Abstract
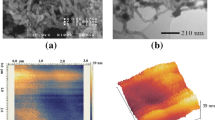
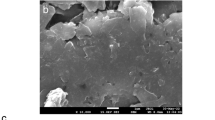
This article highlighting the electrochemical response of phenyl hydrazine and 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine-based polymeric materials for the quantification of the neurotransmitter thrombotonin. The electrochemical analysis was performed on phenyl hydrazine and 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine electropolymers on pencil graphite electrode using cyclic and differential pulse voltammetry. The electrochemical behavior of thrombotonin on the modified electrode was investigated in pH 7 buffer solution of 0.1 M and the oxidation of thrombotonin seemed to be an irreversible adsorption-diffusion-controlled process The modification of the pencil graphite electrode was confirmed by field-emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and Fourier transmittance infrared spectrometry. The fabricated electrochemical sensor can be applied for the quantification of thrombotonin from human blood sample in the linear range from 0.1 to 250 μM with a lower detection limit of 0.01 μM and the sensitivity of the electrode obtained was 2.47 μA/μM/cm2. The fabricated electrode shows enhanced sensitivity, selectivity with good reproducibility, and prolonged stability compared to previously reported differential pulse voltammetric sensors.
Graphic abstract
The research paper is entitled as “Phenyl hydrazine and 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine-based polymeric materials for the electrochemical quantification of thrombotonin”. The developed sensor is highly selective and sensitive and can be used for the determination of thrombotonin in real samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated and analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
A. Getinet, Common Neurotransmitters: criteria for neurotransmitters, key locations, classifications and functions. Am. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 4, 91–95 (2016)
K. Khoshnevisan, H. Maleki, E. Honarvarfard, H. Baharifar, M. Gholami, F. Faridbod, B. Larijani, R.F. Majidi, M.R. Khorramizadeh, Nanomaterial based electrochemical sensing of the biomarker serotonin: a comprehensive review. Microchim. Acta 186, 49 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3069-y
A. Abbaspour, A. Noori, A cyclodextrin host-guest recognition approach to an electrochemical sensor for simultaneous quantification of serotonin and dopamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 4674–4680 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.04.061
A. Özcan, Selective and sensitive electrochemical sensing of serotonin in human blood serum by means of electrochemically treated pencil graphite electrode. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 17, 551–562 (2016)
A. Özcan, S. Ilkbas, Poly(pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid)-modified pencil graphite electrode for the determination of serotonin in biological samples by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Sensors Actuators B 215, 518–524 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.03.100
H.S. Han, H.K. Lee, J.M. You, H. Jeong, S. Jeon, Electrochemical biosensor for simultaneous determination of dopamine and serotonin based on electrochemically reduced GO-porphyrin. Sensors Actuators B 190, 886–895 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.09.022
M.J. Song, S. Kim, K.K. Min, J.H. Jin, Electrochemical serotonin monitoring of poly(ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate)-modified fluorine-doped tin oxide by predeposition of self-assembled 4-pyridylporphyrin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 52, 411–416 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.08.040
G. Ran, X. Chen, Y. Xia, Electrochemical detection of serotonin based on a poly (bromocresol green) film and Fe3O4 nanoparticles in a chitosan matrix. RSC Adv. 7, 1847–1851 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA25639B
A. Babaei, A.R. Taheri, Nafion/Ni(OH)2 nanoparticles-carbon nanotube composite modified glassy carbon electrode as a sensor for simultaneous determination of dopamine and serotonin in the presence of ascorbic acid. Sensors Actuators B 176, 543–551 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.09.021
H.S. Han, J.M. You, H. Jeong, S. Jeon, Synthesis of graphene oxide grafted poly(lactic acid) with palladium nanoparticles and its application to serotonin sensing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 284, 438–445 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.07.116
X. Wang, D. Gao, M. Li, H. Li, C. Li, X. Wu, CVD graphene as an electrochemical sensing platform for simultaneous detection of biomolecules. Sci. Rep. 7, 7044 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07646-2
M. Satyanarayana, K.K. Reddy, K.V. Gobi, Nanobiocomposite based electrochemical sensor for sensitive determination of serotonin in presence of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid in vitro. Electroanalysis 26, 2365–2372 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201400243
J.M. Zen, I.L. Chen, Y. Shih, Voltammetric determination of serotonin in human blood using a chemically modified electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 369, 103–108 (1998). https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6210.1000154
Z.H. Wang, Q.L. Liang, Y.M. Wang, G.A. Luo, Carbon nanotube-intercalated graphite electrode for simultaneous determination of dopamine and serotonin in the presence of ascorbic acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 540, 129–134 (2003). https://doi.org/10.3390/s131014029
G.M. Anderson, L.M. Hall, J.X. Yang, D.J. Cohen, Platelet dense granule release reaction monitored by high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorometric determination of endogenous serotonin. Anal. Biochem. 206, 64–67 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2697(05)80011-9
T. Fujimori, Y. Yamanishi, K. Yamatsu, T. Tajima, High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) determination of endogenous serotonin released from aggregating platelets. J Pharmacol Methods 7, 105–113 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0160-5402(82)90022-5
M. Kim, J.G. Lee, C.H. Yang, S. Lee, Silica stationary phase-based on-line sample enrichment coupled with LC-MS/MS for the quantification of dopamine, serotonin and their metabolites in rat brain microdialysates. Anal. Chim. Acta 923, 55–65 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.03.021
A. Guillermo, M. Hernández, A.O. Dilia, G.G. Mario, J.L. Hector, Q. Naser, G.T. Carlos, Fluorescence of serotonin in the visible spectrum upon multiphotonic photoconversion. Biomed. Opt. Express 11, 1432 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.380412
W.H.A. de Jong, H.L. Marianne, I. Wilkens, E.G.E. de Vries, P.K. Ido, Automated mass spectrometric analysis of urinary and plasma serotonin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 396, 2609–2616 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3466-5
R. Rejithamol, S. Beena, Electrochemical quantification of pyridoxine (VB6) in human blood from other water-soluble vitamins. Chem. Pap. 74, 2011–2020 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-01049-5
R. Rejithamol, G.K. Rajasree, S. Beena, Electrochemical quantification of l-tryptophan via molecular imprinted pyromellitic acid polymer-based indium tin oxide electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 117507 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/aba33e
G.K. Rajasree, R. Rejithamol, S. Beena, Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor for the simultaneous determination of adenosine, adenine and uric acid in whole blood and urine. Microchem. J. 155, 104745 (2020)
R. Rejithamol, G.K. Rajasree, S. Beena, Disposable pencil graphite electrode decorated with a thin film of electro-polymerized 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10-octahydropyrimido [1, 2-a] azepine for simultaneous voltammetric analysis of dopamine, serotonin and tryptophan. Mater. Chem. Phys. 258, 123857 (2020)
A. Krishnan, S. Beena, S.M.A. Shibli, A novel high performance Ti/Ti-W-reinforced polyaniline functionalized Ni-P electrode for high-sensitive detection of dopamine from urine sample. Mater. Chem. Phys. 244, 122680 (2020)
S. Ramakrishnan, K.R. Pradeep, A. Raghul, R. Senthilkumar, M. Rangarajan, N.K. Kothurkar, One-step synthesis of pt-decorated graphene-carbon nanotube for electrochemical sensing of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid. Anal. Methods 7, 779–786 (2015)
A. Vadivaambigai, P.A. Senthilvasan, A.N. Kothurkar, M. Rangarajan, Graphene-oxide-based electrochemical sensor for salicylic acid. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 7, 140–146 (2015)
A.R. Rajamani, R. Kannan, S. Krishnan, S. Ramakrishnan, S.M. Raj, D. Kumaresan, M. Rangarajan, Electrochemical sensing of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid using tRGO-TiO2 nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 15, 5042–5047 (2015)
S.A. Ozkan, J.M. Kauffmann, P. Zuman, Electroanalysis in Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences (Springer, Berlin, 2015)
M.J. O’Neil, The Merck Index—An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (UK, Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2013), p. 883
I. Svancara, J. Zima, Possibilities and limitations of carbon paste electrodes in organic electrochemistry. Curr. Org. Chem. 15, 3043–3058 (2011)
P.Y. Khashaba, H.R. Ali, M.M. El-Wekil, Simultaneous voltammetric analysis of anti-ulcer and D2—antagonist agents in binary mixture using redox sensor and their determination in human serum. Mater. Sci. Eng. 75, 733–741 (2017)
P.Y. Khashaba, H.R. Ali, M.M. El-Wekil, Highly sensitive and selective complexation based voltammetric methods for the analysis of rabeprazole sodium in real samples. RSC Adv. 7, 3043–3050 (2017)
M.H. Mahnashi, A.M. Mahmoud, S.A. Alkahtani, H.R. Ali, M.M. El-Wekil, Facile fabrication of a novel disposable pencil graphite electrode for simultaneous determination of promising immunosuppressant drugs mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus in human biological fluids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 412, 355–364 (2020)
F.A. Mohamed, P.Y. Khashaba, R.Y. Shahin, M.M. El-Wekil, Tunable ternary nanocomposite prepared by electrodeposition for biosensing of centrally acting reversible acetyl cholinesterase inhibitor donepezil hydrochloride in real samples. Colloids Surf. A 567, 76–85 (2019)
X. Zhang, Y. Wang, X. Ning, L. Li, J. Chen, D. Shan, Three dimensional porous self-assembled chestnut-like nickel-cobalt oxide structure as an electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of hydrazine in water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 1022, 28–36 (2018)
P. Ning, G. Debin, H. Ting, W. Ruibing, W. Ian, J. Yongdong, X. Chuanqin, Removal of Th4+ ions from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide. J Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 298, 1999–2008 (2013)
M.S. Robert, X.W. Francis, J.K. David, Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th edn. (Wiley, Hoboken, 2005)
K. Aoki, K. Akimoto, K. Tokuda, H. Matsuda, J. Osteryoung, Linear sweep voltammetry at very small stationary disk electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 171, 219–230 (1984)
F. Lida, B.H. Ayemeh, M.H. Majid, Electrochemical behaviour and voltammetric determination of sulphadiazine using a multiwalled carbon nanotube composite film-glassy carbon electrode. J. Exp. Nanosci. 8, 947–956 (2013)
N. Nasirizadeh, Z. Shekari, H.R. Zare, S.A. Ardakani, H. Ahmar, Developing a sensor for the simultaneous determination of dopamine, acetaminophen and tryptophan in pharmaceutical samples using a multi-walled carbon nanotube and oxadiazole modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 24, 1846–1856 (2013)
L.E. Amanda, F. Daniel, J.A. Shaw, J.M. Thomas, Electrochemistry of redox-active self-assembled monolayers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 25, 1769–1802 (2010)
U. Sivasankaran, A.E. Vikraman, D. Thomas, K. Girish Kumar, Nanomolar level determination of octyl gallate in fats and oils. Food Anal. Methods 9, 2115–2123 (2016)
B.V. Sarada, T.N. Rao, D.A. Tryk, A. Fujishima, Electrochemical oxidation of histamine and serotonin at highly boron-doped diamond electrodes. Anal. Chem. 72, 1632–2163 (2000)
N.S. Lopa, M. Rahman, H. Jang, S.C. Sutradhar, F. Ahmed, T. Ryu, W. Kim, A glassy carbon electrode modified with poly (2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine) for simultaneous detection of dihydroxybenzene isomers. Microchim. Acta 23, 185 (2017)
M. Valcárcel, M.D. Luque de Castro (eds.), Sensors in analytical chemistry, in Techniques and Instrumentation in Analytical Chemistry, vol. 16 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1994), pp. 13–47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RR conducted all experiments and analyses. SB supervised RR. SB and RR co-wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The authors confirmed that obtained approval from the institution and consent from the donor for the experiments involving human subjects (blood).
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rejithamol, R., Beena, S. Phenyl hydrazine and 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine-based polymeric materials for the electrochemical quantification of thrombotonin. MRS Advances 6, 750–757 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-021-00116-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-021-00116-y