Abstract
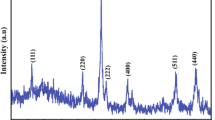
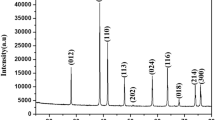
A simple and modified solvothermal method using oxalate precursor, used to synthesize Cd1−xNixO (x = 0.047, 0.102, and 0.163) nanoparticles and their phase structure, morphology, optical and magnetic properties, have been investigated. X-ray diffraction studies revealed that as-prepared Ni-doped CdO solid solutions are highly crystalline and stabilized in a monophasic cubic CdO structure. X-ray diffraction and ICP-MS studies confirmed the incorporation of Ni2+ in a CdO matrix. The average grain size was found to be 30, 15, and 11 nm, respectively, using transmission electron microscopic studies. High surface area in the range of 118–143 m2/g has been achieved for these solid solutions using the multipoint BET method, which increases on increasing Ni concentration in Cd lattice site. The optical band gap of these solid solutions shows red shift to the undoped CdO. Ni-doped CdO nanoparticles exhibit co-existence of paramagnetism and ferromagnetism.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Zhao, D.L. Morel, and C.S. Ferekides: Electrical and optical properties of tin-doped CdO films deposited by atmospheric metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. Thin Solid Films 413, 203 (2002).
L.M. Su, N. Grote, and F. Schmitt: Diffused planar InP bipolar transistor with a cadmium oxide film emitter. Electron. Lett. 20, 716 (1984).
B.G. Lewis and D.C. Paine: Applications and processing of transparent conducting oxides. Mater. Res. Soc. Bull. 25, 22 (2000).
M. Yan, M. Lane, C.R. Kannewurf, and R.P.H. Chang: Highly conductive epitaxial CdO thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 2342 (2001).
K. Baedeker: By the electrical conductivity and the thermoelectric power of some heavy metal compounds. Ann. Phys. 22, 749 (1907).
D.R. Kammler, T.O. Mason, D.L. Young, T.J. Coutts, D. Ko, K.R. Poeppelmeier, and D.L. Williamson: Comparison of thin film and bulk forms of the transparent conducting oxide solution Cd1+xIn2−2xSnxO4. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 5979 (2001).
T.O. Mason, G.B. Gonzalez, D.R. Kammler, N.M. Hadavi, and B.J. Ingram: Defect chemistry and physical properties of transparent conducting oxides in the CdO-In O -SnO system. Thin Solid Films 411, 106 (2002).
A.W. Metz, J.R. Ireland, J.G. Zheng, R.P.S.M. Lobo, Y. Yang, J. Ni, C.L. Stern, V.P. Dravid, N. Bontemps, C.R. Kannewurf, K.R. Poeppelmeier, and T.J. Marks: Transparent conducting oxides: texture and microstructure effects on charge carrier mobility in MOCVD-derived CdO thin films grown with a thermally stable, low-melting precursor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 8477 (2004).
S. Jin, Y. Yang, J.E. Medvedeva, J.R. Ireland, A.W. Metz, J. Ni, C.R. Kannewurf, A.J. Freeman, and T.J. Marks: Dopant ion size and electronic structure effects on transparent conducting oxides. Sc-doped CdO thin films grown by MOCVD. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 13787 (2004).
C.S. Ferekides, R. Mamazza, U. Balasubramanian, and D.L. Morel: Transparent conductors and buffer layers for CdTe solar cells. Thin Solid Films 480, 224 (2005).
A. Wang, J.R. Babcock, N.L. Edleman, A.W. Metz, M.A. Lane, R. Asahi, V.P. Dravid, and C.R. Kannewurf: Indium-cadmium-oxide films having exceptional electrical conductivity and optical transparency: Clues for optimizing transparent conductors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 7113 (2001).
H.M. Ali, H.A. Mohamed, M.M. Wakkad, and M.F. Hasaneen: Properties of transparent conducting oxides formed from CdO alloyed with In2O3. Thin Solid Films 515, 3024 (2007).
M.A. Flores, R. Castanedo, G. Torres, and O. Zelaya: Optical, electrical and structural properties of indium-doped cadmium oxide films obtained by the sol-gel technique. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 93, 28 (2009).
R. Maity and K.K. Chattopadhyay: Synthesis and characterization of aluminum-doped CdO thin films by sol-gel process. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90, 597 (2006).
Y. Yang, S. Jin, J.E. Medvedeva, J.R. Ireland, A.W. Metz, J. Ni, M.C. Hersam, A.J. Freeman, and T.J. Marks: CdO as the archetypical transparent conducting oxide. Systematics of dopant ionic radius and electronic structure effects on charge transport and band structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 8796 (2005).
A.A. Dakhel: Electrical and optical properties of iron-doped CdO. Thin Solid Films 518, 1712 (2010).
A.A. Dakhel: Correlated transport and optical phenomena in Ga-doped CdO films. Sol. Energy 82, 513 (2008).
V. Srihar, V. Sridharan, S. Chandra, V.S. Sastry, H.K. Sahu, and C.S. Sundar: Wide band gap tunability of bulk Cd1−xCaxO. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 013510 (2011).
F. Yakuphanoglu: Preparation of nanostructure Ni doped CdO thin films by sol gel spin coating method. J. Sol. Gel Sci. Technol. 59, 569 (2011).
I.A. Wani, S. Khatoon, A. Ganguly, J. Ahmed, A.K. Ganguli, and T. Ahmad: Silver nanoparticles: Large scale solvothermal synthesis and optical properties Mater. Res. Bull. 45, 1033 (2010).
S. Khatoon and T. Ahmad: Synthesis, optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 2(6), 325 (2012).
C.J. Cong, L. Liao, J.C. Li, L.X. Fan, and K.L. Zhang: Synthesis, structure and ferromagnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechology 16, 981 (2005).
C.J. Cong, L. Liao, Q.Y. Liu, J.C. Li, and K.L. Zhang: Effects of temperature on the ferromagnetism of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles and Mn-related raman vibration. Nanotechnology 17, 1520 (2006).
S. Thota, T. Dutta, and J. Kumar: On the sol-gel synthesis and thermal, structural, and magnetic studies of transition metal (Ni, Co, Mn) containing ZnO powders. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 18, 2473 (2006).
B.V. Donkova, K.I. Milenova, and D.R. Mehandjiev: Investigation on the catalytic activity of doped low-percentage oxide catalysts Mn/ZnO obtained from oxalate precursor. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 6, 115 (2008).
T. Ahmad, S. Khatoon, and K. Coolahan: Optical, magnetic and structural characterization of Zn1−xCoxO nanoparticles synthesized by solvothermal method. Bull. Mater. Sci. Accepted, Ms. No. BOMS-D-12–00330R1 (2013).
S. Khatoon, K. Coolahan, S.E. Lofland, and T. Ahmad: Optical and magnetic properties of solid solutions of In2−xMnxO3 (0.05, 0.10 and 0.15) nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 545, 162 (2012).
T. Ahmad, S. Khatoon, K. Coolahan, and S.E. Lofland: Solvothermal synthesis, optical and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Cd1−xMnxO (0.04 < x = 0.10) solid solutions. J. Alloys Compd. 558, 117 (2013).
L.S. Birks and H. Friedman: Particle size determination from x-ray line broadening. J. Appl. Phys. 17, 687 (1946).
B.E. Warren and B.L. Averbach: The effect of cold work distortion on x-ray patterns. J. Appl. Phys. 21, 595 (1950).
B.E. Warren and B.L. Averbach: The separation of cold work distortion and particle size broadening in x-ray patterns. J. Appl. Phys. 23, 497 (1952).
G. Kortum: Reflectance Spectroscopy: Principles, Methods, Applications (Springer, New York, 1969).
P.N. Kotru, A.K. Razdan, and B.M. Wanklyn: Imperfections and impurity phases in flux grown RCrO3 (R = La, Yb) single crystals. J. Mater. Sci. 24, 2401 (1989).
S.M.D. Prakash and P.M. Rao: Microhardness investigations on gel-grown barium cadmium oxalate mixed crystals. Cryst. Res. Technol. 22, 1095 (1987).
M. Kamruddin, P.K. Ajikumar, R. Nithya, G. Mangamma, A.K. Tyagi, and B. Raj: Effect of water of crystallization on synthesis of nanocrystalline ceria by non-hydrolytic method. Powder Technol. 161, 145 (2006).
G.C. Jones and B. Jackson: Infrared Transmission Spectra of Carbonate Minerals (Springer, Chapman and Hall, Netherlands, 1993).
K. Nakamoto: Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1986).
S.M.D. Prakash and P.M. Rao: Infrared absorption spectra of Ba1−xCdxC2O4.2.5 H2O. Cryst. Res. Technol. 23, K143 (1988).
E.D. Bacce, A.M. Pires, M.R. Davalos, and M. Jafelicci Jr.: Thermal decomposition and rehydration of strontium oxalate: Morphological evolution. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 3, 443 (2001).
A.M.E. Raj, D.D. Jayanthi, V.B. Jothy, M. Jayachandran, and C. Sanjeeviraja: Crystal structure and thermal characterization of cadmium oxalate [CdC2O4.3H2O] and barium-doped cadmium oxalate [Ba0.5Cd0.5(C2O4)2.5H2O] single crystals grown in silica gel. Inorg. Chim. Acta 362, 1535 (2009).
R.D. Shannon: Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A 32, 751 (1976).
R.S. De Baisi and M.L.N. Grillo: Influence of manganese concentration on the electron magnetic resonance spectrum of Mn2+ in CdO. J. Alloys Compd. 485, 26 (2009).
N. Rajkumar, V.M. Susila, and K. Ramachandran: On the possibility of ferromagnetism in CdO: Mn at room temperature. J. Exp. Nanosci. 6, 389 (2011).
X. Wei, G. Xu, Z. Ren, Y. Wang, G. Shen, and G. Han: Size-controlled synthesis of BaTiO3 nanocrystals via a hydrothermal route. Mater. Lett. 62, 3666 (2008).
S.J. Lee, K.Y. Kang, S.K. Han, M.S. Jang, B.G. Chae, Y.S. Yang, and S.H. Kim: Phase formation and ferroelectricity of sol-gel derived (Pb, La)TiO3 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 299 (1998).
P.H. Jefferson, S.A. Hatfield, T.D. Veal, P.D.C. King, C.F. Mc Connville, J.Z. Perez, and V.M. Sanjose: Bandgap and effective mass of epitaxial cadmium oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 022101 (2008).
S.B. Ogale, R.J. Choudhary, J.P. Buban, S.E. Lofland, S.R. Shinde, S.N. Kale, V.N. Kulkarni, J. Higgins, C. Lanci, J.R. Simpson, N.D. Browning, S.D. Sarma, H.D. Drew, R.L. Greene, and T. Venkatesan: High temperature ferromagnetism with a giant magnetic moment in transparent Co-doped SnO2−δ. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 077205 (2003).
M. Bouloudenine, N. Viart, S. Colis, and A. Dinia: Bulk Zn1−xCoxO magnetic semiconductors prepared by hydrothermal technique. Chem. Phys. Lett. 397, 73 (2004).
S. Colis, H. Bieber, S.B. Colin, G. Schmerber, C. Leuvrey, and A. Dinia: Magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors prepared by low-temperature mechanosynthesis. Chem. Phys. Lett. 422, 529 (2006).
A. Bouaine, N. Brihi, G. Schmerber, C.U. Bouillet, S. Colis, and A. Dinia: Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Co-doped SnO2 powders synthesized by the coprecipitation technique. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 2924 (2007).
K.S.W. Sing, D.H. Everett, R.A.W. Haul, L. Moscou, R.A. Pierotti, J. Rouquerol, and T. Siemieniewska: Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 57, 603 (1985).
K.C. Barick, M. Aslam, V.P. Dravid, and D. Bahadur: Self-aggregation and assembly of size-tunable transition metal doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 15163 (2008).
H. Ohno, H. Munekata, T. Penney, S. Von Molnar, and L.L. Chang: Magnetotransport properties of p-type (In, Mn)As diluted magnetic III-V semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 2664 (1992).
G.Y. Ahn, S.I. Park, I.B. Shim, and C.S. Cim: Mossbauer studies of ferromagnetism in Fe-doped ZnO magnetic semiconductor. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 282, 166 (2004).
O.D. Jayakumar, I.K. Gopalakrishnan, R.M. Kadam, A. Vinu, A. Asthana, and A.K. Tyagi: Magnetization and structural studies of Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles: Prepared by reverse micelle method. J. Cryst. Growth 300, 358 (2007).
Acknowledgments
TA thanks CSIR, Govt. of India for financial support of the research project [Grant No. 01(2448)/10EMR-II]. SK thanks UGC and CSIR for research fellowships. The authors also thank Prof. K. V. Ramanujachary, Rowan University, USA for ICP and magnetic measurements as well as for valuable discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, T., Khatoon, S., Coolahan, K. et al. Structural characterization, optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped CdO dilute magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Research 28, 1245–1253 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.69
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.69