Abstract
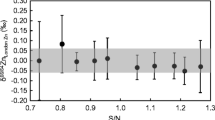
Precise 66Zn/64Zn and 68Zn/64Zn isotopic ratios of biochemical samples have been measured using multiple collector-ICP-mass spectrometry (MC-ICPMS). In order to eliminate the mass spectrometric interferences on Zn isotopes (e.g., 64Ni+ and 136Ba2+), we chemically purified the analyte using an ion chromatographic technique. The resulting precisions of the 66Zn/64Zn and 68Zn/64Zn ratio measurements were 0.05‰ and 0.10‰ (2SD), respectively, which were enough to detect the isotopic variation of Zn in nature. Red blood cell (RBC) samples were collected from five volunteers (four males and one female), including a series of 12 RBC samples from one person through monthly-based sampling over a year. These were analyzed to test possible seasonal changes and variations in 66Zn/64Zn and 68Zn/64Zn ratios among the individuals. The 66Zn/64Zn and 68Zn/64Zn ratios for a series of 12 RBC samples collected over a year were 0.43‰ and 0.83‰ higher than the values of highly purified Zn metal (JMC Zn), and no seasonal change could be found. The 66Zn/64Zn and 68Zn/64Zn ratios for RBC samples collected from five volunteers did not vary significantly. In order to investigate Zn isotopic heterogeneity in a human body, Zn isotopic ratios of a hair sample collected from one of the volunteers was also analyzed. The 66Zn/64Zn and 68Zn/64Zn ratios for the hair sample were 0.59‰ and 1.14‰ lower than the mean value of RBC samples. This result demonstrates that detectable isotopic fractionation occurs in the human body. The data obtained here suggest that the isotopic ratios of trace metals could provide new information about transportation of metal elements in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. L. Maréchal, P. Télouk, and F. Albarède, Chem. Geol., 1999, 158, 251.
B. L. Beard, C. M. Johnson, L. Cox, H. Sun, K. H. Nealson, and C. Aguilar, Science, 1999, 285, 1889.
X. K. Zhu, R. K. O’Nions, Y. Guo, and B. C. Reynolds, Science, 2000, 287, 2000.
T. D. Bullen, A. F. White, C. W. Childs, D. V. Vivit, and M. S. Schulz, Geology, 2001, 29, 699.
J. Baring, G. L. Arnold, and A. D. Anbar, Earth Planet Sci. Lett., 2001, 193, 447.
T. Walczyk and F. von Blanckenburg, Science, 2002, 295, 2065.
X. K. Zhu, Y. Guo, R. J. P. Williams, R. K. O’Nions, A. Matthews, N. S. Belshaw, G. W. Canters, E. C. de Waal, U. Weser, B. K. Burgess, and B. Salvato, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2002, 200, 47.
A. Stenberg, D. Malinovsky, I. Rodushkin, H. Andrén, C. Pontér, B. Öhlander, and D. C. Baxter, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2003, 18, 23.
B. L. Beard, C. M. Johnson, J. L. Skulan, K. H. Nealson, L. Cox, and H. Sun, Chem. Geol., 2003, 195, 87.
T. Ohno, A. Shinohara, I. Kohge, M. Chiba, and T. Hirata, Anal. Sci., 2004, 20, 617.
A. D. Anbar, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2004, 217, 223.
A. Stenberg, H. Andrén, D. Malinovsky, E. Engström, I. Rodushkin, and D. C. Baxter, Anal. Chem., 2004, 76, 3971.
A. S. Parasad, Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 1991, 53, 403.
M. E. Wastney, R. L. Aamodt, W. F. Rumble, and R. I. Henkin, Am. J. Physiol., 1986, 251, R398.
S. J. Fairweather-Tait, M. J. Jackson, T. E. Fox, S. G Wharf, J. Eagles, and P. C. Croghan, Br. J. Nutr., 1993, 70, 221.
L. M. W. Owen, H. M. Crews, R. C. Hutton, and A. Walsh, Analyst, 1992, 117, 649.
S. F. Durrant, A. Krushevska, D. Amarasiriwardena, M. D. Argentine, S. Romon-Guesnier, and R. M. Barnes, J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom., 1994, 9, 199.
F. A. Mellon and B. Sandstrom (ed.), “Stable Isotope in Human Nutrition”, 1996, Academic Press, London.
I. J. Griffin, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2002, 17, 1186.
A. Shinohara, M. Chiba, and Y. Inaba, Anal. Sci., 1998, 14, 713.
T. Hirata, Analyst, 1996, 121, 1407.
T. N. Van der Walt, F. W. E. Strelow, and R. Verheij, Solvent Extr. Ion Exch., 1985, 3, 723.
W. R. Shields, T. J. Murphy, and E. L. Garner, J. Res. NBS, 1964, 68A, 589.
H. Haraguchi, J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom., 2004, 19, 5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohno, T., Shinohara, A., Chiba, M. et al. Precise Zn Isotopic Ratio Measurements of Human Red Blood Cell and Hair Samples by Multiple Collector-ICP-Mass Spectrometry. ANAL. SCI. 21, 425–428 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.21.425
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.21.425