Abstract
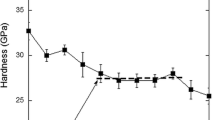
The depth dependence of hardness in a well-annealed single crystal of silver has been characterized in nanoindentation experiments. The work is based on similar experiments performed by Chen and Hendrickson, but extends their results to indent depths on the nanometer scale. The hardness is generally found to increase with decreasing depth, with a rather sharp increase observed at depths of less than 50 nm. Using etch pitting to reveal the surface dislocation structure after indentation, the sharp rise in hardness is found to be associated with the disappearance of dislocation rosette patterns and any signs of near-surface dislocation activity, thereby suggesting that very small scale indentation plasticity may take place by nondislocation mechanisms. However, order of magnitude calculations show that possible alternatives, specifically, diffusional mechanisms, are too slow to make significant contributions. It is suggested that for very small indents, either the surface dislocation debris is quickly annealed out before it can be observed or indentation plasticity is accommodated entirely by subsurface dislocation activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. B. Pethica, R. Hutchings, and W. C. Oliver, Philos. Mag. A 48, 593 (1983).
W. C. Oliver, R. Hutchings, and J. B. Pethica, in ASTM STP 889, edited by P. J. Blau and B. R. Lawn (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1986), pp. 90–108.
D. Newey, M. A. Wilkens, and H. M. Pollock, J. Phys. E: Sci. Instrum. 15, 119 (1982).
D. Stone, W. R. LaFontaine, P. Alexopoulos, T.-W. Wu, and Che-Yu Li, J. Mater. Res. 3, 141 (1988).
M. F. Doerner and W. D. Nix, J. Mater. Res. 1, 601 (1986).
J. Loubet, J. M. Georges, O. Marchesini, and G. Meille, J. Tribology 106, 43 (1984).
M. Kh. Shorshorov, S. I. Bulychev, and V. P. Alekhin, Sov. Phys. Dokl. 26, 769 (1982).
N. Gane and J. M. Cox, Philos. Mag. 22, 881 (1970).
G. P. Upit and S. A. Varchenya, in The Science of Hardness Testing and Its Research Applications, edited by J. H. Westbrook and H. Conrad (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1973), pp. 135–146.
A. A. Ivan’ko, Handbook of Hardness Data, edited by G. V. Samsanov (Israel Program for Scientific Translations, Jerusalem, 1971), p. 3.
C. C. Chen and A. A. Hendrickson, in The Science of Hardness Testing and Its Research Applications, edited by J. H. Westbrook and H. Conrad (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1973), pp. 274–290.
C. C. Chen and A. A. Hendrickson, J. Appl. Phys. 42, 2208 (1971).
C. C. Chen and A. A. Hendrickson, Metall. Trans. 2, 328 (1971).
S. N. G. Chu and J. C. M. Li, J. Mater. Sci. 12, 2200 (1977).
V. V. Gall, P. L. Gruzin, and G. Y. Yudina, Fiz. Metall. Metalloved 30, 950 (1970).
C. T. Tomizuka and E. Sonder, Phys. Rev. 103, 11 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pharr, G.M., Oliver, W.C. Nanoindentation of silver-relations between hardness and dislocation structure. Journal of Materials Research 4, 94–101 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1989.0094
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1989.0094