Abstract
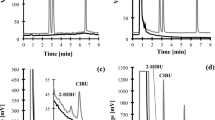
An environmentally friendly reversed-phase HPLC method for simultaneous determination of creatinine and uric acid in human urine samples has been developed. Human urine samples were pretreated by dilution, protein precipitation, centrifugation and filtration, followed by HPLC separations using a reversed-phase C18 column with an aqueous mobile phase of phosphate buffer. The retention loss of a C18 column when using the highly aqueous mobile phases was avoided by employing a gradient elution using a small volume (<0.23 mL) of acetonitrile and phosphate buffer at pH 4.75. This developed method provides a simple, rapid separation and sensitive detection for the species of interest in 10 min with UV detection at 205 nm. Quantitation was carried out by relating the peak areas of the identified compounds to that of hypoxanthine as an internal standard. The detection limits for creatinine and uric acid were 0.045 and 0.062 μg mL-1. respectively. The recoveries of the standards added to urine samples were 87.3 - 102.2% for creatinine and 97.3 - 108.6% for uric acid, and the relative standard deviation for both analytes was less than 1.0%. This method has been successfully applied to estimating of creatinine and uric acid in human urine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Shankar, R. Klein, B. E. K. Klein, and S. E. Moss, Exp. Clin. Endocrinol Diabetes, 2007,775, 203.
J. Lee, D. Sparrow, P. S. Vokonas, L. Landsberg, and S. T. Weiss, Am. J. Epidemiol, 1995, 142, 288.
A. D. Liese, H. W. Hense, H. Lowel, A. Doring, M. Tietze, and U. Keil, Epidemiol, 1999, 10, 391.
T. E. Madsen, J. B. Muhlestein, B. D. Home, J. F. Carlquist, T. L. Bair, J. D. Jackson, J. Lappe, R. R. Pearson, J. B. Muhlestein, and J. L. Anderson, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol, 2000, 35, 284A.
I. Ohno, T. Hosoya, H. Gomi, K. Ichida, H. Okabe, and M. Hikita, Nephron, 2001, 87, 333.
M. E. Ochiai, A. C. P. Barretto, M. T. Oliveira, R. T. Munhoz, P. C. Morgado, and J. A. F. Ramires, Eur. J. Heart Fail, 2005, 7, 468.
E. Golembiewska, K. Ciechanowski, K. Safranow, K. K. Kedzierska, and J. Kabat-Koperska, Arch. Med. Res., 2005, 36, 32.
P. Verdecchia, G. Schillaci, G. Reboldi, F. Santeusanio, C. Porcellati, and P. Brunetti, Hypertension, 2000, 36, 1072.
M. Langlois, D. De Bacquer, D. Duprez, M. De Buyzere, J. Delanghe, and V. Blaton, AtheroSci.erosis, 2003, 168, 163.
M. Jaffe, Z. Physiol. Chem., 1886, 10, 391.
W. Junge, B. Wilke, A. Halabi, and G. Klein, Clin. Chim. Acta, 2004, 344, 137.
W. T. Caraway, Uric Acid. Stand. Methods Clin. Chem., 1963, 4, 239.
R. J. Elin, E. Johnson, and R. Chesler, Clin. Chem., 1982, 28, 2098.
X. Fuentes-Arderiu, Clin. Chem., 2001, 47, 1327.
J. A. Weber and A. P. van Zanten, Clin. Chem., 1991, 37, 695.
C. J. Kochansky and T. G. Strein, J. Chromatogr, B, 2000, 747, 217.
R. Kock, B. Delvoux, and H. Greiling, Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem., 1993, 31, 303.
Y. M. Chen, R. A. Pietrzyk, and P. A. Whitson, J. Chromatogr, A, 1997, 763, 187.
J. F. Jen, S. L. Hsiao, and K. H. Liu, Talanta, 2002, 58, 711.
A. K. Hewavitharana and H. L. Bruce, J. Chromatogr, B, 2003, 784, 275.
S. K. George, M. T. Dipu, U. R. Mehra, P. Singh, A. K. Verma, and J. S. Ramgaokar, J. Chromatogr, B, 2006, 832, 134.
Y. Zuo, L. Zhang, J. Wu, J. W Fritz, S. Medeiro, and C. Rego, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2004, 526, 35.
L. H. Keith, L. U. Gron, and J. L. Young, Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 2695.
Y. Zuo, K. Zhang, and Y. Lin, J. Chromatogr, A, 2007, 7748, 211.
T. H. Walter, P. Iraneta, and M. Capparella, J. Chromatogr, A, 2005, 7075, 177.
B. A. Bidlingmeyer and A. D. Broske, J. Chromatogr. Sci., 2004, 42, 100.
T. S. Reid and R. A. Henry, Am. Lab., 1999, 31, 24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, Y., Wang, C., Zhou, J. et al. Simultaneous Determination of Creatinine and Uric Acid in Human Urine by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. ANAL. SCI. 24, 1589–1592 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.24.1589
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.24.1589