Abstract
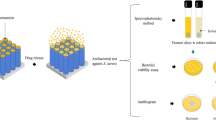
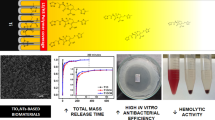
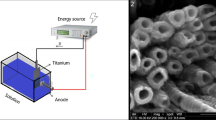
In the present study, TiO2NT coatings grown on simulated body fluid-based electrolyte were investigated as drug delivery devices. Nanotubes (NTs) were grown over commercially pure Ti and Ti6Al4V alloy. Morphology analysis showed that NTs in alloy samples present an inner diameter of 10 nm smaller in average than NTs grown over pure Ti. The surface wettability in water decreased with the anodizing time for both substrates. The application of coatings as drug delivery devices has been studied through the incorporation of ciprofloxacin. To control the drug release, collagen was used as the diffusional barrier. It was observed the drug release follows a Fick’s kinetics. Bioactivity assays showed the absence of hemolytic activity. The concentration of the drug during the release interval remained below the toxic concentration limit, presenting a bacteriostatic activity. All coatings prepared presented a high antibacterial activity, being the area of inhibition of bacterial growth above 13 times the area of the implant.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.C. Gurtner, M.J. Callaghan, and M.T. Longaker: Progress and potential for regenerative medicine. Annu. Rev. Med. 58, 299 (2007).
H. Habazaki, T. Onodera, K. Fushimi, H. Konno, and K. Toyotake: Spark anodizing of β-Ti alloy for wear-resistant coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 201, 8730 (2007).
B.M. Holzapfel, J. Reichert, J. Schantz, U. Gbureck, L. Rackwitz, U. Nöth, F. Jakob, M. Rudert, J. Groll, and D. Werner: How smart do biomaterials need to be? A translational science and clinical point of view. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 65, 581–603 (2012).
R. Murugan and S. Ramakrishna: Development of nanocomposites for bone grafting. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65, 2385 (2005).
J.M. Macak, H. Tsuchiya, L. Taveira, A. Ghicov, and P. Schmuki: Self-organized nanotubular oxide layers on Ti–6Al–7Nb and Ti–6Al–4V formed by anodization in NH4F solutions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A 75, 928 (2005).
D. Gong, C.A. Grimes, O.K. Varghese, W. Hu, R.S. Singh, Z. Chen, and E.C. Dickey: Titanium oxide nanotube arrays prepared by anodic oxidation. J. Mater. Res. 16, 3331 (2011).
D. Kubies, L. Himmlová, T. Riedel, E. Chánová, K. Balík, M.D.Ě. Rová, J. Bártová, and V. Pešáková: The interaction of osteoblasts with bone-implant materials: 1. The effect of physicochemical surface properties of implant materials. Physiol. Res. 8408, 95 (2011).
L. Le Guehennec, B. Enkel, P. Weiss, Y. Amouriq, and P. Layrolle: Osteoblastic cell behaviour on different titanium implant surfaces. Acta Biomater. 4, 535 (2008).
D.M.D. Ehrenfest, P.G. Coelho, B. Kang, Y. Sul, and T. Albrektsson: Classification of osseointegrated implant surfaces: Materials, chemistry and topography. Trends Biotechnol. 28, 198 (2010).
E. Rieger, A. Dupret-bories, L. Salou, P. Layrolle, C. Debry, P. Lavalle, and N.E. Vrana: Controlled implant/soft tissue interaction by nanoscale surface modifications of 3D porous titanium implants. Nanoscale 7, 9908 (2015).
J. Wei, T. Igarashi, N. Okumori, T. Igarashi, T. Maetani, B. Liu, and M. Yoshinari: Influence of surface wettability on competitive protein adsorption and initial attachment of osteoblasts. Biomed. Mater. 4, 45002 (2009).
K. Hori and S. Matsumoto: Bacterial adhesion: From mechanism to control. Biochem. Eng. J. 48, 424 (2010).
K.G. Neoh, X. Hu, D. Zheng, and E.T. Kang: Balancing osteoblast functions and bacterial adhesion on functionalized titanium surfaces. Biomaterials 33, 2813 (2012).
C. Yao and T.J. Webster: Prolonged antibiotic delivery from anodized nanotubular titanium using a co-precipitation drug loading method. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part B 91, 587 (2009).
J.M. Unagolla and A.C. Jayasuriya: Drug transport mechanisms and in vitro release kinetics of vancomycin encapsulated chitosan–alginate polyelectrolyte microparticles as a controlled drug delivery system. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 114, 199 (2018).
D. Wei, R. Zhou, W. Feng, B. Li, and Y. Wang: Microarc oxidized TiO2 based ceramic coatings combined with cefazolin sodium/chitosan composited drug fi lm on porous titanium for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 33, 4118 (2013).
L. Mohan, C. Anandan, and N. Rajendran: Drug release characteristics of quercetin-loaded TiO2 nanotubes coated with chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 93, 1633 (2016).
M.D. Shoulders and R.T. Raines: Collagen structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78, 929 (2009).
C. Roehlecke, M. Witt, M. Kasper, E. Schulze, C. Wolf, A. Hofer, and R.H.W. Funk: Synergistic effect of titanium alloy and collagen type I on cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells. Cells Tissues Organs 168, 178 (2001).
W.J. Landis and F.H. Silver: Mineral deposition in the extracellular matrices of vertebrate tissues: Identification of possible apatite nucleation sites on type I collagen. Cells Tissues Organs 189, 20 (2009).
J.M. Macak, H. Tsuchiya, and P. Schmuki: High-aspect-ratio TiO2 nanotubes by anodization of titanium Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 44, 2100 (2005).
J.M. Macak, H. Tsuchiya, A. Ghicov, K. Yasuda, R. Hahn, S. Bauer, and P. Schmuki: TiO2 nanotubes: Self-organized electrochemical formation, properties and applications. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 11, 3 (2007).
D. Regonini, C.R. Bowen, A. Jaroenworaluck, and R. Stevens: A review of growth mechanism, structure and crystallinity of anodized TiO2 nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 74, 377 (2013).
A. Ghicov and P. Schmuki: Self-ordering electrochemistry: A review on growth and functionality of TiO2 nanotubes and other self-aligned MOx structures. Chem. Commun. 20, 2791 (2009).
M.T. Mohammed, Z.A. Khan, and A.N. Siddiquee: Surface modifications of titanium materials for developing corrosion behavior in human body environment: A review. Procedia Mater. Sci. 6, 1610 (2014).
M. Kulkarni, A. Mazare, P. Schmuki, and A. Iglič: Biomaterial surface modification of titanium and titanium alloys for medical applications. Nanomedicine 45, 111 (2017).
P. Scherrer: Determination of the size and internal structure of colloidal particles using X-rays. Math-Phys Klasse 2, 98 (1918).
D.H. Shin, T. Shokuhfar, C.K. Choi, S.H. Lee, and C. Friedrich: Wettability changes of TiO2 nanotube surfaces. Nanotechnology 22, 315704–315711 (2011).
T. Sun and M. Wang: A comparative study on titania layers formed on Ti, Ti–6Al–4V and NiTi shape memory alloy through a low temperature oxidation process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 205, 92 (2010).
P.L. Ritger and N.A. Peppas: A simple equation for description of solute release II. Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices 5, 23 (1987).
W. Feng, Z. Geng, Z. Li, Z. Cui, S. Zhu, Y. Liang, Y. Liu, R. Wang, and X. Yang: Controlled release behaviour and antibacterial effects of antibiotic-loaded titania nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 62, 105 (2016).
A. Zitting and E. Skyttä: Biological activity of titanium dioxides. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 43, 93 (1979).
A.P. Simon and M.d.S. Sikora: Eletrólito para síntese eletroquímica de biomateriais a base de titânio. BR Patent No. 10 2018 002514 7, 2018.
T. Kokubo, H. Kim, and M. Kawashita: Novel bioactive materials with different mechanical properties. Biomaterials 24, 2161 (2003).
C.A. Schneider, W.S. Rasband, K.W. Eliceiri, and C. Instrumentation: NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 9, 671 (2012).
K. Gulati, M. Kogawa, M. Prideaux, D.M. Findlay, G.J. Atkins, and D. Losic: Drug-releasing nano-engineered titanium implants: Therapeutic efficacy in 3D cell culture model, controlled release and stability. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 69, 831 (2016).
H.M. Abdou: Dissolution, bioavailability and bioequivalence. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 16, 185 (1990).
M. Sinn Aw, M. Kurian, and D. Losic: Non-eroding drug-releasing implants with ordered nanoporous and nanotubular structures: Concepts for controlling drug release. Biomater. Sci. 2, 10 (2014).
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, Pennsylvania, 2015).
F. Krichen, W. Karoud, A. Sila, B.E. Abdelmalek, R. Ghorbel, S. Ellouz-Chaabouni, and A. Bougatef: Extraction, characterization and antimicrobial activity of sulfated polysaccharides from fish skins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 75, 283 (2015).
V. Bulmus, M. Woodward, L. Lin, N. Murthy, P. Stayton, and A. Hoffman: A new pH-responsive and glutathione-reactive, endosomal membrane-disruptive polymeric carrier for intracellular delivery of biomolecular drugs. J. Controlled Release 93, 105 (2003).
R. Palanivelu and A. Ruban Kumar: Synthesis, characterization, in vitro anti-proliferative and hemolytic activity of hydroxyapatite. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 127, 434 (2014).
Acknowledgment
The authors thank the UTFPR, Central Analysis of UTFPR-PB, UFSCar, Biocenter Clinical Analysis Laboratory, and to Brazilian Nanotechnology National Laboratory (LNNano) in National Center of Energy and Materials Research (CNPEM) and Analysis Center of UTFPR-PB. This work was supported by UTFPR [PAPCDT 06/2016 and 07/2017]. This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, C.H., Simon, A.P., Santos, V.A.Q. et al. Nanotexturization of Ti-based implants in simulated body fluid: Influence of synthesis parameters on coating properties and kinetics of drug release. Journal of Materials Research 34, 2828–2836 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.216
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.216