Abstract
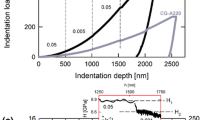
A nanoindentation strain-rate jump technique has been developed for determining the local strain-rate sensitivity (SRS) of nanocrystalline and ultrafine-grained (UFG) materials. The results of the new method are compared to conventional constant strain-rate nanoindentation experiments, macroscopic compression tests, and finite element modeling (FEM) simulations. The FEM simulations showed that nanoindentation tests should yield a similar SRS as uniaxial testing and generally a good agreement is found between nanoindentation strain-rate jump experiments and compression tests. However, a higher SRS is found in constant indentation strain-rate tests, which could be caused by the long indentation times required for tests at low indentation strain rates. The nanoindentation strain-rate jump technique thus offers the possibility to use single indentations for determining the SRS at low strain rates with strongly reduced testing times. For UFG-Al, extremely fine-grained regions around a bond layer exhibit a substantial higher SRS than bulk material.













Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
H. Gleiter: Nanostructured materials: Basic concepts and microstructure. Acta Mater. 48, 1 (2000).
R.Z. Valiev, I.V. Alexandrov, Y.T. Zhu, and T.C. Lowe: Paradoxon of strength and ductility in metals processed by SPD. J. Mater. Res. 17, 5 (2002).
K.S. Kumar, H. Van Swygenhoven, and S. Suresh: Mechanical behaviour of nanocrystalline metals and alloys. Acta Mater. 51, 5743 (2003).
J. May, H.W. Höppel, and M. Göken: Strain-rate sensitivity of ultra-fine grained aluminium produced by SPD. Scr. Mater. 53, 189 (2005).
Y.J. Li, J. Mueller, H.W. Höppel, M. Göken, and W. Blum: Deformation kinetics of nanocrystalline nickel. Acta Mater. 55, 5708 (2007).
A. Vevecka-Piftaj, A. Böhner, J. May, H.W. Höppel, and M. Göken: Strainrate sensitivity of ultrafine grained aluminium alloy AA6061. Mater. Sci. Forum 584, 741 (2008).
F. Dalla Torre, H. Van Swygenhoven, and M. Victoria: Nanocrystalline electrodeposited Ni: Microstructure and tensile properties. Acta Mater. 50, 3957 (2002).
H.W. Höppel, J. May, and M. Göken: Enhanced strength and ductility in ultrafine grained aluminium produced by ARB. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 781 (2004).
H. Vehoff, D. Lemaire, K. Schüler, T. Waschkies, and B. Yang: The effect of grain size on strain-rate sensitivity and activation volume—from nano to ufg nickel. Int. J. Mat. Res. 98, 259 (2007).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
M.J. Mayo and W.D. Nix: A micro-indentation study of superplasticity in Pb, Sn and Sn-38wt%Pb. Acta Metall. 36, 2183 (1988).
M.J. Mayo, R.W. Siegel, A. Narayanasamy, and W.D. Nix: Mechanical properties of nanophase TiO2 as determined by nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 5, 1073 (1990).
M.J. Mayo, R.W. Siegel, Y.X. Liao, and W.D. Nix: Nanoindentation on nanocrystal ZnO. J. Mater. Res. 7, 973 (1992).
A.F. Bower, N.A. Fleck, A. Needleman, and N. Ogbonna: Indentation of power law creeping solid. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 441, 97 (1993).
T.O. Mulhearn and D. Tabor: Creep and hardness of metals: A physical study. J. Inst. Met. 89, 7 (1960).
B.N. Lucas and W.C. Oliver: Indentation power-law creep of high purity. Int. Metal. Mater. Trans. A 30A, 601 (1999).
J. Alkorta, J.M. Martinez-Esnaola, and J.G. Sevillano: Critical examinations of strain-rate sensitivity measured by nanoindentation methods: Application to severely deformed niobium. Acta Mater. 56, 884 (2008).
E.W. Hart: Theory of the tensile test. Acta Metall. 15, 351 (1967).
L. Lu, R. Schwaiger, Z.W. Shan, M. Dao, K. Lu, and S. Suresh: Nano-sized twins induce high rate sensitivity of flow stress in pure copper. Acta Mater. 53, 2169 (2005).
W.D. Nix and H. Gao: Indentation size effect of crystalline materials: A law for strain grading plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46, 411 (1998).
K. Durst, B. Backes, and M. Göken: Indentation size effect of metallic materials: Correcting for the size of the plastic zone. Scr. Mater. 52, 1093 (2005).
B. Backes, K. Durst, and M. Göken: Determination of plastic properties of polycrystalline metallic materials by nanoindentation: Experiments and finite element simulations. Philos. Mag. 86, 5541 (2006).
R.A. Mirshams and P. Parakala: Nanoindentation of nanocrystalline Ni with geometrically different indenters. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 372, 252 (2004).
H. Natter and R. Hempelmann: Tailor-made nanomaterials designed by electrochemical methods. Electrochim. Acta 49, 51 (2003).
A. Böhner, V. Maier, K. Durst, H.W. Höppel, and M. Göken: Macro- and nanomechanical properties and strain-rate sensitivity of accumulative roll bonded and equal channel angular pressed ultrafine-grained materials. Adv. Eng. Mater. 13, 251 (2011).
K. Durst, O. Franke, A. Böhner, and M. Göken: Indentation size effect in Ni-Fe solid-solutions. Acta Mater. 55, 6825 (2007).
G.M. Pharr, J. Strader, and W.C. Oliver: Critical issues in making small-depth mechanical property measurements by nanoindentation with continuous stiffness measurement. J. Mater. Res. 24, 653 (2009).
J. Mueller, K. Durst, D. Amberger, and M. Göken: Local investigations of the mechanical properties of ufg metals by nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Forum 503 /, 31 (2006).
W. Blum and Y.J. Li: Flow stress and creep rate of nanocrystalline Ni. Scr. Mater. 57, 429 (2007).
A.G. Atkins and D. Tabor: Plastic indentation in metals with cones. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 13, 149 (1965).
B. Backes, Y.Y. Huang, M. Göken, and K. Durst: The correlation between the internal material length scale and the microstructure in nanoindentation experiments and simulations using the conventional mechanism-based strain gradient plasticity theory. J. Mater. Res. 24, 1197 (2009).
C.D. Gu, J.S. Lian, Q. Jiang, and W.T. Zheng: Experimental and modeling investigations on the strain-rate sensitivity of an electrodeposited 20 nm grain sized Ni. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40, 7440 (2007).
R. Schwaiger, B. Moser, M. Dao, N. Chollacoop, and S. Suresh: Some critical experiments on the strain-rate sensitivity of nc nickel. Acta Mater. 51, 5159 (2003).
Y.F. Shen, W.Y. Xue, Y.D. Wang, Z.Y. Liu, and L. Zuo: Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline nickel film deposited by pulse plating. J. Surf. Coat. 202, 5140 (2008).
X. Shen, J. Lian, Z. Jiang, and Q. Jiang: High strength and high ductility of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni with broad grain size distribution. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 487, 410 (2008).
F. Dalla Torre, P. Spätig, R. Schäublin, and M. Victoria: Deformation behavior and microstructure of nanocrystalline electrodeposited and high pressure torsioned nickel. Acta Mater. 53, 2337 (2005).
Y.M. Wang, A.V. Hamza, and E. Ma: Temperature-dependent strain-rate sensitivity and activation volume in nanocrystalline Ni. Acta Mater. 54, 2715 (2006).
H.W. Höppel, J. May, P. Eisenlohr, and M. Göken: Strain-rate sensitivity of ultrafine grained materials. Z. Metallk. 96, 6 (2005).
M.A. Meyers, A. Misha, and D.J. Benson: Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 51, 427 (2006).
E. Schweitzer, K. Durst, D. Amberger, and M. Göken: The mechanical properties in the vicinity of grain boundaries in ultrafine-grained and polycrystalline materials studied by nanoindentation, in Nanoscale Materials and Modeling—Relations Among Processing, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, edited by P.M. Anderson, T. Foecke, A. Misra, and R.E. Rudd (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 821, Warrendale, PA, 2004), P4.9.1/N4.9.1.
S.H. Lee, Y. Saito, T. Sakai, and H. Utsunomiya: Microstructure and mechanical properties of 6061 aluminum alloy processed by accumulative roll bonding. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 325, 228 (2002).
S.H. Lee, Y. Saito, N. Tsuji, H. Utsunomiya, and T. Sakai: Role of shear strain in ultragrain refinement by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process. Scr. Mater. 46, 281 (2002).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding of the German Research Council, which, within the framework of its “Excellence Initiative” supports the Cluster of Excellence “Engineering of Advanced Materials” at the University of Erlangen-Nuernberg and the support of “Galvano 21” by the Bayerische Forschungsstiftung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maier, V., Durst, K., Mueller, J. et al. Nanoindentation strain-rate jump tests for determining the local strain-rate sensitivity in nanocrystalline Ni and ultrafine-grained Al. Journal of Materials Research 26, 1421–1430 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.156
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.156