Abstract
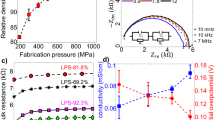
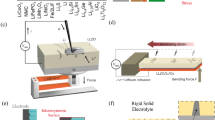
Solid-state batteries are generally considered to be safer than their liquid-state counterparts due to their decreased potential for fire or short circuiting. The fabrication of solid-state batteries relies on the application of stack crimping pressure that increases the interfacial surface contacts between electrolytes and the electrodes. However, excessive compressive crimping stresses (that occur in cell assembly) can give rise to cracking phenomena that can degrade battery performance and lead to thermal runaway or failure. It is, therefore, important to develop an understanding of failure mechanisms in solid-state Li-ion electrolytes. In this paper, we use a combination of in-situ optical microscopy and Digital Imaging Correlation (strain mapping) techniques to study compressive deformation and cracking phenomena in a novel solid-state Li-ion electrolyte. The stress states associated with the different stages of compressive deformation are also presented along with those due to charge–discharge cycles. The implications of the results are discussed for the material design of robust solid-state Li ion batteries.
Graphic Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
D. Deng, Energy Sci. Eng. 3, 385 (2015)
Y. Yan, R.-S. Kühnel, A. Remhof, L. Duchêne, E.C. Reyes, D. Rentsch, Z. Łodziana, C. Battaglia, Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1700294 (2017)
C. Cao, Z.-B. Li, X.-L. Wang, X.-B. Zhao, and W.-Q. Han, Front. Energy Res. 2 (2014).
H. Maekawa, M. Matsuo, H. Takamura, M. Ando, Y. Noda, T. Karahashi, S. Orimo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 894 (2009)
M.M. Kabir, D.E. Demirocak, Int. J. Energy Res. 41, 1963 (2017)
H.-K. Tian, A. Chakraborty, A.A. Talin, P. Eisenlohr, Y. Qi, J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 090541 (2020)
P. Li, Y. Zhao, Y. Shen, S.-H. Bo, J. Phys. 2, 022002 (2020)
J.-M. Doux, Y. Yang, D.H.S. Tan, H. Nguyen, E.A. Wu, X. Wang, A. Banerjee, Y.S. Meng, J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 5049 (2020)
W. Fitzhugh, L. Ye, X. Li, J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 23604 (2019)
O.V. Oyelade, O.K. Oyewole, D.O. Oyewole, S.A. Adeniji, R. Ichwani, D.M. Sanni, W.O. Soboyejo, Sci. Rep. 10, 7183 (2020)
J. Du, T. Tong, W. Akande, A. Tsakiridou, W. Soboyejo, J. Display Technol. 9, 601 (2013)
P. Ramanarayanan, B. Srinivasan, K. Cho, B.M. Clemens, J. Appl. Phys. 96, 7095 (2004)
Acknowledgments
The work was funded and supported by the GEM Fellowship, IBM CVFA team, Worcester Polytechnic Institute. Special thanks to Reisya Ichiwani, Deborah Oyewole, and Vanessa Uzonwanne for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogunfunmi, T., Ebechidi, N., Ahmed, R. et al. An investigation into compressive deformation and failure mechanisms in a novel Li-ion solid-state electrolyte. MRS Advances 6, 154–161 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-021-00014-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-021-00014-3