neuron precursors in vitro: differential impact of mu and delta receptor activation on proliferation and neurite elongation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 1281–1293.
Hodges H., Veizovic T., Bray N., French S. J., Rashid T. P., Chadwick A., et al. (2000) Conditionally immortal neuroepithelial stem cell grafts reverse age-associated memory impairments in rats. Neuroscience 101, 945–55.
Hsiao K., Chapman P., Nilsen S., Eckman C., Harigaya Y., Younkin S., et al. (1996) Correlative memory deficits, Abeta elevation, and amyloid plaques in transgenic mice. Science 274, 99–102.
Ingram D. K., Weindruch R., Spangler E. L., Freeman J. R., and Walford R. L. (1987) Dietary restriction benefits learning and motor performance of aged mice. J. Gerontol. 42, 78–81.
Irizarry M. C., McNamara M., Fedorchak K., Hsiao K., and Hyman B. T. (1997) APPSw transgenic mice develop age-related A beta deposits and neuropil abnormalities, but no neuronal loss in CA1. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 56, 965–973.
Jankovski A., Garcia C., Soriano E., and Sotelo C. (1998) Proliferation, migration and differentiation of neuronal progenitor cells in the adult mouse subventricular zone surgically separated from its olfactory bulb. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10, 3853–3868.
Kempermann G., Kuhn H. G., and Gage F. H. (1997) More hippocampal neurons in adult mice living in an enriched environment. Nature 386, 493–495.
Kovacs T., Cairns N. J., and Lantos P. L. (2001) Olfactory centres in Alzheimer’s disease: olfactory bulb is involved in early Braak’s stages. Neuroreport 12, 285–288.
Kruman I., Bruce-Keller A. J., Bredesen D., Waeg G., and Mattson M. P. (1997) Evidence that 4-hydroxynonenal mediates oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis. J. Neurosci. 17, 5089–5100.
Kuhn H. G., Dickinson-Anson H., and Gage F. H. (1996) Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J. Neurosci. 16, 2027–2033.
Kwon Y. T. and Tsai L. H. (1998) A novel disruption of cortical development in p35(-/-) mice distinct from reeler. J. Comp. Neurol. 395, 510–522.
Larson J., Lynch G., Games D., and Seubert P. (1999) Alterations in synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices from young and aged PDAPP mice. Brain Res. 840, 23–35.
Lee J., Duan W., Long J. M., Ingram D. K., and Mattson M. P. (2000a) Dietary restriction increases survival of newly-generated neural cells and induces BDNF expression in the dentate gyrus of rats. J. Mol. Neurosci. 15, 99–108.
Lemaire V., Koehl M., Le Moal M., and Abrous D. N. (2000) Prenatal stress produces learning deficits associated with an inhibition of neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11,032–11,037.
Liu J., Solway K., Messing R. O., and Sharp F. R. (1998) Increased neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus after transient global ischemia in gerbils. J. Neurosci. 18, 7768–7778.
Loo D. T., Copani A., Pike C. J., Whittemore E. R., Walencewicz A. J., and Cotman C. W. (1993) Apoptosis is induced by beta-amyloid in cultured central nervous system neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 7951–7955.
Luskin M. B. (1998) Neuroblasts of the postnatal mammalian forebrain: their phenotype and fate. J. Neurobiol. 36, 221–233.
Mark R. J., Hensley K., Butterfield D. A., and Mattson M. P. (1995) Amyloid beta-peptide impairs ion-motive ATPase activities: evidence for a role in loss of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis and cell death. J. Neurosci. 15, 6239–6249.
Mark R. J., Keller J. N., Kruman I., and Mattson M. P. (1997) Basic FGF attenuates amyloid beta-peptide-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and impairment of Na+/K+-ATPase activity in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 756, 205–214.
Mattson M. P. (1990) Antigenic changes similar to those seen in neurofibrillary tangles are elicited by glutamate and Ca2+ influx in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron 4, 105–117.
Mattson M. P. (1992) Calcium as sculptor and destroyer of neural circuitry. Exp. Gerontol. 27, 29–49.
Mattson M. P., Cheng B., Davis D., Bryant K., Lieberburg I., and Rydel R. E. (1992) beta-amyloid peptides destabilize calcium homeostasis and render human cortical neurons vulnerable to excitotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 12, 376–389.
Mattson M. P. (1997) Cellular actions of beta-amyloid precursor protein and its soluble and fibrillogenic derivatives. Physiol. Rev. 77, 1081–1132.
Mattson M. P., Partin J., and Begley J. G. (1998) Amyloid beta-peptide induces apoptosis-related events in synapses and dendrites. Brain Res. 807, 167–176.
Mattson M. P (2000) Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 120–129.
Mattson M. P., LaFerla F. M., Chan S. L., Leissring M. A., Shepel P. N., and Geiger J. D. (2000) Calcium signaling in the ER: its role in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci. 23, 222–229.
Morys J., Sadowski M., Barcikowska M., Maciejewska B., and Narkiewicz O. (1994) The second layer neurones of the entorhinal cortex and the perforant path in physiological ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 54, 47–53.
Nilsson M., Perfilieva E., Johansson U., Orwar O., and Eriksson P. S. (1999) Enriched environment increases neurogenesis in the adult rat dentate gyrus and improves spatial memory. J. Neurobiol. 39, 569–578.
Nitta A., Fukuta T., Hasegawa T., and Nabeshima T. (1997) Continuous infusion of beta-amyloid protein into the rat cerebral ventricle induces learning impairment and neuronal and morphological degeneration. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 73, 51–57.
Roberts J. S., O’Rourke N. A., and McConnell S. K. (1993) Cell migration in cultured cerebral cortical slices. Dev. Biol. 155, 396–408.
Selkoe D. J. (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 81, 741–766.
Shoji M., Kanai M., Matsubara E., Tomidokoro Y., Shizuka M., Ikeda Y., et al. (2001) The levels of cerebrospinal fluid Abeta40 and Abeta42(43) are regulated age-dependently. Neurobiol. Aging 22, 209–215.
Shors T. J., Miesegaes G., Beylin A., Zhao M., Rydel T., and Gould E. (2001) Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature 410, 372–376.
Spitzer N. C. (1995) Spontaneous activity: functions of calcium transients in neuronal differentiation. Perspect. Dev. Neurobiol. 2, 379–386.
Teuchert-Noodt G., Dawirs R. R., and Hildebrandt K. (2000) Adult treatment with methamphetamine transiently decreases dentate granule cell proliferation in the gerbil hippocampus. J. Neural. Transm. 107, 133–143.
Uchida N., Buck D. W., He D., Reitsma M. J., Masek M., Phan T. V., et al. (2000) Weissman IL. Direct isolation of human central nervous system stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 14,720–14,725.
van Praag H., Kempermann G., and Gage F. H. (1999) Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 266–270.
Yankner B. A. (1996) Mechanisms of neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 16, 921–932.
Young D., Lawlor P. A., Leone P., Dragunow M., and During M. J. (1999) Environmental enrichment inhibits spontaneous apoptosis, prevents seizures and is neuroprotective. Nat. Med. 5, 448–453.
Zhu H., Guo Q., and Mattson M. P. (1999) Dietary restriction protects hippocampal neurons against the death-promoting action of a presenilin-1 mutation. Brain Res. 842, 224–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haughey, N.J., Liu, D., Nath, A. et al. Disruption of neurogenesis in the subventricular zone of adult mice, and in human cortical neuronal precursor cells in culture, by amyloid β-peptide. Neuromol Med 1, 125–135 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:1:2:125
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:1:2:125