Abstract
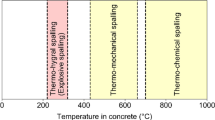
Results of an experimental study, which measured thermally-induced pore pressure and corresponding concrete temperatures in high-strength concrete (HSC) and normal strength concrete (NSC), to quantify the effects of factors influencing pore pressure buildup and potential for explosive spalling in HSC and NSC are presented. The specimens are 100 × 200 × 200 mm concrete blocks, heated to a maximum temperature of 600°C (1,112°F) at 5°C/min (41°F/min) and 25°C/min (77°F/min). The complex heat-induced moisture transport process, which varied with specific levels of concrete temperature and significantly influenced the developments of pore pressure and concrete temperature, is explained. Pore pressure developments are shown to be directly related to the moisture transport process and have a significant influence on occurrence of explosive spalling. Effects of water-to-cementitious materials ratios (w/cm), curing conditions, heating rates, and polypropylene (PP) fibers on pore pressure buildup and explosive spalling are quantified and described.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phan LT, Carino NJ (2002) Effects of test conditions and mixture proportions on behavior of high-strength concrete exposed to high temperatures. ACI Mater J 99(1):54–66
Kalifa P, Menneteau D, Quenard D (2000) Spalling and pore pressure in HPC at high temperature. Cement Concrete Res 30:1915–1927
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phan, L.T. Pore pressure and explosive spalling in concrete. Mater Struct 41, 1623–1632 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-008-9353-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-008-9353-2