Abstract
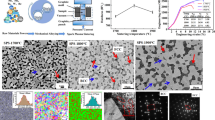
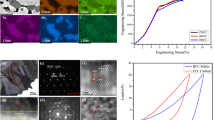
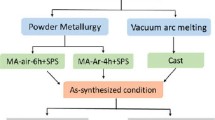
In the present study, the phase evolution and microstructure of CrMoNbTiW, a new equi-atomic refractory high-entropy alloy, are studied. The alloy was synthesized through mechanical alloying (MA) followed by consolidation using spark plasma sintering. After MA, a major BCC solid solution along with residual Cr and Nb were observed. However, secondary phases such as Laves and carbides were also observed in addition to the major BCC solid solution after sintering. Unsolicited contamination from the milling media is found to be one of the reasons for the formation of secondary phases. The high hardness of 8.9 GPa after sintering was attributed to the presence of secondary phases along with the nanocrystalline nature of the alloy. To understand the phase evolution, calculation of phase diagram was carried out using CALPHAD. Further, binary phase diagram inspection and simple empirical parameters were also used to assess their effectiveness in predicting phases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang: Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299 (2004).
B. Cantor, I.T.H. Chang, P. Knight, and A.J.B. Vincent: Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 375–377, 213 (2004).
O.N. Senkov, D.B. Miracle, K.J. Chaput, and J.P. Couzinie: Development and exploration of refractory high entropy alloys—A review. J. Mater. Res. 1, 37 (2018).
E. Eshed, N. Larianovsky, A. Kovalevsky, V. Popov, I. Gorbachev, V. Popov, and A. Katz-Demyanetz: Microstructural evolution and phase formation in 2nd-generation refractory-based high entropy alloys. Materials 11, 2 (2018).
R.I. Jaffee, W.J. Harris, and N.E. Promisel: Development of refractory metal sheet in the United States. J. Less-Common Met. 2, 95 (1960).
S.A. Hewitt and K.A. Kibble: Effects of ball milling time on the synthesis and consolidation of nanostructured WC—Co composites. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 27, 937 (2009).
C. Suryanarayana: Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 46, 1 (2001).
B.S. Murty and S. Ranganathan: Novel materials synthesis by mechanical alloying/milling. Int. Mater. Rev. 43, 101 (1998).
Q. Wei, H.T. Zhang, B.E. Schuster, K.T. Ramesh, R.Z. Valiev, L.J. Kecskes, R.J. Dowding, L. Magness, and K. Cho: Microstructure and mechanical properties of super-strong nanocrystalline tungsten processed by high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 54, 4079 (2006).
A.K. Srivastav: Effect of alloying on microstructural stability and densification during sintering of nanocrystalline tungsten. Ph.D. thesis, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai, 2014.
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, W.M. Wang, S.W. Lee, and K. Niihara: Characterization of nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiTiAl high-entropy solid solution processed by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 495, 33 (2010).
S. Praveen, J. Basu, S. Kashyap, and R. Sankar: Exceptional resistance to grain growth in nanocrystalline CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy at high homologous temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 662, 361 (2016).
M. Vaidya, A. Karati, A. Marshal, K.G. Pradeep, and B.S. Murty: Phase evolution and stability of nanocrystalline CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 770, 1004 (2019).
B. Kang, J. Lee, H.J. Ryu, and S.H. Hong: Ultra-high strength WNbMoTaV high-entropy alloys with fine grain structure fabricated by powder metallurgical process. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 712, 616 (2018).
O.A. Waseem and H.J. Ryu: Powder metallurgy processing of a WxTaTiVCr high-entropy alloy and its derivative alloys for fusion material applications. Sci. Rep. 7, 1 (2017).
C.C. Juan, M.H. Tsai, C.W. Tsai, C.M. Lin, W.R. Wang, C.C. Yang, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, and J.W. Yeh: Enhanced mechanical properties of HfMoTaTiZr and HfMoNbTaTiZr refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 62, 76 (2015).
T. Chookajorn: Enhancing stability of powder-route nanocrystalline tungsten-titanium via alloy thermodynamics. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, 2013.
R.A. Young and D.B. Wiles: Profile shape functions in Rietveld refinements. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 15, 430 (1982).
E. Prince and J.K. Stalick: Accuracy in Powder Diffraction II (NIST, Spec. Publ. No. 846, US Dept of Commerce, Gaithersburg, 1992).
N. Saunders and A.P. Miodownik: CALPHAD (Calculation of Phase Diagrams): A Comprehensive Guide Pergamon, Oxford; New York (1998).
B. Sundman, B. Jansson, and J.O. Andersson: The Thermo-Calc databank system. Calphad 9, 153 (1985).
S.K. Pabi, J. Joardar, and B.S. Murty: Mechanism and Kinetics of alloying and nanostructure formation by mechanical methods. PINSA 1, 1 (2001).
J. Joardar, S.K. Pabi, and B.S. Murty: Milling criteria for the synthesis of nanocrystalline NiAl by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 429, 204 (2007).
J.B. Nelson and D.P. Riley: An experimental investigation of extrapolation methods in the derivation of accurate unit-cell dimensions of crystals. Proc. Phys. Soc. 57, 160 (1945).
A.K. Srivastav, A.M. Panindre, and B.S. Murty: XRD characterization of microstructural evolution during mechanical alloying of W–20 wt% Mo. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 66, 409 (2013).
N. Burgio, A. Iasonna, M. Magini, S. Martelli, and F. Padella: Mechanical alloying of the Fe—Zr system. Correlation between input energy and end products. Nuovo Cim. D 13, 459 (1991).
Y. Zhang, H. Liu, and Z. Jin: Thermodynamic assessment of the Mo—Nb—Ta system. Calphad 21, 6 (2000).
C.P. Wang, J. Wang, S.H. Guo, X.J. Liu, I. Ohnuma, R. Kainuma, and K. Ishida: Intermetallics experimental investigation and thermodynamic calculation of the phase equilibria in the Co—Mo—W system. Intermetallics 17, 1 (2009).
S.V.N. Naidu, A.M. Sriramamurthy, and P. Rama Rao: Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Second Edition, Ed. T.B. Massalski, ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, 2 (1990).
S. Jonsson: Reevaluation of the Ti—W system and prediction of the Ti—W–N phase diagram. Z. Metallkd 87, 784 (1996).
D.M. Cupid, M.J. Kriegel, O. Fabrichnaya, F. Ebrahimi, and H.J. Seifert: Thermodynamic assessment of the Cr—Ti and first assessment of the Al—Cr—Ti systems. Intermetallics 19, 1222 (2011).
P.E.A. Turchi, L. Kaufman, and Z.K. Liu: Modeling of Ni—Cr—Mo based alloys: Part I-phase stability. Calphad 30, 70 (2006).
J.G. Costa Neto, S.G. Fries, H.L. Lukas, S. Gama, and G. Effenberg: Thermodynamic optimisation of the Nb—Cr system. Calphad 17, 219 (1993).
A. Takeuchi and A. Inoue: Mixing enthalpy of liquid phase calculated by Miedema’s scheme and approximated with sub-regular solution model for assessing forming ability of amorphous and glassy alloys. Intermetallics 18, 1779 (2010).
S. Diliberto, O. Kessler, C. Rapin, P. Steinmetz, and P. Berthod: Development of chromia forming Mo—W–Cr alloys: Synthesis and characterization. J. Mater. Sci. 37, 3277 (2002).
Z.C. Cordero and C.A. Schuh: Phase strength effects on chemical mixing in extensively deformed alloys. Acta Mater. 82, 123 (2015).
A.Y. Badmos and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: The evolution of solutions: A thermodynamic analysis of mechanical alloying. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 28, 2189 (1997).
C.C. Koch: Materials synthesis by mechanical alloying. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 19, 121 (1989).
H.O. Pierson: Handbook of refractory carbides and nitrides: Properties, characteristics, processing, and applications, Noyes Publications, Westwood, New Jersey, U.S.A, Vol. 362 (1996).
Y. Choi and S.W. Rhee: Equilibrium in the reaction of Ti and C to form substoichiometric TiCx. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 13, 323 (1994).
S.R. Shatynski: The thermochemistry of transition metal carbides. Oxid. Met. 13, 105 (1979).
S.V. Meschel and O.J. Kleppa: Standard enthalpies of formation of some 3d transition metal carbides by high temperature reaction calorimetry. J. Alloys Compd. 257, 227 (1997).
K. Vasanthakumar, N.S. Karthiselva, N.M. Chawake, and S.R. Bakshi: Formation of TiCx during reactive spark plasma sintering of mechanically milled Ti/carbon nanotube mixtures. J. Alloys Compd. 709, 829 (2017).
S. Praveen, A. Anupam, R. Tilak, and R.S. Kottada: Phase evolution and thermal stability of AlCoCrFe high entropy alloy with carbon as unsolicited addition from milling media. Mater. Chem. Phys. 210, 57 (2018).
P. Sathiyamoorthi, J. Basu, S. Kashyap, K.G. Pradeep, and R.S. Kottada: Thermal stability and grain boundary strengthening in ultrafine-grained CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy composite. Mater. Des. 134, 426 (2017).
R. Sriharitha, B.S. Murty, and R.S. Kottada: Alloying, thermal stability and strengthening in spark plasma sintered AlxCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloys. 583, 2013 (2014).
B. Zhang, M.C. Gao, Y. Zhang, S. Yang, and S.M. Guo: Senary refractory high entropy alloy MoNbTaTiVW. Mater. Sci. Technol. 31, 1207 (2015).
Y. Zhang, Y.J. Zhou, J.P. Lin, G.L. Chen, and P.K. Liaw: Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10, 534 (2008).
N. Yurchenko, N. Stepanov, and G. Salishchev: Laves-phase formation criterion for high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 33, 17 (2016).
S. Guo, C. Ng, J. Lu, and C.T. Liu: Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 103505 (2011).
M.G. Poletti and L. Battezzati: Electronic and thermodynamic criteria for the occurrence of high entropy alloys in metallic systems. Acta Mater. 75, 297 (2014).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank ISRO-IITM cell for the financial support through the project ICSR/ISRO-IITM/MET/13-14/150/BSMT. The authors are grateful to Ms. Dilpreet Danjal (former B.Tech student, NIT Rourkela), Mr. Adil Shaik (MS scholar, IIT Madras), Mr. G. Karthick, Mr. N.T.B.N. Koundinya, Dr. Soumya Sridar (Ph.D. students, Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering at IIT Madras) and Dr. Niraj Chawake (former Ph.D. student, Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering at IIT Madras) for their valuable suggestions and discussion. The authors thank NFAPT team for their assistance in the EBSD analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raman, L., Guruvidyathri, K., Kumari, G. et al. Phase evolution of refractory high-entropy alloy CrMoNbTiW during mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Journal of Materials Research 34, 756–766 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.483
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.483